Are you curious about how to quickly find out if your weight is in a healthy range? The formula for getting your Body Mass Index (BMI) is a simple yet powerful tool that puts this information right at your fingertips.
By using just your height and weight, you can calculate a number that helps you understand where you stand in terms of body fat and health risks. Want to know the exact steps and why this number matters for you?
Keep reading to discover the easy formula for calculating your BMI and how it can guide you toward better health decisions.
Bmi Basics
Understanding BMI Basics helps you learn what BMI is and why it matters. BMI, or Body Mass Index, is a simple number that shows if your weight is healthy. It uses your weight and height to give a quick idea of your body size. This section explains what BMI measures and why tracking it is important.
What Bmi Measures
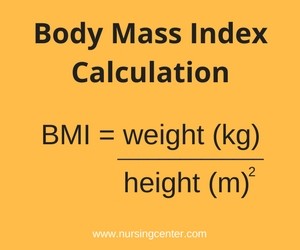
BMI measures the relationship between your weight and height. It calculates a number by dividing your weight in kilograms by your height in meters squared. This number shows if you are underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese. BMI does not measure body fat directly but gives a good estimate for most people.
Importance Of Tracking Bmi
Tracking BMI helps you keep an eye on your health. A high BMI can signal risk for health problems like heart disease and diabetes. A low BMI may show you need more nutrition. By checking BMI regularly, you can make better choices about diet and exercise. It acts as a useful tool to monitor changes in your body over time.

Credit: www.wikihow.com
Bmi Calculation Methods
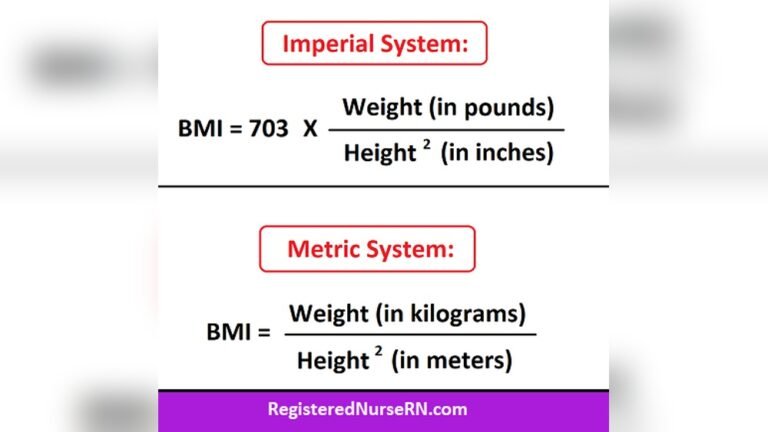
BMI, or Body Mass Index, measures body fat using height and weight. It helps identify healthy or unhealthy weight levels. Two main methods exist for BMI calculation. One uses the metric system, the other uses US customary units. Each method has a simple formula.
Metric Formula
The metric formula uses kilograms and meters. You divide your weight in kilograms by your height in meters squared.
Formula: BMI = weight (kg) / [height (m)]²
This method is common worldwide and easy to use with metric measurements. It gives a quick estimate of body fat levels.
Us Customary Formula
The US customary formula uses pounds and inches. Multiply your weight in pounds by 703. Then divide by your height in inches squared.
Formula: BMI = (weight (lbs) × 703) / [height (in)]²
This formula fits the units used in the United States. It provides the same type of BMI result as the metric formula.
Step-by-step Bmi Calculation
Calculating your Body Mass Index (BMI) is simple and requires just a few steps. This process helps you understand if your weight is in a healthy range for your height. Follow these clear steps to measure your weight and height, then apply the formula to find your BMI.
Measuring Weight
Use a reliable scale to measure your weight. Stand still and barefoot on the scale for an accurate reading. Record your weight in kilograms for the metric formula. If you use pounds, note that the formula differs slightly.
Measuring Height
Stand straight against a wall without shoes. Use a flat ruler or tape measure to find your height. Measure in meters for the metric BMI formula. For height in inches, use the formula for pounds and inches.
Applying The Formula
The most common BMI formula uses metric units: weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared. Write it as BMI = weight (kg) / [height (m)]². For pounds and inches, multiply by 703: BMI = (weight in lbs / height in inches²) × 703. Calculate the value to get your BMI number.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Interpreting Bmi Results
Interpreting BMI results helps understand your body weight relative to height. It shows if you are underweight, normal, overweight, or obese. This guide explains what different BMI numbers mean for your health. Knowing your BMI category can aid in making better lifestyle choices.
Bmi Categories
BMI values fall into several groups. Each group describes a different weight status.
- Underweight: BMI less than 18.5
- Normal weight: BMI 18.5 to 24.9
- Overweight: BMI 25 to 29.9
- Obesity: BMI 30 or more
These categories help identify if your weight is healthy or needs attention.
Health Risks By Bmi Range
Different BMI ranges link to different health risks. Being underweight can cause weak bones and fatigue. Overweight and obesity increase risks of diabetes and heart disease. Maintaining a normal BMI supports overall health and lowers illness chances.
Doctors use BMI as a quick health check. It guides further tests and treatments. Remember, BMI is only one measure. Other factors like muscle and age also matter.
Limitations Of Bmi
The Body Mass Index (BMI) is a simple formula used to estimate body fat based on height and weight. It helps identify if a person is underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese. Despite its popularity, BMI has several important limitations. It does not measure body composition directly. This can lead to misleading results for some individuals.
Understanding these limitations is key to using BMI wisely. It is just one tool among many to assess health and fitness.
Muscle Vs Fat Confusion
BMI cannot tell the difference between muscle and fat. Muscular people may have a high BMI but low body fat. Athletes often fall into this category. They may be classified as overweight or obese despite being healthy. This can cause unnecessary worry or incorrect health advice. BMI only uses weight and height, not body makeup.
Age And Gender Considerations
BMI does not adjust for age or gender differences. Women usually have more body fat than men at the same BMI. Older adults may lose muscle but keep the same weight, affecting BMI accuracy. Children and teenagers also need special BMI charts to account for growth. Using one formula for all ages and genders can give false readings.
Alternatives And Supplements To Bmi
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a common tool to assess body weight relative to height. It helps identify weight categories but does not tell the whole story about health. Many experts suggest using other methods alongside BMI for a clearer picture of body health. These alternatives can show fat distribution, muscle mass, and overall body composition better than BMI alone.
Waist Circumference
Measuring waist size offers insight into abdominal fat. Excess belly fat links to higher risks of heart disease and diabetes. Waist circumference is easy to measure with a tape. It helps identify health risks that BMI might miss. For adults, a waist measurement over 40 inches for men and 35 inches for women signals increased health risk.
Body Fat Percentage
Body fat percentage shows how much of your weight is fat. It separates fat from muscle, bone, and water. This measure is more accurate for athletes and muscular people. Various tools estimate body fat, including skinfold calipers and bioelectrical impedance scales. Knowing body fat percentage helps track fat loss or muscle gain effectively.
New Bmi Formulas
Traditional BMI uses weight divided by height squared. Some researchers propose new formulas using different powers of height. For example, height raised to 2.5 instead of 2. These new formulas aim to better match body fat and health risks across ages and body types. Although not widely used yet, they may improve BMI’s accuracy in the future.
Using Bmi For Health Tracking
Using BMI for health tracking offers a simple way to understand body weight in relation to height. It helps to identify whether a person is underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese. Tracking BMI regularly can guide better decisions about diet and exercise. This method supports maintaining a healthy lifestyle over time.
Setting Health Goals
Start with knowing your current BMI number. Use it to set realistic targets. For example, aim to reach a BMI within the normal range. Setting clear goals helps keep motivation high. It also allows for measurable progress. Choose goals that match your health needs and lifestyle.
Regular Monitoring Tips
Check your BMI at least once a month. Use the same method and tools for accuracy. Record the results to spot trends or changes. Combine BMI tracking with other measures like waist size. Avoid obsessing over small fluctuations. Focus on overall patterns to guide health choices.
Credit: www.nursingcenter.com
Conclusion
Calculating BMI is simple and useful for understanding body weight. Use the formula: weight divided by height squared. This helps identify if weight is healthy, under, or over the ideal range. Remember, BMI does not show muscle or fat differences.
Always consider other health measures for a full picture. Knowing your BMI supports better health choices and awareness. Keep track regularly to monitor changes over time. Simple math can guide you toward healthier living.