Are you curious about how obesity is shaping the health landscape across the United States? Understanding obesity statistics isn’t just about numbers—it’s about your health, your community, and the steps you can take to make a difference.
From state-by-state differences to recent trends showing shifts in obesity rates, the data reveals surprising insights that could affect you and your loved ones. Dive in to discover what these statistics mean for you and how ongoing efforts aim to turn the tide on this growing challenge.
Keep reading to uncover the facts that can empower you to take control of your health today.

Credit: www.cdc.gov
Current Obesity Rates
The current obesity rates in the United States show a significant health challenge. Both adults and children face high obesity levels. These rates impact public health, healthcare costs, and quality of life. Understanding these numbers helps highlight the scope of the issue and the need for action.
Adult Obesity Statistics
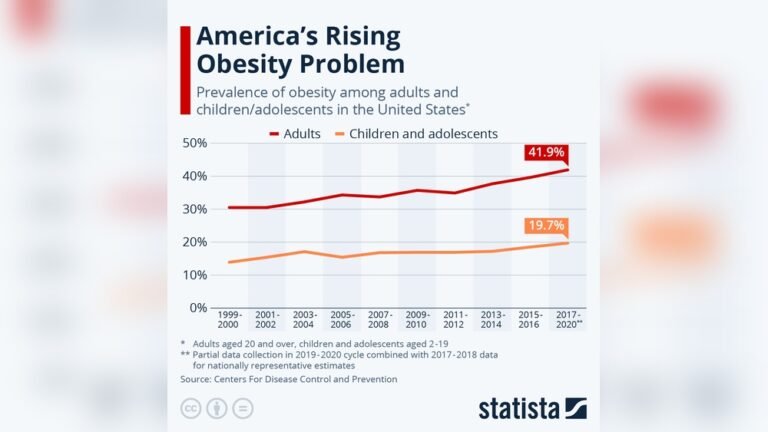
More than 40% of U.S. adults are obese. This means nearly half of the adult population struggles with excess weight. Obesity rates are higher in the South and Midwest regions. These areas show rates above the national average. The prevalence has slowed but remains very high. Severe obesity, a more dangerous form, affects about 9% of adults. This condition increases the risk of heart disease, diabetes, and other illnesses.
Childhood Obesity Numbers
Childhood obesity affects about 20% of U.S. children and teens. This rate has increased in recent decades. Obese children often face health problems like type 2 diabetes and high blood pressure. The highest rates appear in children from low-income families. Schools and communities are working to promote healthier eating and more physical activity. Early intervention is key to preventing long-term health issues.
State Variations
Obesity rates in the United States differ widely from state to state. These differences highlight the impact of lifestyle, environment, and access to health resources. Understanding state variations helps target efforts to reduce obesity effectively.
Highest Rates In South
The Southern states report the highest obesity rates in the country. States like Mississippi, Louisiana, and West Virginia have obesity rates exceeding 35%. Poor diet, low physical activity, and economic challenges contribute to these high numbers. Health programs in these states focus on improving nutrition and encouraging exercise.
Midwest Obesity Levels
The Midwest also shows high obesity levels, with states such as Indiana, Ohio, and Missouri facing rates above 30%. Rural areas in the Midwest face barriers like limited healthcare access and fewer recreational facilities. Efforts in these states aim to improve community health and increase awareness about obesity risks.
Regional Comparisons
Obesity rates in the West and Northeast are generally lower than in the South and Midwest. States like Colorado and California have rates closer to 25%. These regions benefit from more active lifestyles and better access to healthy food options. However, urban areas still face challenges linked to obesity.
Trends Over Time
Understanding the trends over time in obesity rates in the United States helps reveal the progress and challenges ahead. Tracking changes over decades shows how public health efforts impact this major issue. It also highlights areas needing more attention to reduce obesity-related health problems.
Rate Of Increase Slowing
The rise in obesity rates has slowed in recent years. After many years of sharp growth, the numbers are now growing more gradually. This suggests some progress in awareness and prevention efforts. Yet, obesity remains a serious health concern for millions of Americans. The slower increase offers hope but also signals the need for continued action.
Long-term Patterns
Obesity rates have climbed steadily since the 1980s. The rise has affected both adults and children across all states. Southern and Midwestern states show the highest rates consistently. These long-term patterns point to lifestyle and environmental factors that influence obesity. Understanding these patterns helps guide future health policies and programs.

Credit: www.niddk.nih.gov
Urban Vs Rural Differences
The obesity rates in the United States show clear differences between urban and rural areas. These differences highlight unique challenges and factors influencing health in each setting. Understanding these contrasts helps target efforts to reduce obesity more effectively.
Obesity In Urban Areas
Urban areas often have better access to healthcare and fitness centers. People in cities may find more opportunities for physical activity. Urban residents usually have access to a variety of fresh foods at markets.
Still, many city dwellers face high stress and fast-paced lifestyles. These factors can lead to unhealthy eating habits. Fast food outlets are also more common in urban neighborhoods. These conditions contribute to rising obesity rates in some cities.
Rural Obesity Challenges
Rural areas face different obstacles that increase obesity risks. Limited access to healthcare and fewer exercise facilities are common. Many rural residents live far from grocery stores with fresh produce.
Transportation issues can make healthy food harder to get. Jobs in rural areas may involve long hours and less physical activity. Social and economic factors also play a role in higher obesity rates found in rural communities.
Health And Economic Impact
Obesity in the United States affects both health and the economy deeply. The rising number of obese individuals creates challenges for the healthcare system. Costs increase as more treatments and care are needed. The economy also suffers as obesity impacts workers and businesses.
Understanding these effects helps to see why tackling obesity is urgent. The following sections explore healthcare costs, workforce productivity, and links to chronic diseases.
Healthcare Costs
Obesity leads to higher medical expenses for patients and insurers. Treating obesity-related illnesses requires ongoing care and medications. Hospitals spend more on surgeries and emergency visits linked to obesity. This increases the burden on public health programs like Medicare and Medicaid. The overall national healthcare spending rises because of obesity.
Workforce Productivity
Obesity reduces worker productivity due to more sick days and fatigue. Employees with obesity may face physical limits that affect job performance. Businesses lose money from lower output and higher disability claims. Some workers struggle to maintain energy and focus throughout the day. Companies invest more in health benefits to support affected staff.
Chronic Disease Links
Obesity increases the risk of many chronic diseases. These include diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers. Chronic diseases require long-term treatment and management. They also lower quality of life and increase mortality rates. Addressing obesity can help prevent these serious health problems.
Efforts To Combat Obesity
Efforts to combat obesity in the United States focus on changing lifestyles and improving health services. These actions aim to reduce obesity rates by encouraging better habits and making care easier to get. Many programs support healthier choices and more active living. Healthcare providers also work to offer better help to those affected.
Promoting Healthy Eating
Promoting healthy eating involves teaching people to choose nutritious foods. Schools and communities run programs to increase knowledge about balanced diets. Efforts include making fruits and vegetables more available and affordable. Food labeling improvements help consumers make informed decisions. Reducing sugary drinks and fast food intake is a key target.
Increasing Physical Activity
Increasing physical activity is vital to fight obesity. Communities create safe parks and walking trails to encourage exercise. Schools add more physical education classes for children. Workplaces promote movement through wellness programs and breaks. Public campaigns motivate people to stay active daily.
Improving Healthcare Access
Improving healthcare access helps people get support early. Health providers screen for obesity and related diseases regularly. Insurance plans cover nutrition counseling and weight management services. Telehealth expands reach to remote and underserved areas. Early intervention can prevent severe health problems linked to obesity.
Obesity And Policy
Obesity is a serious health challenge in the United States. It affects millions of adults and children. Policymakers play a key role in fighting this epidemic. They create rules and programs to promote healthier lifestyles. These efforts target many causes of obesity.
Policies focus on improving food choices, physical activity, and access to care. The goal is to lower obesity rates and improve public health. Various strategies involve government, communities, and the food industry. Each sector works to make healthy living easier and more affordable.
Government Initiatives
The government funds programs to educate people about healthy habits. It supports research on obesity causes and solutions. Agencies set nutrition standards for schools and federal meals. They also promote physical activity through public campaigns. These actions aim to prevent obesity from a young age.
Community Programs
Local groups offer programs that encourage exercise and good nutrition. They create safe spaces for walking, biking, and sports. Many communities host cooking classes and health workshops. These programs help families adopt healthier daily routines. Community support makes it easier to maintain long-term changes.
Food Industry Regulations
Regulations guide food labeling to help consumers make better choices. Limits on added sugars and unhealthy fats are set for some products. The industry faces rules to reduce portion sizes and control marketing to children. These policies aim to improve the quality of foods available. They encourage companies to create healthier options.

Credit: www.statista.com
Reliable Data Sources
Accurate data is crucial to understand obesity trends in the United States. Reliable sources provide trustworthy statistics for research and policy-making. These sources collect information from large populations using scientific methods. They update data regularly to reflect current conditions. Accessing these resources helps track obesity rates and identify areas needing attention.
Cdc Resources
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) offers extensive obesity data. Their reports cover adult and childhood obesity rates across all states. They use surveys like the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) for data collection. The CDC also provides maps and charts for easy visualization of trends. Their data helps public health officials plan obesity prevention programs.
National Institutes Of Health
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) funds studies on obesity causes and treatments. NIH databases include research findings and clinical trial results. They support efforts to understand genetic and environmental factors in obesity. NIH resources offer information on obesity-related diseases and health risks. Their data aids scientists and healthcare providers in designing better interventions.
American Society For Metabolic And Bariatric Surgery
The American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS) focuses on surgical treatment data. They collect statistics on the number and types of weight-loss surgeries performed. ASMBS tracks patient outcomes and long-term success rates. Their information guides medical professionals and patients considering surgery. ASMBS also highlights regional variations in obesity surgery trends.
Conclusion
Obesity remains a serious health challenge in the United States. Rates differ widely by state and region. The rise in obesity has slowed but still affects millions. Efforts focus on healthy eating, exercise, and better healthcare access. Understanding these statistics helps us see the scale of the issue.
Small changes in lifestyle can make a big difference. Staying informed and active supports healthier communities. Together, progress is possible to reduce obesity’s impact.