What does obesity really look like? You might think it’s just about weight, but there’s more to it than meets the eye.
It affects how you feel every day—your energy, your confidence, even your skin. You may notice breathlessness during simple activities, or find yourself sweating more than usual. Maybe snoring keeps you or your loved ones awake at night. These signs are clues your body is trying to tell you something important.
Understanding what obesity looks like—beyond just numbers on a scale—can be the first step to taking control of your health. Keep reading to discover how to recognize these signs and what you can do next to feel better and live healthier.
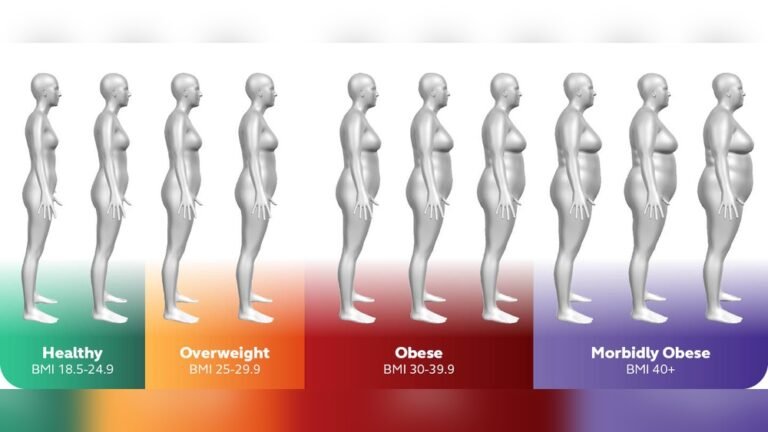
Visual Signs Of Obesity
Obesity shows itself through visible changes in the body. These changes can help identify obesity by sight. Recognizing these signs aids early awareness and health action. The visual signs vary by individual but share common traits. Understanding these traits helps in noticing obesity more clearly.
Common Physical Features
Obesity often causes excess fat buildup around the stomach, hips, and thighs. The face may appear rounder or fuller. Neck size can increase, sometimes causing a double chin. Arms and legs may look thicker than usual. Movement can become slower or more difficult due to weight. Clothes may fit tighter, especially around the waist.
Body Shape Variations
Obesity does not look the same on everyone. Some people carry weight mainly around the belly, called an apple shape. Others store fat in hips and thighs, known as a pear shape. A rectangular shape shows weight spread evenly. Each shape has unique health risks. Body shapes change as weight increases or decreases.
Skin Changes And Issues
Obesity can cause skin problems in certain areas. Skin folds may become darker or thickened, a condition called acanthosis nigricans. Stretch marks often appear on the stomach and thighs. Sweat buildup in skin folds may cause irritation or rashes. Skin tags, small soft bumps, are common in obese people. Wounds may heal slower due to poor blood flow.

Credit: www.lipedema.org
Measuring Obesity
Measuring obesity helps understand health risks linked to excess body fat. Health experts use several methods to assess how much fat a person carries. These measurements guide treatment and lifestyle changes. Simple tools like Body Mass Index and waist circumference are common. Advanced tests offer deeper insight into fat distribution and amount. Each method has strengths and limits in reflecting true health status.
Body Mass Index (bmi)
Body Mass Index, or BMI, is a quick way to estimate body fat. It uses height and weight in a simple formula. The result places people into categories like underweight, normal, overweight, or obese. BMI is easy to calculate and widely used in clinics. It does not measure fat directly or consider muscle mass. Athletes or muscular people may have a high BMI but low fat. Still, BMI is a useful starting point to spot obesity risk.
Waist Circumference
Waist circumference measures fat around the abdomen. This fat type links closely with heart disease and diabetes risks. To measure, wrap a tape measure around your waist at the top of the hip bone. The number shows how much fat is stored in the belly area. High waist measurements often mean higher health risks. This test adds valuable information beyond BMI alone.
Advanced Body Fat Tests
Advanced tests give detailed views of body fat and its locations. Methods include DEXA scans, bioelectrical impedance, and hydrostatic weighing. These tests measure fat percentage, muscle mass, and bone density. They help understand obesity’s impact on body composition. Doctors use these tests for precise health evaluations. Although more accurate, they need special equipment and cost more.
Physical Symptoms Linked To Obesity
Obesity affects the body in many physical ways. It causes clear symptoms that impact daily life and health. Recognizing these signs helps understand what obesity looks like beyond just weight. The body struggles to cope with excess fat, leading to discomfort and pain. This section highlights common physical symptoms linked to obesity.
Breathlessness And Fatigue
Extra weight makes breathing difficult. The lungs and heart work harder to supply oxygen. This leads to shortness of breath during simple activities. Fatigue often follows because the body tires quickly. People with obesity may feel exhausted after walking or climbing stairs.
Joint And Back Pain
Excess weight puts pressure on joints and the spine. This causes pain in knees, hips, and lower back. Over time, cartilage wears down faster, leading to arthritis. Moving becomes painful, reducing activity and worsening weight gain. Back pain can limit posture and daily tasks.
Increased Sweating And Snoring
Obesity raises body temperature and causes heavy sweating. Sweat glands work overtime to cool the body. Snoring is common due to extra tissue around the throat. This can block airways during sleep, causing breathing pauses. Poor sleep quality affects energy and overall health.

Credit: lighterlife.ie
Emotional And Social Effects
Obesity affects more than just the body. It also changes how people feel inside. The emotional and social effects can be hard to handle. These effects often impact daily life and well-being. Understanding these feelings helps to see the full picture of obesity.
Low Self-confidence
Many people with obesity struggle with low self-confidence. They may feel unhappy with their appearance. This feeling can stop them from trying new things. Low self-confidence often leads to avoiding social events. Negative thoughts about oneself become common. It is a challenge that affects mental health deeply.
Feelings Of Isolation
Obesity can cause feelings of isolation and loneliness. People may feel left out or different from others. Sometimes, they face judgment or unfair treatment. This causes them to withdraw from friends and family. Isolation increases sadness and stress. Support from others is important but often missing.
Health Risks Of Obesity
Obesity affects more than just appearance. It brings serious health risks that can impact daily life. The body struggles with excess weight, which can lead to multiple medical problems. Understanding these risks helps recognize the importance of maintaining a healthy weight.
Cardiovascular Issues
Obesity increases the chance of heart disease. Extra fat forces the heart to work harder. High blood pressure and cholesterol often appear with obesity. These conditions raise the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Blood vessels may become clogged, reducing blood flow.
Diabetes And Metabolic Disorders
Excess weight often leads to type 2 diabetes. The body becomes less able to use insulin properly. Blood sugar levels rise, causing serious damage over time. Obesity also raises the risk of metabolic syndrome. This group of conditions increases heart disease and stroke risks.
Skin Complications
Obesity affects skin health in many ways. Skin folds can trap moisture, causing irritation and infections. People may develop rashes, fungal infections, or skin tags. Healing of wounds slows down due to poor circulation. These issues cause discomfort and require careful skin care.
Credit: www.wbur.org
Assessing Obesity Impact
Assessing the impact of obesity requires more than just measuring weight or body size. It involves understanding the health risks and physical limitations that come with excess body fat. Health professionals use specific tools and methods to evaluate how obesity affects an individual’s well-being. These assessments guide treatment and support better health outcomes.
Edmonton Obesity Staging System
The Edmonton Obesity Staging System (EOSS) helps classify obesity beyond body mass index (BMI). It looks at physical, mental, and functional health factors. EOSS assigns stages from 0 to 4 based on the severity of obesity-related problems. Stage 0 means no risk, while stage 4 indicates severe health issues. This system helps doctors decide the best care plan for each person.
Risk Evaluation By Professionals
Health experts assess obesity risks by checking blood pressure, blood sugar, and cholesterol levels. They also review lifestyle habits like diet and exercise. Physical exams look for conditions such as sleep apnea or joint pain. Mental health is important too, as obesity can affect mood and self-esteem. This thorough evaluation helps identify risks and shape personalized treatment.
Next Steps For Concerned Individuals
Taking steps after recognizing obesity signs is vital for health. Acting early improves outcomes and quality of life. Support and guidance can make the journey easier. Understanding available options helps individuals choose the best path forward.
Consulting Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers offer expert advice tailored to individual needs. They assess health status and risks linked to obesity. Doctors may perform tests and measure body metrics. Open conversations help in setting realistic goals. Regular checkups track progress and adjust plans. Providers can recommend specialists like dietitians or therapists. This professional support builds a strong foundation for change.
Lifestyle And Medical Interventions
Lifestyle changes form the core of obesity management. Balanced diets and regular physical activity promote weight loss. Simple habits like drinking water and reducing sugar help. Medical treatments may include medications or surgery. These options depend on health conditions and severity. Combining lifestyle and medical care improves success rates. Consistency and patience are key to lasting results.
Conclusion
Obesity shows in many ways beyond just weight. It affects breathing, movement, and energy levels. People with obesity may feel tired or have joint pain. Skin problems like rashes or tags can also appear. Measuring BMI and waist size helps identify obesity risks.
Remember, understanding these signs can lead to better health choices. Small changes in daily habits make a big difference. Stay aware and take steps toward a healthier life.