Are you wondering what weight is considered obese and how it might affect your health? Understanding obesity isn’t just about looking at a number on the scale.
Your height, body composition, and overall health play a big role too. You might think you know where you stand, but the truth is, obesity is measured in ways that go beyond just weight alone. You’ll discover how experts define obesity, why your Body Mass Index (BMI) matters, and what other factors could be influencing your health.
Keep reading to get clear answers and take control of your well-being starting now.
Bmi And Weight Categories
Understanding body weight involves more than just a number on the scale. Body Mass Index (BMI) is a common tool used to classify weight categories. It considers both weight and height to give a clearer picture of health risks linked to weight. This section explains how BMI is calculated and what each category means.
Calculating Body Mass Index
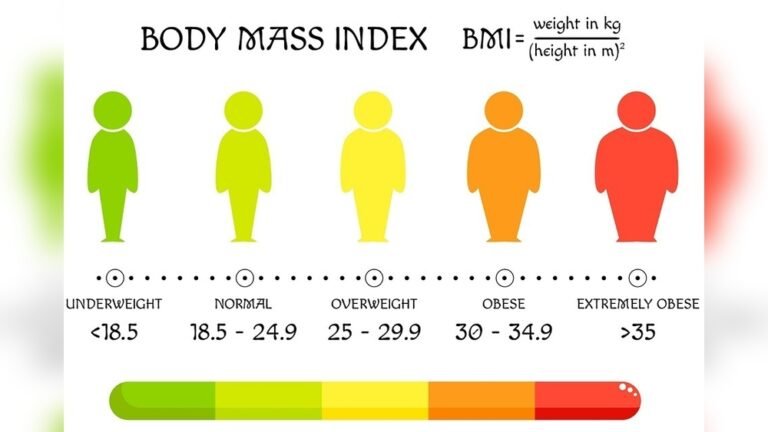
BMI is a simple calculation using weight and height. Divide your weight in kilograms by your height in meters squared. For example, if you weigh 70 kg and are 1.75 meters tall, your BMI is 22.9. This number helps identify if your weight is in a healthy range.
Weight Classifications By Bmi
The BMI scale divides weight into categories. Below 18.5 is underweight. Between 18.5 and 24.9 is normal weight. From 25 to 29.9 is overweight. A BMI of 30 or higher indicates obesity. These categories help predict health risks related to body weight.
Obesity Classes Explained
Obesity is further divided into three classes. Class 1 includes BMI from 30 to 34.9. Class 2 ranges from 35 to 39.9. Class 3, also called severe obesity, is 40 or higher. Higher classes mean greater health risks, like heart disease and diabetes. Knowing your class helps guide medical care and lifestyle changes.

Credit: en.wikipedia.org
Role Of Height In Obesity
The role of height in obesity is crucial for understanding body weight in context. Weight alone does not give a clear picture of whether someone is obese. Height affects how weight is interpreted, especially through measurements like Body Mass Index (BMI). This makes height a key factor in assessing obesity accurately.
How Height Influences Bmi
BMI is a number calculated using weight and height. It divides a person’s weight by the square of their height. Taller people may weigh more but still have a healthy BMI. Shorter people might weigh less but have a higher BMI. This shows height changes how weight relates to obesity.
Limitations Of Using Weight Alone
Using weight alone to judge obesity can be misleading. Two people with the same weight can be very different heights. Without considering height, one person may be wrongly labeled obese. Weight by itself ignores body structure and muscle mass. Height helps provide a fuller, more accurate view of health.
Factors Beyond Bmi
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a common tool for assessing obesity. It uses weight and height to estimate body fat. Yet, BMI alone does not tell the full story. Many factors influence whether a person’s weight is truly unhealthy. Understanding these factors helps give a clearer picture of obesity beyond just numbers.
Muscle Mass And Body Composition
Muscle weighs more than fat but is healthier. People with high muscle mass may have a high BMI but low fat. This means they are not necessarily obese. Body composition tests can separate muscle from fat. These tests provide a better health assessment than BMI alone.
Waist Circumference And Fat Distribution
Fat around the belly is more harmful than fat in other areas. Measuring waist circumference shows where fat is stored. A larger waist size increases the risk of heart disease and diabetes. Waist measurement is a simple way to check health risks linked to obesity.
Physical Fitness And Overall Health
Fitness level affects how weight impacts health. A person can be overweight but fit and healthy. Regular exercise improves heart health and metabolism. Doctors consider fitness and other health markers alongside weight. This helps to understand obesity’s true effect on the body.
Health Risks Linked To Obesity
Obesity is more than just carrying extra weight. It poses serious health risks that affect many parts of the body. Understanding these risks helps in managing weight better and improving overall health. This section explores the main health problems linked to obesity.
Chronic Diseases And Conditions
Obesity increases the chance of developing many chronic diseases. These include heart disease, which is a leading cause of death worldwide. Excess weight puts stress on the heart and raises blood pressure. Type 2 diabetes is common among obese individuals due to insulin resistance. Fat buildup can also cause fatty liver disease and kidney problems. Some cancers, like breast and colon cancer, occur more often in people with obesity. Joint problems such as osteoarthritis arise from extra pressure on bones and cartilage. These conditions reduce quality of life and require long-term care.
Impact On Mental Health
Obesity affects the mind as well as the body. Many people with obesity face low self-esteem and body image issues. Social stigma and discrimination can lead to anxiety and depression. Stress from these feelings might cause unhealthy eating habits, worsening weight problems. Sleep disorders, like sleep apnea, are common and reduce rest quality. Mental health challenges can make weight loss efforts harder. Support and counseling are important parts of obesity treatment.
Methods To Assess Obesity
Assessing obesity involves more than just stepping on a scale. Several methods help determine if a person is obese by measuring body fat and health risks. These methods offer easy ways to check weight status at home or through professional help.
Understanding these methods helps people track their health and make informed decisions. Different tools and evaluations provide a clearer picture of one’s weight and overall health.
Bmi Calculators And Tools
BMI, or Body Mass Index, is the most common way to assess obesity. It uses a simple formula: weight divided by height squared. Many online calculators make this quick and easy. A BMI over 30 usually indicates obesity. This method is fast and accessible for most people.
BMI does not measure body fat directly but gives a good estimate. It helps identify risk for health problems linked to excess weight.
Professional Medical Evaluations
Doctors use more detailed methods to assess obesity accurately. They may check waist size, body fat percentage, and overall health. Medical tests can find hidden risks like high blood pressure or diabetes. Professionals provide a full picture beyond just numbers.
These evaluations guide treatment plans and lifestyle advice. They ensure any health issues are caught early and managed well.
Alternative Measurement Techniques
Other methods measure obesity by focusing on fat distribution. Waist-to-hip ratio compares waist size to hip size. High ratios suggest more belly fat, which raises health risks. Skinfold thickness tests use calipers to measure fat under the skin. These methods add detail to BMI results.
They can be done at home or by a professional. Combining methods gives a more complete view of obesity and health.
Common Misconceptions
Many people have wrong ideas about what counts as obese weight. These misunderstandings can cause confusion and stress. It is important to clear up some common myths. Understanding the facts helps people make better health decisions. Obesity is not just about the number on the scale. Several factors affect whether weight is healthy or not.
Why Bmi Isn’t Always Accurate
BMI, or Body Mass Index, is a simple tool. It uses height and weight to classify body size. Many think BMI perfectly shows if someone is obese. This is not always true. BMI does not measure muscle, bone, or fat directly. Some people with high muscle mass may seem obese by BMI. Others with low muscle and high fat may appear normal. BMI also does not consider body shape or fat distribution. It works best as a quick screening tool, not a full diagnosis.
When To Consider Other Health Indicators
Weight alone does not tell the whole health story. Waist size can show belly fat, which is risky. Blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels matter too. These signs help assess health risks better than weight alone. A doctor may use scans or tests to check fat and muscle. Fitness level and lifestyle habits also play a role. Look beyond the scale to understand health fully. This approach helps identify real health risks linked to obesity.
Seeking Medical Advice
Seeking medical advice is essential to understand what is considered obese weight. Body weight alone does not give the full picture. A healthcare provider looks at many factors to provide an accurate diagnosis. They can guide you on the best steps to take for your health.
Importance Of Professional Diagnosis
Only a medical professional can confirm if you are obese. They use tools like Body Mass Index (BMI) and other measurements. These tools help assess your health risks related to weight. Self-assessment can be misleading and cause unnecessary worry or false assurance.
A doctor may also check for other health conditions linked to obesity. These include diabetes, high blood pressure, and heart disease. Early diagnosis helps in managing these issues effectively. Professional advice ensures you receive personalized care and support.
Discussing Health Concerns With Providers
Talking openly with your healthcare provider about your weight is important. Share your medical history and any symptoms you experience. This helps the provider understand your overall health better.
Ask questions about your weight and its impact on your body. Discuss lifestyle changes, diet, and exercise options. Your provider can suggest safe and effective strategies to improve your health. Regular check-ups allow monitoring progress and adjusting plans as needed.

Credit: centralpetvet.com
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_illustration_BAF8FF3-8c364807534d4b52adc4a9d649036dee.png)
Credit: www.verywellhealth.com
Conclusion
Understanding what counts as obese weight helps you take better health steps. Obesity depends on weight, height, and body composition together. BMI is a useful tool but not the only measure. Always talk to a healthcare provider for a full health check.
Small changes in lifestyle can make a big difference over time. Stay informed and focus on overall health, not just the number on the scale. Your well-being matters most.