When it comes to your infant’s health, understanding their growth and development is key. You might have heard about BMI—Body Mass Index—as a way to check if someone is at a healthy weight.
But what does BMI mean for infants? Can you use it to track your baby’s growth? This guide will help you discover how BMI applies to infants, why it matters, and how you can keep an eye on your little one’s healthy development.
By the end, you’ll feel confident in knowing the right steps to support your baby’s growth and when to seek advice from healthcare professionals. Keep reading to learn how this simple measure can make a big difference for your infant’s health journey.
Bmi Basics For Infants
Understanding BMI for infants helps monitor their growth and health. It shows if an infant’s weight matches their height in a healthy way. Parents and doctors use it to check if a baby grows well. Infant BMI differs from adult BMI and needs special methods.
Knowing the basics of BMI for infants guides better care. It helps identify any early weight concerns. This keeps infants on a healthy growth path.
How Bmi Is Calculated
BMI is the ratio of weight to height squared. For infants, weight is in kilograms and height in meters. The formula is weight divided by height times height. This gives a number used to assess growth. Doctors compare this number to growth charts for infants.
Differences From Adult Bmi
Infant BMI differs because babies grow fast and unevenly. Adults have stable growth patterns, infants do not. Infant BMI is interpreted with age and sex-specific charts. Adult BMI categories do not apply to babies. Infant BMI helps track early growth trends, not diagnose obesity.
Weight-for-length Vs Bmi
Weight-for-length is often used instead of BMI for infants. It compares weight directly to length without squaring height. This measure suits babies under two years old. Weight-for-length helps spot underweight or overweight infants. BMI becomes more useful as children grow older.

Credit: www.researchgate.net
Growth Charts And Percentiles
Growth charts and percentiles help track an infant’s development over time. They show how your baby’s body mass index (BMI) compares to other infants of the same age and sex. This comparison helps identify healthy growth patterns and signals any concerns early.
Using growth charts, parents and doctors can monitor weight, height, and BMI trends. Percentiles indicate the position of your infant’s BMI among peers. Understanding these charts supports better care and nutrition decisions for your baby.
Who Growth Standards
The World Health Organization (WHO) created growth standards for children worldwide. These charts focus on breastfed infants and reflect optimal growth. They cover weight, length, and BMI from birth to 2 years old.
WHO charts use data from healthy, well-nourished infants from different countries. The goal is to show how infants should grow under ideal conditions. Doctors often recommend using WHO standards for infants under 2 years old.
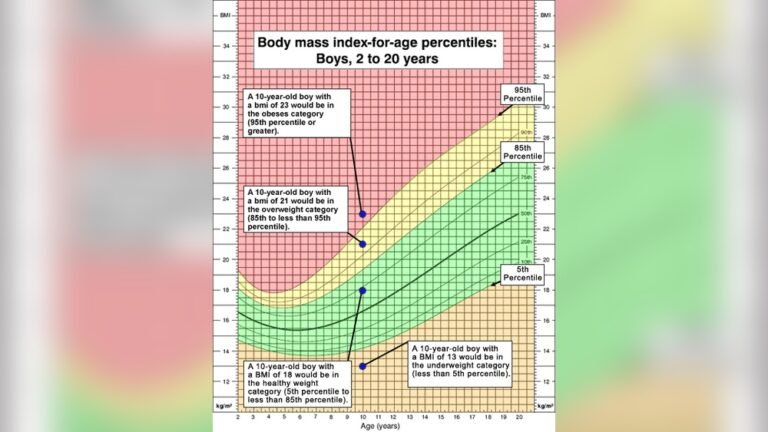
Cdc Bmi-for-age Charts
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) offers BMI-for-age charts for children aged 2 years and older. These charts are based on data from American children collected over decades. They help track BMI changes as children grow.
CDC charts classify BMI into categories like underweight, healthy weight, overweight, and obesity. Pediatricians use these to assess a child’s health risks. For infants younger than 2, weight-for-length charts are preferred over BMI charts.
Reading Percentile Rankings
Percentiles rank your infant’s BMI compared to peers of the same age and sex. For example, a BMI in the 50th percentile means half of the infants have lower BMI and half have higher. A BMI below the 5th percentile may signal underweight concerns.
A BMI above the 95th percentile might indicate overweight or obesity risk. Percentiles help doctors spot growth problems early. Regular monitoring supports proper nutrition and healthy development for your infant.
Tracking Healthy Growth
Tracking an infant’s healthy growth is key to ensuring proper development. Body Mass Index (BMI) helps caregivers and health professionals observe growth patterns. Regular checks can detect potential health issues early. Understanding how to track BMI supports better care and nutrition for infants.
Regular Monitoring Schedule
Set a routine to measure your infant’s weight and length. Pediatricians often check these at well-baby visits. Frequent monitoring helps spot changes in growth quickly. Keep records to compare measurements over time. Consistency in timing gives clearer insights into growth trends.
Using Online Bmi Calculators
Online BMI calculators make tracking easier for parents. Enter your infant’s weight and length to get the BMI. These tools use standard formulas designed for babies. They provide instant results without complex math. Choose calculators that use age-specific charts for accuracy.
Interpreting Chart Fluctuations
BMI charts for infants show percentiles, not exact numbers. Small fluctuations are normal as babies grow. Look for steady growth along a percentile line. Sudden drops or rises may need a doctor’s advice. Charts help understand overall trends, not single data points.
Factors Affecting Infant Bmi
Infant BMI is influenced by many factors that shape their growth and health. Understanding these factors helps caregivers support healthy development. Genetics, feeding habits, and activity all play important roles. Each affects an infant’s body mass index in unique ways.
Genetics And Family History
Genes inherited from parents affect infant BMI. Family history can indicate tendencies toward higher or lower body weight. Some infants may naturally carry more body fat or muscle due to their DNA. This genetic background sets the foundation for growth patterns. It also influences metabolism and how the body uses energy.
Feeding Patterns And Nutrition
Nutrition directly impacts infant BMI. Breastfeeding or formula feeding choices shape calorie intake. The timing and amount of solid foods also matter. Balanced nutrition supports steady growth and healthy weight gain. Overfeeding or underfeeding can lead to BMI outside the normal range. Quality of food is important for proper development.
Physical Activity Levels
Even infants move and explore their surroundings. Physical activity helps burn calories and build muscle. Tummy time and crawling encourage healthy weight management. Active infants tend to have better muscle tone and coordination. Limited movement may affect BMI and overall health. Encouraging safe activity supports healthy growth.
Risks Linked To Abnormal Bmi
Abnormal BMI in infants can signal health risks that need attention. Both low and high BMI values affect an infant’s growth and development. Monitoring BMI helps detect potential problems early and supports timely care. Understanding the risks linked to abnormal BMI is crucial for parents and caregivers.
Underweight Concerns
Underweight infants may lack essential nutrients. This can weaken their immune system and delay growth. They risk developmental delays and lower muscle strength. Regular check-ups can identify underweight issues early. Proper nutrition and medical advice help improve their health.
Overweight And Obesity Risks
Overweight infants face increased chances of health problems. Excess weight can lead to breathing difficulties and joint stress. It raises the risk of early childhood obesity. This condition often continues into adulthood. Healthy feeding habits and physical activity reduce these risks.
Long-term Health Implications
Abnormal BMI in infancy impacts health later in life. It can cause chronic diseases like diabetes and heart issues. Early BMI problems may affect mental health and self-esteem. Tracking BMI supports healthier growth patterns. Early intervention improves lifelong well-being.

Credit: www.childnurture.com
When To Consult A Pediatrician
Monitoring your infant’s BMI helps track their growth and health. Sometimes, the numbers may signal a need for professional guidance. Knowing when to consult a pediatrician ensures timely support for your baby’s well-being.
Signs Of Growth Issues
Watch for sudden changes in weight or height. Slow growth or rapid weight gain can be warning signs. Difficulty feeding or lack of interest in food may also indicate problems. Persistent fussiness or low energy could suggest health concerns. Early detection helps address issues before they worsen.
Personalized Growth Advice
Every infant grows at their own pace. A pediatrician can interpret BMI numbers in the context of your child’s unique needs. They provide tailored advice on nutrition, feeding, and activity. This personalized guidance supports healthy development and prevents future problems. Regular check-ups keep growth on track.
Special Conditions Impacting Bmi
Certain medical conditions affect an infant’s BMI and growth. Premature birth, genetic disorders, or chronic illnesses may change weight patterns. These cases require specialized care and monitoring. Pediatricians adjust growth plans based on these conditions. Early intervention improves long-term health outcomes.
Supporting Healthy Infant Growth
Supporting healthy infant growth is essential for strong development. Monitoring BMI helps track growth patterns in infants. Parents play a key role in guiding their baby’s nutrition and activity. Creating good habits early supports long-term health and wellbeing.
Balanced nutrition and a nurturing environment help infants reach growth milestones. Caregivers should focus on gentle encouragement and safe spaces for babies to explore. These steps promote healthy weight and muscle development.
Balanced Feeding Tips
Provide breast milk or formula as the main food source. Introduce solid foods at around six months carefully. Offer a variety of fruits, vegetables, and grains. Avoid sugary drinks and excessive salt. Feed on demand but watch for hunger cues. Ensure feeding times are calm and loving.
Encouraging Movement And Play
Encourage tummy time daily to build strength. Allow safe floor space for crawling and reaching. Use toys that stimulate movement and curiosity. Limit time in seats or carriers to promote activity. Playtime supports muscle growth and coordination. Movement also aids digestion and sleep quality.
Creating A Growth-friendly Environment
Keep the home safe and comfortable for exploration. Maintain a regular sleep schedule for proper rest. Monitor the baby’s weight and height regularly. Consult a pediatrician for growth concerns. Avoid exposure to smoke and harmful substances. A calm environment reduces stress and supports growth.

Credit: www.researchgate.net
Conclusion
Tracking BMI for infants helps monitor their growth and health effectively. Use simple tools and charts to keep measurements consistent. Always share concerns with your pediatrician for personalized guidance. Healthy growth varies, so avoid strict comparisons. Focus on balanced nutrition and regular check-ups to support your baby’s development.
Remember, early attention to BMI can prevent future health issues. Stay informed and proactive for your infant’s well-being.