Are you wondering what weight actually counts as obesity? You might have heard terms like BMI or body fat percentage but still feel unsure about where you stand.
Understanding the weight thresholds for obesity is more than just a number—it’s about knowing how your health might be affected and what steps you can take to feel better. You’ll discover how obesity is measured, why weight alone doesn’t tell the full story, and what factors play a role in defining a healthy or unhealthy weight for you.
Keep reading to get clear answers that can help you take control of your well-being starting today.

Credit: commons.wikimedia.org
Obesity And Weight Basics
Understanding obesity starts with knowing how weight plays a role. Weight alone does not always tell the full story. Many factors affect whether a person is considered obese. This section explains the basics of weight and obesity.
It is important to measure weight correctly. Also, understanding tools that assess obesity helps in knowing health risks.
How Weight Relates To Obesity
Obesity means having too much body fat. Weight is one way to estimate this. But two people can weigh the same and have different fat levels. Excess weight often means more fat, but not always. Muscle and bone density affect total weight too.
Doctors look at weight to screen for obesity. It helps identify those who need further health checks.
Bmi As A Measurement Tool
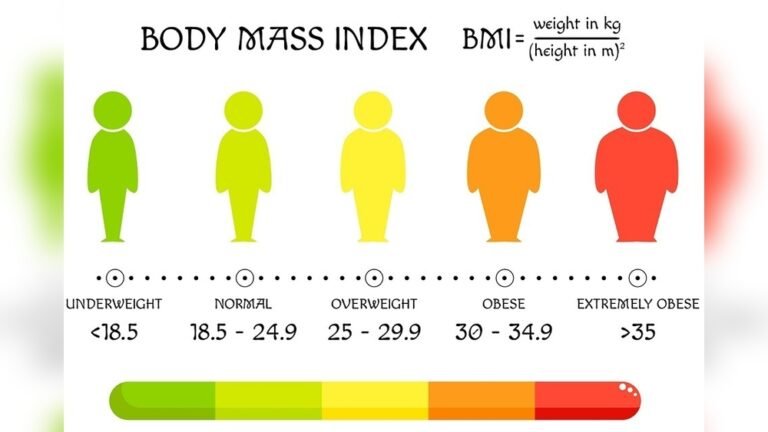
BMI stands for Body Mass Index. It uses weight and height to estimate body fat. The formula divides weight in kilograms by height in meters squared. BMI categories include underweight, normal, overweight, and obese. This tool is easy and quick to use for most people.
Health experts use BMI to track obesity rates worldwide. It helps guide treatment decisions and public health policies.
Limitations Of Bmi
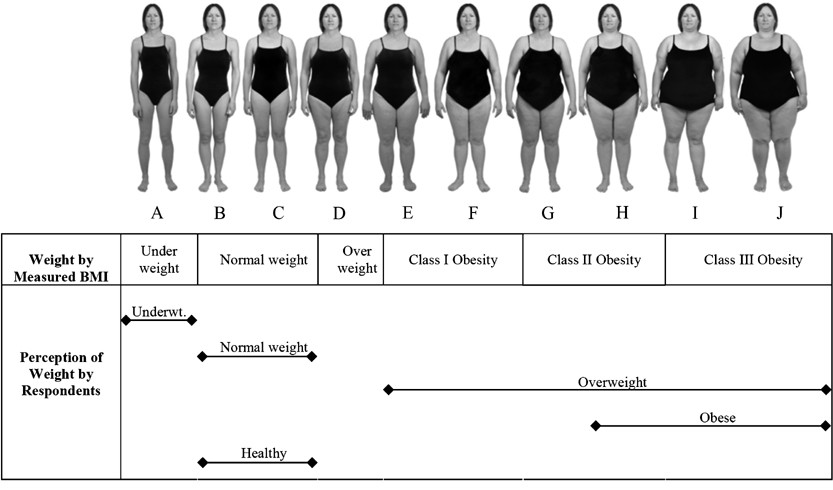
BMI does not measure body fat directly. It cannot tell muscle from fat. Athletes with high muscle may have a high BMI but low fat. BMI also ignores fat distribution, like belly fat, which affects health more.
Other factors like age, gender, and ethnicity affect BMI’s accuracy. Doctors often use other tests along with BMI for a full health picture.
Credit: www.nature.com
Weight Ranges And Obesity Categories
Understanding weight ranges and obesity categories helps clarify health risks. Weight alone does not define obesity. Body Mass Index (BMI) is a common tool used. It compares weight to height to estimate body fat. Different BMI ranges classify weight status and obesity levels. These categories guide medical advice and health decisions.
Normal Weight Vs Overweight
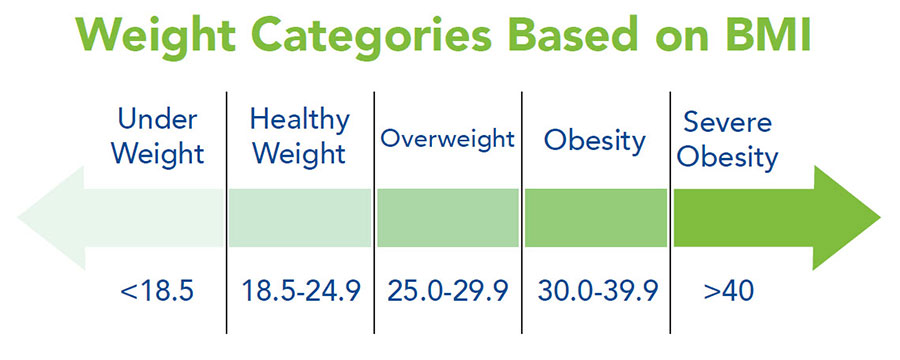
Normal weight means having a BMI between 18.5 and 24.9. This range suggests a healthy balance of body fat. Overweight is when BMI is from 25 to 29.9. People in this range have more body fat than normal. It raises the risk of health issues but is less severe than obesity.
Classifications Of Obesity
Obesity starts at a BMI of 30 or higher. It breaks down into three classes. Class 1 obesity ranges from 30 to 34.9 BMI. Class 2 covers BMI 35 to 39.9. These categories indicate increasing health risks. Higher classes usually require more medical attention.
Extreme And Morbid Obesity
Extreme obesity means a BMI of 40 or more. It is also called morbid obesity. This level greatly increases the chance of serious health problems. Heart disease, diabetes, and joint issues are common risks. Medical help is often needed to manage health at this stage.
Factors Influencing Weight Assessment
Weight assessment for obesity involves more than just a number on the scale. Several factors influence how weight relates to health and obesity risk. Understanding these elements helps provide a clearer picture of an individual’s condition. This section explores key aspects that affect weight evaluation.
Role Of Height In Weight
Height is a major factor in weight assessment. Taller people naturally weigh more due to larger body frames. Body Mass Index (BMI) uses height and weight to estimate obesity. It divides weight by height squared to adjust for different statures. However, height alone cannot determine health or fat levels.
Impact Of Muscle Mass And Body Composition
Muscle mass greatly affects weight readings. Muscle is denser and weighs more than fat. Two people with the same weight may have different health profiles if muscle and fat amounts differ. Body composition tests measure fat percentage and muscle, giving a fuller health picture. This helps avoid mislabeling muscular individuals as obese.
Age, Gender, And Ethnicity Considerations
Age changes how weight impacts health. Older adults tend to lose muscle and gain fat, affecting weight assessment. Gender also plays a role; women usually have higher body fat than men at the same weight. Ethnicity can influence body fat distribution and risk factors. These differences make personalized assessment important for accurate obesity evaluation.
Credit: www.obesityaction.org
Health Risks Linked To Obesity
Obesity impacts more than just appearance. It raises the risk of serious health problems. Understanding these risks helps in managing weight and improving well-being.
Common Obesity-related Conditions
Obesity increases the chance of heart disease, diabetes, and stroke. High blood pressure often accompanies excess weight. Joint problems and sleep apnea also occur more frequently. These conditions reduce life quality and increase healthcare needs.
Waist Circumference And Risk
Waist size shows fat distribution and health risk better than weight alone. A larger waist means more fat around vital organs. This fat type raises the risk of metabolic diseases. Measuring waist circumference is a simple way to check risk levels.
Beyond Weight: Overall Health Indicators
Weight is not the only health marker. Body fat percentage, muscle mass, and fitness matter too. A doctor can assess these factors for a clearer health picture. Regular check-ups help track progress beyond just the scale.
Weight Management Approaches
Managing weight effectively is essential for controlling obesity. Various approaches help individuals achieve a healthier weight. These methods include professional assessments, lifestyle changes, and medical treatments. Each approach plays a vital role in supporting weight loss and overall health.
Professional Medical Assessments
Doctors use medical assessments to understand weight issues better. They measure body mass index (BMI), body fat, and waist size. These tests help identify obesity and related health risks. Medical history and physical exams provide a full health picture. Professionals use this data to create personalized weight plans.
Lifestyle And Dietary Changes
Changing daily habits is key to weight management. Healthy eating with fewer calories and balanced nutrients supports fat loss. Regular physical activity burns calories and improves fitness. Small, consistent changes in diet and exercise yield long-term results. Support from nutritionists or counselors can guide these adjustments.
Medications And Treatments
Medications may help when lifestyle changes are not enough. Doctors prescribe weight loss drugs to reduce appetite or fat absorption. In some cases, surgery is an option for severe obesity. Treatments must be supervised by healthcare professionals. Combining medication with lifestyle changes improves success chances.
Tools And Resources
Understanding obesity requires more than just knowing your weight. Tools and resources help measure and assess obesity effectively. They provide clear information on body composition and health risks. Using simple methods, anyone can get an idea about their obesity status. These tools guide you toward better health decisions.
Using Bmi Calculators
BMI calculators estimate body fat based on height and weight. They are easy to use and widely available online. Enter your height and weight to get your BMI score. This score helps categorize your weight as underweight, normal, overweight, or obese. BMI is a quick screening tool but does not measure body fat directly.
Body Fat Percentage Measurements
Body fat percentage shows the amount of fat in your body. It is a better indicator of obesity than weight alone. Methods include skinfold calipers, bioelectrical impedance, and DEXA scans. These tests provide more detailed insight into your body composition. Knowing your fat percentage helps tailor diet and exercise plans.
Consulting Health Professionals
Health professionals offer personalized obesity assessments. They consider BMI, body fat, waist circumference, and medical history. Doctors and dietitians can create safe weight management plans. They monitor progress and adjust treatments as needed. Professional advice ensures a balanced approach to obesity and overall health.
Conclusion
Understanding obesity means knowing the weight ranges linked to health risks. Body Mass Index (BMI) helps classify obesity by comparing weight and height. Still, muscle mass and body fat percentage also affect health. Doctors consider many factors to give the best advice.
Maintaining a healthy weight supports overall well-being and reduces disease risk. Small changes in lifestyle can make a big difference. Stay informed and focus on balanced habits for long-term health.