Are you wondering if your weight falls into the overweight range? Understanding where you stand on the Body Mass Index (BMI) scale can give you quick insight into your health.
The BMI overweight range is more than just a number — it’s a signal that your body might be carrying extra weight that could affect your well-being. But what exactly does it mean to be in this range? And how can you use this information to make smarter choices for your health?
Keep reading to uncover the facts about BMI, what the overweight range really indicates, and practical steps you can take to stay on a healthy path. Your journey to better health starts with knowing your numbers.
Bmi Basics
Body Mass Index, or BMI, helps measure if a person is underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese. It uses weight and height to give a number. This number helps show if your body weight is healthy.
BMI is an easy and quick way to check weight categories. It is used by doctors and health experts worldwide. Knowing your BMI can guide you to make better health choices.
How Bmi Is Calculated
BMI is calculated by dividing your weight in kilograms by your height in meters squared. The formula is simple: weight (kg) ÷ [height (m)]². You can also use pounds and inches with a different formula. Many online calculators make this process easier.
Bmi Categories And Numbers
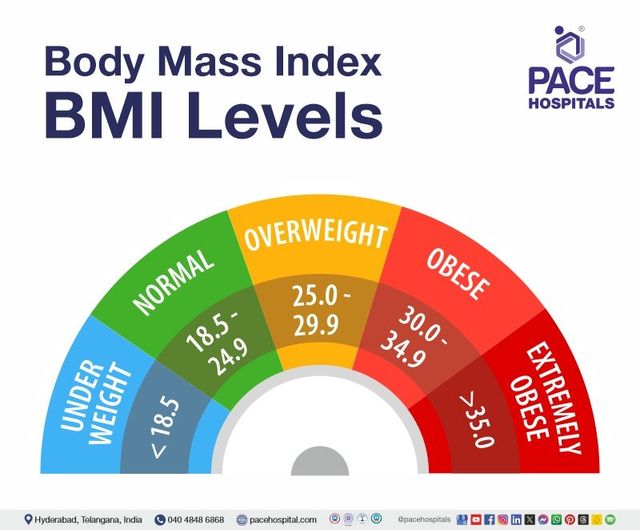
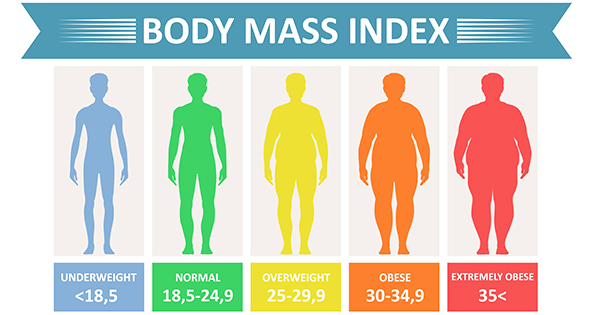
BMI numbers fall into specific categories. Below 18.5 is underweight. A BMI between 18.5 and 24.9 is normal weight. A BMI between 25 and 29.9 means overweight. A BMI of 30 or more means obesity. These categories help identify health risks linked to weight.
Limitations Of Bmi
BMI does not measure body fat directly. It does not consider muscle mass, bone density, age, or gender. A muscular person may have a high BMI but low body fat. BMI is just a screening tool. For a full health picture, consult a healthcare provider.
Credit: www.pacehospital.com
Overweight Range Explained
The overweight range on the BMI scale helps identify people with higher body weight than is healthy. It is a key measure used to assess health risks related to body fat. Understanding this range can guide better lifestyle choices and early health interventions.
BMI does not measure body fat directly but gives a good estimate for most adults. It considers weight relative to height. This makes it a simple, quick tool to screen for potential weight issues.
Bmi Values For Overweight
The BMI overweight range covers values from 25.0 to 29.9. Anyone with a BMI in this range is considered overweight. Below 25.0 is normal weight, and 30.0 or above marks obesity. This scale helps classify weight status clearly and simply.
Health Risks Linked To Overweight
Being overweight increases the risk of many health problems. These include high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease. Overweight individuals may also face joint pain and sleep apnea. Early action can reduce these risks and improve quality of life.
Difference Between Overweight And Obese
The overweight range is a step below obesity on the BMI scale. Obesity begins at a BMI of 30.0 or higher. Obesity carries a higher risk of serious health conditions than being overweight. Both conditions require attention, but obesity often needs more urgent care.
Factors Affecting Bmi Accuracy
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a simple tool to estimate if a person is underweight, normal, overweight, or obese. Despite its ease, BMI does not always show the full picture of health. Several factors can affect its accuracy. These factors can cause BMI to overestimate or underestimate body fat. Understanding these can help interpret BMI results better.
Role Of Muscle And Bone Density
Muscle weighs more than fat. People with high muscle mass may have a higher BMI. This does not mean they have excess fat. Athletes often fall into the overweight or obese BMI range despite low body fat. Similarly, bone density influences BMI. Those with denser bones may have higher weight. This adds to BMI but not to fat levels.
Age, Sex, And Ethnicity Influences
Age changes body composition. Older adults tend to lose muscle and gain fat. BMI may not reflect this shift well. Men and women have different body fat distributions. Women usually have higher body fat at the same BMI. Ethnicity also plays a role. Some ethnic groups have higher body fat at lower BMI values. These variations affect BMI’s accuracy across populations.
When Bmi May Mislead
BMI can mislead in various cases. Pregnant women may show higher BMI due to added weight. Children and teens are still growing, so BMI must be interpreted differently. People with certain medical conditions may have abnormal body composition. Relying on BMI alone may cause wrong health assumptions. For a full health assessment, other tests and professional advice are essential.

Credit: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Health Implications
The BMI overweight range signals potential health risks linked to excess weight. Understanding these risks helps people take steps toward better health. Being in this range means the body carries more fat than is ideal, which can affect how the body functions. This section explains key health concerns, why tracking BMI is crucial, and when to seek medical help.
Common Weight-related Health Conditions
Excess weight can lead to many health problems. High blood pressure is common in overweight individuals. It forces the heart to work harder than normal. Type 2 diabetes often develops due to insulin resistance from excess fat. Joint issues like osteoarthritis appear because extra weight strains bones and cartilage. Sleep apnea, a condition causing breathing pauses during sleep, also affects many overweight people. These conditions lower quality of life and increase health care costs.
Why Monitoring Bmi Matters
Tracking BMI helps identify health risks early. It is a simple way to check if weight is within a healthy range. Changes in BMI over time can show if lifestyle adjustments are working. Regular monitoring encourages better eating and exercise habits. It also helps prevent the onset of serious diseases. BMI alone does not give a full health picture but is a useful initial tool.
When To Seek Medical Advice
Consult a doctor if BMI enters the overweight range. Seek advice if weight gain happens quickly or unexpectedly. Medical help is necessary when facing symptoms like fatigue, shortness of breath, or joint pain. A healthcare provider can assess overall health, including blood tests and physical exams. They may suggest diet changes, exercise plans, or treatments to reduce health risks. Early guidance improves chances of staying healthy.
Managing Overweight Bmi
Managing an overweight BMI involves making changes to improve health and lower risks. Small, steady steps can lead to lasting results. Understanding different methods helps create a balanced approach. This section covers key strategies to manage overweight BMI effectively.
Lifestyle Changes And Diet
Start with simple lifestyle changes. Eat more fruits and vegetables. Choose whole grains over refined ones. Limit sugary drinks and high-fat foods. Drink plenty of water. Avoid skipping meals to keep energy stable. Control portion sizes to avoid overeating. Try to eat at regular times daily. These habits support weight management and overall health.
Exercise Recommendations
Physical activity is essential for managing overweight BMI. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly. Walking, cycling, or swimming are good options. Include strength training twice a week. Exercise burns calories and builds muscle. It also improves heart health and mood. Start slowly and increase activity over time. Consistency is key to seeing results.
Medical Treatments And Medications
Sometimes lifestyle changes are not enough. Doctors may suggest medical treatments or medications. Prescription drugs can help reduce appetite or absorption of fat. Medical supervision is important to avoid side effects. Surgery may be an option for severe cases. Always discuss benefits and risks with a healthcare provider. Regular check-ups help track progress and adjust treatment.
Special Considerations
BMI is a useful tool to estimate body fat. It helps identify overweight and obesity risks. Still, BMI has limits and special cases need attention. Certain conditions and groups require a different approach to BMI results. Understanding these special considerations improves health assessment accuracy.
Bmi During Pregnancy
Pregnancy changes a woman’s body weight and shape. BMI does not separate weight from baby and fluid gain. Using normal BMI ranges during pregnancy can be misleading. Doctors often use other methods to track healthy weight gain. Pregnant women should discuss weight concerns with their healthcare provider.
Bmi For Different Age Groups
BMI ranges vary for children, adults, and seniors. Children use BMI percentiles based on age and sex. Older adults may lose muscle but keep fat, affecting BMI accuracy. Age affects body composition, so BMI alone can misclassify health risks. Consider age-specific guidelines and other health measures for better results.
Using Bmi Alongside Other Measures
BMI should not be the only health measure used. Waist circumference helps show fat distribution around the belly. Body fat percentage gives a clearer picture of body composition. Physical fitness and diet are also important health indicators. Combining BMI with other tools gives a fuller understanding of health.
Tools And Resources
Understanding your BMI and the overweight range can be easier with the right tools. These resources help you track your health and make informed choices. They provide clear information about your weight status and what steps to take next.
Using Online Bmi Calculators
Online BMI calculators offer a quick way to check your body mass index. You only need to enter your height and weight. The calculator instantly shows your BMI number and weight category. Many websites provide free, easy-to-use BMI tools. These calculators help you monitor changes over time. Keep in mind, they only give an estimate and do not replace medical advice.
Professional Bmi Assessment
Healthcare professionals can provide a thorough BMI assessment. They measure your height and weight accurately. Professionals also consider factors like muscle mass and body composition. This gives a clearer picture of your health. Doctors can explain what your BMI means for you personally. They may suggest further tests or health plans if needed. A professional assessment is the best way to understand your weight status fully.
Support And Guidance Options
Support is available for those in the overweight BMI range. Many clinics offer counseling and weight management programs. These programs include diet advice and exercise plans. Support groups can provide motivation and share experiences. Online forums also connect people facing similar challenges. Professional guidance helps you set realistic goals. It encourages healthy habits for long-term success.
Credit: rtaesthetics.co.uk
Conclusion
Understanding the BMI overweight range helps you see where your weight stands. It shows if you might face health risks linked to extra weight. Remember, BMI is a simple guide, not a full health test. Muscle and bone can affect your BMI numbers.
Speak with a doctor for a better health picture. They can suggest the best steps for your body. Keeping a healthy weight supports overall well-being and energy. Small changes in diet and activity often bring big benefits. Stay informed and take care of your body every day.


