Are you relying on your BMI to understand your health? It might not be telling the whole story.
While BMI gives you a quick number based on your weight and height, it doesn’t reveal how much of your body is actually fat. This matters because knowing your body fat percentage gives you a clearer picture of your true health risks and fitness level.
You’ll discover why BMI alone can be misleading, how body fat percentage offers a better insight, and simple ways you can measure it yourself. Keep reading to learn how to get a more accurate view of your body and take control of your health the smart way.
Bmi Basics
BMI, or Body Mass Index, is a simple tool used to assess body weight relative to height. It helps identify if a person is underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese. This measurement guides many health decisions and provides a quick snapshot of health risks linked to weight.
Understanding the basics of BMI is essential for interpreting its results correctly. The following sections explain what BMI measures, its common categories, and its limitations.
What Bmi Measures
BMI calculates the ratio of weight to height. It uses a simple formula: weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared. This number gives a general idea of body size but does not measure body fat directly.
BMI is useful for large groups and public health studies. It helps identify trends in weight-related health risks in populations.
Common Bmi Categories
BMI results fall into several categories. Below 18.5 is underweight. Between 18.5 and 24.9 is normal weight. From 25 to 29.9 is overweight. A BMI of 30 or above is classified as obese.
These categories help doctors and individuals understand potential health risks and decide on lifestyle changes.
Limitations Of Bmi
BMI does not distinguish between muscle and fat. A muscular person may have a high BMI but low body fat. This can lead to false health risk assessments.
BMI also does not show fat distribution. Fat around organs is more harmful than fat under the skin. BMI cannot reveal this difference.
Factors like age, gender, ethnicity, and bone density affect BMI accuracy. These are not considered in the BMI calculation.
Body Fat Percentage Explained
Body fat percentage is a key measure of health. It shows how much of your body is fat compared to other tissues. Unlike BMI, body fat percentage gives a clearer picture of your body composition. Knowing this number helps understand fitness and health better.
Body fat includes essential fat needed for bodily functions and storage fat. Tracking body fat helps monitor changes in muscle and fat over time. It also guides diet and exercise choices.
Difference Between Fat And Muscle
Fat and muscle weigh differently but affect your body in unique ways. Muscle is dense and burns more calories at rest. Fat is lighter but takes up more space. Two people with the same weight can look very different based on muscle and fat levels. Muscle improves strength and metabolism. Fat stores energy and cushions organs. Knowing your fat percentage helps separate these components.
Why Body Fat Matters
Body fat plays a major role in overall health. Too much fat can lead to problems like diabetes and heart disease. Too little fat can harm hormone balance and immune function. Healthy fat levels support energy, temperature regulation, and cell health. Measuring fat percentage helps track if you are within a healthy range. This is better than just tracking weight or BMI alone.
Health Risks Linked To Fat Distribution
Where fat is stored affects health risks. Visceral fat surrounds organs and increases heart disease risk. Subcutaneous fat lies under the skin and is less harmful. Fat around the waist signals higher health risks than fat in hips or thighs. Tracking fat distribution helps identify risk early. It guides doctors to recommend lifestyle changes for better health.
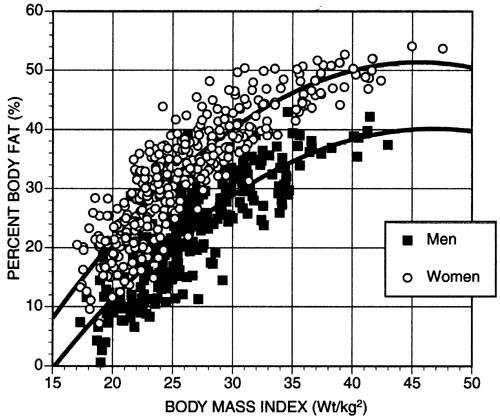
Bmi Vs Body Fat Percentage
BMI and body fat percentage are two common ways to measure health related to weight. BMI uses height and weight to give a number. Body fat percentage measures how much of your weight is fat. Both numbers give clues about health, but they are different. Understanding their differences helps you choose the best way to track your health.
How Bmi Can Mislead
BMI is a simple number based on weight and height. It does not separate fat from muscle. Muscle weighs more than fat, so muscular people may have a high BMI but low body fat. This can make BMI give wrong ideas about health. Some people with normal BMI may have high body fat. This shows BMI can sometimes be wrong.
Cases Where Bmi Fails
Athletes often have high BMI but low fat. Older adults may have normal BMI but more fat. BMI does not show where fat is stored. Fat around organs is more risky than fat under the skin. People with different bone sizes or ethnic backgrounds may get wrong BMI results. BMI does not change with age or gender, which limits its accuracy.
Why Body Fat Percentage Is More Accurate
Body fat percentage measures actual fat in the body. It shows how much fat you carry, not just weight. This helps find hidden health risks. It also shows fat distribution better than BMI. Body fat percentage changes with age and gender, giving a clearer health picture. Methods like skinfold tests or body scans give better fat measurements. This makes body fat percentage a stronger health tool than BMI.

Credit: www.researchgate.net
Methods To Measure Body Fat
Measuring body fat accurately helps understand health better than BMI alone. Various methods exist, each with its own benefits and limits. Some are simple and inexpensive. Others require special tools or experts. Choosing the right method depends on your needs and resources.
Skinfold Calipers
Skinfold calipers measure fat under the skin at specific body points. The tester pinches the skin and fat, then uses calipers to measure thickness. These numbers estimate total body fat. This method is affordable and quick. Accuracy depends on skill and consistent measurement sites.
U.s. Navy Circumference Method
This method uses measurements of the waist, neck, and height for men. For women, it includes waist, neck, hips, and height. The numbers enter a formula that estimates body fat percentage. It is easy and requires only a tape measure. It works best for average body types.
Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis
BIA sends a small electrical current through the body to measure resistance. Fat has different resistance compared to muscle and water. The device calculates body fat based on this data. BIA devices range from handheld to scales. Accuracy varies with hydration and other factors.
Advanced Techniques
More precise methods include DEXA scans, hydrostatic weighing, and MRI. DEXA uses X-rays to measure bone, muscle, and fat. Hydrostatic weighing calculates density by water displacement. MRI creates detailed images of fat distribution. These methods offer high accuracy but cost more and need special equipment.
Calculating Body Fat From Bmi
Calculating body fat from BMI is not straightforward. BMI measures weight relative to height but does not directly reveal fat content. Understanding how body fat relates to BMI helps interpret health better. This section explains why direct calculation is not possible, explores formulas that combine BMI with other factors, and introduces online calculators that estimate body fat percentage.
Why Direct Calculation Is Not Possible
BMI only compares weight to height without distinguishing muscle or fat. Muscle weighs more than fat, so muscular people may have a high BMI but low fat. BMI does not show where fat is stored, which matters for health risks. It ignores age, gender, and ethnicity, which affect body composition. These limits make direct body fat calculation from BMI inaccurate.
Formulas Combining Bmi With Other Factors
Some formulas include BMI plus age, gender, and other measures to estimate fat better. These equations improve accuracy by considering body differences. For example, the Deurenberg formula uses BMI, age, and gender to estimate body fat percentage. Such formulas give a more useful fat estimate than BMI alone but still have some margin of error.
Online Body Fat Calculators
Online tools use these formulas to estimate body fat quickly. Users enter BMI, age, gender, and sometimes waist size. The calculator processes data and shows an estimated fat percentage. These tools are easy to use and help people track body fat trends over time. They offer a practical way to assess fat without complex tests.
Interpreting Body Fat Percentage
Body fat percentage shows the amount of fat in your body. It gives a clearer picture than just weight or BMI. Understanding this number helps track fitness and health better. It reveals whether fat levels are healthy or risky.
Healthy Ranges For Men And Women
Healthy body fat ranges differ between men and women. Men usually have lower body fat than women. For men, 6% to 24% is considered healthy. Women’s healthy range is higher, from 14% to 31%. Athletes often have lower fat percentages than average adults. Staying within these ranges supports good physical function and energy levels.
Age And Gender Considerations
Body fat naturally changes with age. Older adults tend to have more body fat even if weight stays the same. Women generally carry more fat for reproductive health reasons. Hormonal changes affect fat distribution. Men may gain fat around the belly as they age. Age and gender must be factored in when interpreting body fat percentage.
Impact On Overall Health
High body fat increases risk for many health problems. These include heart disease, diabetes, and joint issues. Low body fat can cause hormone imbalances and weaken the immune system. Maintaining a healthy fat percentage supports metabolism and organ function. It also helps control blood sugar and cholesterol levels.
Improving Your Body Composition
Improving your body composition means reducing fat and increasing muscle. This change helps you look healthier and feel stronger. It also lowers risks of many diseases. Focus on habits that burn fat and build muscle. Small, steady steps bring lasting results.
Exercise For Fat Loss And Muscle Gain
Combine cardio and strength training for best results. Cardio burns calories and helps reduce fat. Strength training builds muscle and boosts metabolism. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate cardio weekly. Add two or more days of strength exercises. Use weights, resistance bands, or bodyweight moves. Focus on large muscle groups for greater impact.
Nutrition Tips
Eat balanced meals with protein, carbs, and healthy fats. Protein supports muscle growth and repair. Choose lean meats, fish, beans, and dairy. Limit sugary and processed foods to reduce fat gain. Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated. Control portion sizes to avoid overeating. Plan meals and snacks to maintain steady energy.
Tracking Progress Beyond Bmi
BMI does not show fat versus muscle changes. Use body fat scales or calipers for better tracking. Take measurements of waist, hips, and arms regularly. Notice how your clothes fit and how you feel. Keep a log of workouts and nutrition habits. Celebrate improvements in strength and endurance. This approach offers a clearer picture of your health.
Credit: www.nature.com
When To Consult Professionals
Knowing when to seek professional advice about your BMI and body fat percentage is important. Professionals help you understand your health better. They provide accurate assessments and tailored advice. Consulting experts can prevent misunderstandings about your weight and body fat. It ensures you take the right steps for your well-being.
Medical Assessments
Doctors use precise tools to measure body fat and BMI. They check for health risks linked to fat levels. Medical tests can reveal hidden problems like high visceral fat. This fat surrounds organs and can cause serious issues. Regular check-ups help track changes and guide treatment if needed.
Personalized Health Guidance
Each person’s body is different. Professionals create plans that fit your needs and goals. They consider age, gender, and lifestyle for better advice. Personalized guidance helps you lose fat safely and keep muscles strong. Experts also support you with motivation and practical tips.
Using Technology Wisely
Many tools estimate body fat at home, but they have limits. Professionals teach you how to use devices correctly. They help interpret results and avoid mistakes. Combining technology with expert advice gives the clearest picture of your health. Smart use of technology improves your weight management journey.
Credit: www.cnet.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is A Good Body Fat Percentage For Bmi?
A good body fat percentage varies by age and gender. Generally, 10-20% for men and 18-28% for women is healthy. BMI alone can’t accurately measure body fat. Use specialized formulas or methods like skinfold calipers for better assessment.
Can You Calculate Fat Percentage From Bmi?
No, BMI alone cannot accurately calculate body fat percentage. It does not distinguish muscle from fat or consider body composition. Use specialized formulas or other methods like skinfold calipers for better fat percentage estimates. Consult a healthcare provider for precise assessment and guidance.
Does Bmi Tell You Body Fat Percentage?
BMI does not directly measure body fat percentage. It estimates weight relative to height but ignores muscle and fat differences. Use specialized formulas or methods like skinfold calipers for accurate body fat assessment.
Is 29% Body Fat Overweight?
A 29% body fat is generally considered overweight for women but borderline for men. Health risks increase above recommended ranges.
Conclusion
Understanding BMI alongside body fat percentage gives a clearer health picture. BMI alone can mislead, especially for muscular people. Body fat percentage shows fat levels more directly. Use simple tools or formulas for better estimates. Always consider age, gender, and body type differences.
For precise advice, talk with a healthcare professional. Tracking both numbers helps guide healthier lifestyle choices. Stay informed and focus on overall well-being.

