Are you curious about what your Body Mass Index (BMI) really says about your health? Understanding BMI Calculation is a simple yet powerful way to get a snapshot of your body’s weight relative to your height.
But it’s more than just a number—it can be your first step toward making smarter choices for your well-being. You’ll discover how to calculate your BMI easily, what the numbers mean for you personally, and why knowing your BMI matters more than you might think.
Ready to take control of your health? Let’s dive in and decode your BMI together.

Credit: www.usz.ch
Bmi Basics
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a simple way to check if your weight is healthy. It compares your weight to your height. This helps to estimate if you are underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese.
BMI is used by doctors and health experts worldwide. It is a quick screening tool to assess body fat levels. Though it does not measure fat directly, it gives a useful starting point.
What Bmi Measures
BMI measures the ratio between your weight and height. It uses a mathematical formula to calculate a number. This number indicates if your weight is in a healthy range for your height.
The result helps to identify risk factors linked to weight. High BMI can indicate higher chances of heart disease, diabetes, or other health problems. Low BMI may signal malnutrition or other health issues.
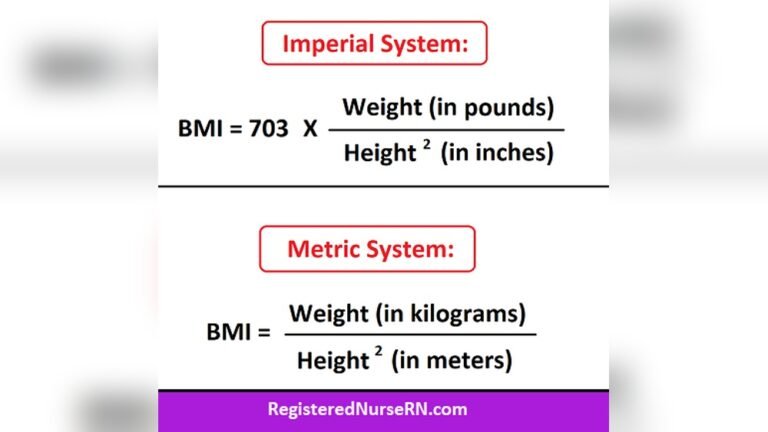
Common Bmi Formulas
The most common BMI formula uses kilograms and meters:
For those using pounds and inches, the formula is:
BMI = (weight (lbs) ÷ height (in)²) × 703
These formulas give a quick estimate of your BMI value. Health professionals use this number to guide further health assessments.
Step-by-step Bmi Calculation
Calculating Body Mass Index (BMI) helps assess if weight is healthy for height. The process is simple and uses basic math. This section explains how to calculate BMI step-by-step. It covers metric and imperial methods and using online calculators for ease.
Metric Method
Measure your weight in kilograms (kg). Measure your height in meters (m). Square your height by multiplying it by itself.
Divide your weight by your squared height. The formula is BMI = weight ÷ (height × height). For example, if weight is 70 kg and height is 1.75 m, BMI = 70 ÷ (1.75 × 1.75) = 22.86.
Imperial Method
Measure your weight in pounds (lbs). Measure your height in inches (in). Square your height by multiplying it by itself.
Multiply your BMI by 703 to adjust units. The formula is BMI = (weight ÷ (height × height)) × 703. For example, if weight is 154 lbs and height is 69 inches, BMI = (154 ÷ (69 × 69)) × 703 = 22.73.
Using Online Calculators
Many websites offer free BMI calculators. Enter your weight and height in metric or imperial units. The calculator does the math instantly. Results appear with BMI value and weight category.
This method is fast and reduces errors. Use trusted health websites or apps for accurate results.
Interpreting Bmi Results
Interpreting BMI results gives a snapshot of a person’s weight relative to height. It helps identify if someone is underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese. Understanding these results guides health decisions and lifestyle changes.
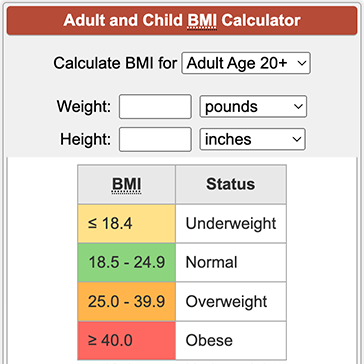
Bmi Categories
BMI values fall into specific ranges. Below 18.5 means underweight. A BMI from 18.5 to 24.9 is normal weight. Between 25 and 29.9 is overweight. A BMI of 30 or higher is obesity. These categories help assess health risks linked to body weight.
Age And Gender Differences
BMI does not adjust for age or gender. Children and teens have different BMI charts. Women and men may carry weight differently. Muscle mass affects BMI too. Older adults tend to lose muscle, which may change their BMI meaning.
Limitations Of Bmi
BMI does not measure body fat directly. It cannot distinguish muscle from fat. Athletes may have high BMI but low fat. It also ignores fat distribution, like belly fat. Other tools are needed for a full health picture.

Credit: www.gastroclinix.com
Beyond Traditional Bmi
The traditional Body Mass Index (BMI) has been a simple tool for assessing weight relative to height. It offers a quick way to categorize individuals as underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese. Yet, this method does not tell the full story about body health. Muscle mass, bone density, and fat distribution are not reflected in BMI alone. This calls for newer, more precise ways to evaluate body composition and health risks.
New Bmi Formulas
Researchers have developed new BMI formulas to improve accuracy. These formulas adjust for body shape and fat distribution. One approach uses different powers of height instead of the standard square. This helps better represent people with varied body types. Some new models also separate muscle and fat contributions. They aim to reduce misclassification of muscular individuals as overweight or obese.
Waist Circumference And Waist-to-hip Ratio
Waist circumference measures abdominal fat directly. It is a strong indicator of health risks like diabetes and heart disease. The waist-to-hip ratio compares waist size to hip size. A higher ratio signals more fat around the abdomen. This fat type is more harmful than fat in other body parts. Doctors often use these measures along with BMI for a fuller health picture.
Direct Body Fat Measurements
Direct body fat measurements provide the most accurate information. Tools like DEXA scans and bioelectrical impedance analyze fat and lean mass. These methods show how much fat is stored in different body areas. They help identify people at risk even if BMI seems normal. Using these measurements can guide better health decisions and treatments.
Bmi For Special Groups
BMI is a common way to estimate body fat. It helps assess health risks related to weight. But BMI does not fit all groups equally. Some groups need different ways to interpret BMI results.
Understanding BMI for special groups improves health insights. It guides better decisions about diet and activity. Here are key groups where BMI needs careful use.
Children And Teens
Children and teens grow fast. Their body fat changes as they age. BMI must consider age and sex for accuracy. Percentile charts show where a child stands among peers. Doctors use these charts to spot weight problems early. This method helps monitor healthy growth over time.
Older Adults
Older adults often lose muscle and bone mass. BMI may underestimate fat in elderly people. A normal BMI can hide unhealthy fat levels. Health checks should include muscle strength and waist size. These measures give a clearer picture of health risks.
Athletes And Muscular Individuals
Athletes have more muscle, not fat. Muscle is heavier than fat, raising BMI scores. This can wrongly label fit people as overweight or obese. Body fat tests or waist measurements work better here. They show true fat levels and health status more clearly.
Improving Health With Bmi Insights
Body Mass Index (BMI) offers a simple way to understand your weight in relation to your height. It helps identify if you are underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese. Using BMI insights can guide you toward better health choices. Tracking BMI changes shows progress and alerts you to risks early. This knowledge supports a healthier lifestyle and better well-being.
Setting Healthy Weight Goals
Start by knowing your current BMI number. Set realistic targets based on healthy BMI ranges. Small, steady weight changes are easier to maintain. Aim for gradual progress rather than quick fixes. Consider your age, body type, and lifestyle when setting goals. Healthy goals reduce risks like heart disease and diabetes.
Diet And Exercise Tips
Eat balanced meals with fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Limit sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats. Drink plenty of water every day. Include physical activity like walking, cycling, or swimming. Exercise helps burn calories and build muscle. Find activities you enjoy to stay motivated and consistent.
When To Seek Medical Advice
Consult a doctor if your BMI is very high or very low. Seek advice if you have health issues like high blood pressure or diabetes. A healthcare professional can offer personalized plans and tests. Do not ignore sudden weight changes or symptoms like fatigue. Early medical support improves health outcomes and safety.
Credit: www.calculatorsoup.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do You Calculate Your Bmi?
Calculate BMI by dividing your weight in kilograms by height in meters squared (BMI = kg/m²). Use pounds and inches: (weight ÷ height²) × 703.
What Is The New Formula For Bmi?
The new BMI formula adjusts the traditional calculation by incorporating waist circumference and body fat percentage. It better assesses obesity-related health risks.
What Is The Bmi Of 70 Kg 170 Cm?
The BMI for 70 kg and 170 cm is 24. 22. Calculate by dividing weight (kg) by height (m) squared.
What Is A Good Bmi For My Age?
A good BMI varies by age and sex. For adults, 18. 5–24. 9 is healthy. Children use age-specific percentiles.
Conclusion
BMI calculation offers a quick way to check body weight health. It helps identify if weight falls in healthy, underweight, or overweight ranges. Remember, BMI does not measure muscle or fat directly. Use it as a simple guide, not a full health diagnosis.
Combining BMI with other measures gives a clearer health picture. Stay aware of your body and consult health experts for advice. Tracking BMI can support better lifestyle choices and well-being. Keep it simple, stay informed, and use BMI wisely.