Are you curious about what your BMI means and how it relates specifically to women? Understanding the BMI index for females can help you get a clearer picture of your health and guide you toward better lifestyle choices.
But did you know that BMI isn’t just a number? It’s a powerful tool that can reveal insights about your body weight in relation to your height—and highlight areas where you might want to focus your wellness efforts. Whether you’re aiming to maintain a healthy weight or looking to make changes, knowing your BMI can be the first step to achieving your personal health goals.
Keep reading to discover how the female BMI index works, what the numbers really mean, and why it matters for your well-being.
Bmi Basics For Women
BMI Basics for Women help understand body weight and health risks. It is a simple tool used worldwide. Women of different ages and sizes can use BMI to check their health status. This section explains what BMI measures, its categories, and how it changes with age.
What Bmi Measures
BMI stands for Body Mass Index. It measures the relationship between weight and height. This number helps estimate body fat in most people. It does not directly measure fat but gives a good idea. BMI is easy to calculate and widely used by doctors. It helps identify if a woman is underweight, normal, overweight, or obese.
Bmi Categories And Ranges
BMI numbers fall into specific ranges or categories. Each category shows a different health risk level. Underweight is a BMI below 18.5. Normal weight ranges from 18.5 to 24.9. Overweight is from 25.0 to 29.9. Obesity starts at a BMI of 30 or higher. These categories help women understand their health better and encourage healthy choices.
How Bmi Differs By Age
BMI changes naturally as women age. Younger women usually have lower BMI values. Older women may have higher BMI due to muscle loss and fat gain. Growth and hormonal changes also affect BMI in teens and young adults. Health risks linked to BMI vary with age. It is important to consider age when interpreting BMI results for women.

Credit: www.medicalnewstoday.com
Calculating Female Bmi
Calculating BMI for females helps understand weight relative to height. This measure offers a quick way to check if weight falls in a healthy range. Different methods exist to find BMI, each with its own ease and accuracy. Below are simple ways to calculate female BMI effectively.
Simple Bmi Formula
The BMI formula uses weight and height to find a number. It divides weight in kilograms by height in meters squared. The formula is: BMI = weight (kg) / height (m)². For pounds and inches, use: BMI = 703 × weight (lbs) / height (in)². This formula is easy to apply with a calculator or pencil.
Using Online Calculators
Online BMI calculators simplify the process. Enter weight and height, and the tool does the math. Many websites offer free BMI calculators tailored for women. These tools also explain what the BMI number means. They save time and reduce errors in manual calculation.
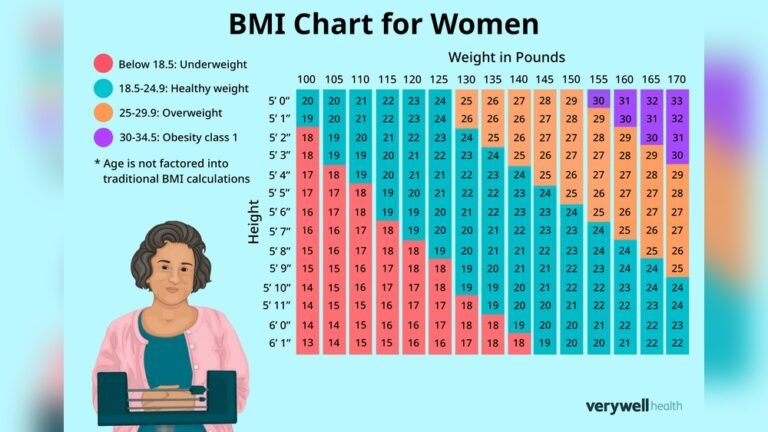
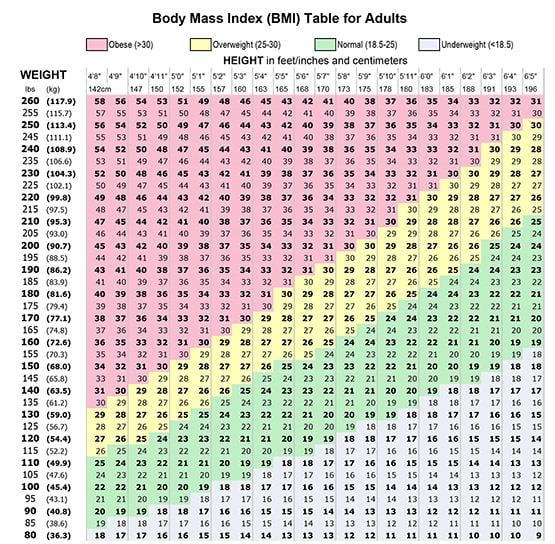
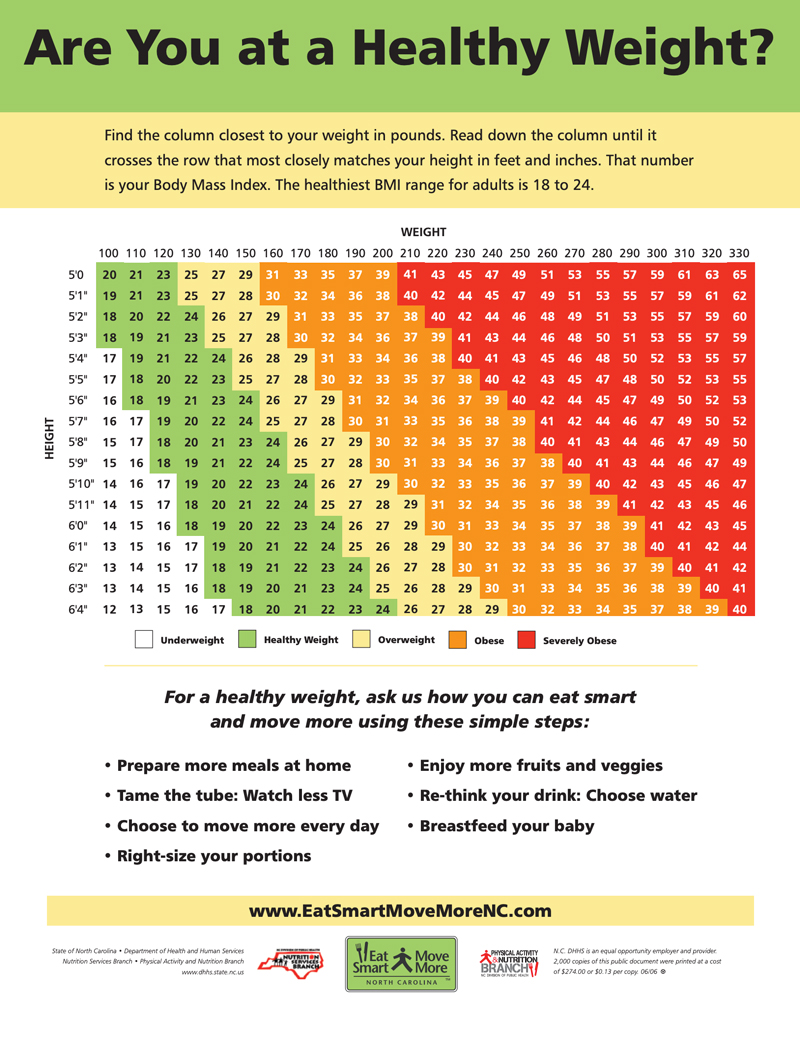
Bmi Charts For Women
BMI charts show ranges for healthy and unhealthy weights by height. Find your height on the chart, then look across to see BMI categories. These charts often separate values by age groups for better accuracy. They provide a quick visual guide without any math needed.
Interpreting Bmi Values
Interpreting BMI values helps women understand their health related to weight. Body Mass Index (BMI) uses height and weight to estimate if weight falls within a healthy range. Different BMI ranges show if a female is underweight, normal, overweight, or obese. Knowing these categories supports better health decisions. The following sections explain each BMI range clearly.
Normal
A normal BMI for females ranges from 18.5 to 24.9. This range suggests a healthy balance between weight and height. Women in this range usually have lower risks of heart disease and diabetes. Maintaining a BMI within this range supports overall well-being. Healthy eating and regular exercise help keep BMI normal.
Underweight
A BMI below 18.5 indicates underweight status. It means body weight is too low for height. Being underweight can lead to weak bones and a poor immune system. Women in this range may need to increase calorie intake or check for health issues. Gaining weight safely improves energy and strength.
Overweight
BMI values between 25.0 and 29.9 show overweight status. This range suggests excess body weight that may increase health risks. Overweight women might face higher chances of high blood pressure and joint problems. Losing weight through diet and exercise lowers these risks. Small lifestyle changes can make a big difference.
Obese
A BMI of 30 or higher indicates obesity. This condition raises the risk of serious health problems like diabetes and heart disease. Obese women should consider weight management plans. Professional guidance supports safe and effective weight loss. Early action improves long-term health outcomes.
Limitations Of Bmi
BMI does not measure muscle, bone, or fat directly. Athletic women may have high BMI but low body fat. It cannot distinguish between fat types or fat location. Age and ethnicity also affect health risks beyond BMI. Use BMI as a general guide, not a complete health test.
When To Consult A Healthcare Provider
Talk to a healthcare provider for personalized advice. Seek help if BMI is very low or very high. Medical professionals assess overall health beyond BMI numbers. They can recommend tests, diet plans, or treatments. Regular checkups support healthy weight management and prevention.
Bmi And Body Composition
BMI, or Body Mass Index, is a common tool used to assess body weight relative to height. It gives a quick number that shows if a person is underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese. But BMI alone does not explain what the number means for body composition. Body composition refers to the amounts of muscle, fat, and bone in the body. Understanding this helps to know if weight is healthy or not.
Women especially can have different body types that affect BMI results. Learning about muscle mass, fat, and bone density helps interpret BMI better. Other measurements can also give a clearer picture of health.
Muscle Mass Vs. Fat
Muscle weighs more than fat but takes up less space. A woman with high muscle mass may have a higher BMI but low body fat. This means she is fit, not overweight. Fat adds to body weight but does not build strength. BMI does not separate muscle from fat, so a strong woman may appear heavier than she is.
Bone Density Impact
Bone density varies among women and affects weight. Denser bones weigh more and can raise BMI. Older women may lose bone density, changing their BMI without weight change. BMI does not measure bone health, so it should be checked with other tests. Knowing bone density helps avoid wrong assumptions about weight and health.
Alternative Measurements
Other methods measure body composition more accurately. Skinfold tests estimate body fat by pinching the skin. Bioelectrical impedance analysis sends a small electric current to estimate fat and muscle. Waist circumference shows fat around the belly, linked to health risks. These tools add details that BMI alone cannot provide.
Bmi During Pregnancy
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a common tool to assess weight relative to height. During pregnancy, BMI helps track health but needs careful interpretation. Pregnancy brings natural weight changes that can affect BMI readings. Understanding how to adjust BMI and monitor weight gain supports healthier pregnancies for women.
Adjusting Bmi Calculations
Standard BMI calculations may not apply during pregnancy. The extra weight from the baby, placenta, and fluids changes the numbers. Doctors often focus on pre-pregnancy BMI for a clearer health picture. Adjustments consider trimester and typical pregnancy weight gain. This approach helps avoid misleading BMI results.
Healthy Weight Gain Guidelines
Weight gain during pregnancy varies by pre-pregnancy BMI. Women with a normal BMI usually gain 25 to 35 pounds. Those underweight may need more, around 28 to 40 pounds. Overweight women should aim for less, about 15 to 25 pounds. These guidelines help support fetal growth and maternal health.
Monitoring Maternal Health
Regular check-ups track weight gain and overall health during pregnancy. Healthcare providers watch for signs of excessive or insufficient weight gain. Balanced nutrition and physical activity are key to safe weight management. Close monitoring reduces risks for mother and baby.
Bmi And Health Risks
BMI, or Body Mass Index, is a simple number based on height and weight. For females, it helps estimate if weight falls in a healthy range. This number links closely to health risks. Understanding these risks can guide better lifestyle choices.
High or low BMI values may increase chances of several health problems. These include issues related to weight, heart, and blood sugar control. Knowing the connection between BMI and these conditions is important for prevention and care.
Weight-related Conditions
Women with high BMI often face weight-related health problems. These include joint pain and arthritis. Excess weight puts pressure on bones and muscles. It can reduce mobility and cause discomfort. Low BMI can lead to weakness and nutrient deficiencies. Both extremes affect daily life and wellness.
Cardiovascular Health
BMI affects heart health in women. A higher BMI raises risks of high blood pressure and stroke. Extra body fat strains the heart and blood vessels. This can cause heart disease over time. Keeping BMI within a healthy range supports better heart function.
Diabetes And Bmi
Diabetes risk rises with increased BMI in females. Extra fat affects how the body uses insulin. This can lead to type 2 diabetes. Maintaining a healthy BMI helps control blood sugar levels. Monitoring weight is key in diabetes prevention and management.
Bmi And Weight Management
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a simple tool used to assess body weight relative to height. For females, maintaining a healthy BMI supports overall health and reduces disease risks. Weight management is key to reaching and keeping an ideal BMI. It involves changes in daily habits, diet, and sometimes medical help.
Lifestyle Changes
Small adjustments in daily routines can improve BMI. Walking more, taking stairs, and standing often increase activity levels. Sleep quality also affects weight and metabolism. Managing stress helps prevent unhealthy eating. These simple steps support weight control and better health.
Role Of Diet And Exercise
Balanced eating is crucial for healthy BMI. Focus on fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Avoid sugary drinks and high-fat foods. Regular exercise burns calories and builds muscle. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate activity weekly. Combining diet and exercise gives the best weight management results.
Medical Interventions
Sometimes lifestyle changes are not enough. Doctors may suggest medications to help reduce weight. In severe cases, surgery might be an option. Medical help should be supervised by professionals. It supports safe and effective BMI improvement.
Medications Linked To Bmi
Medications linked to BMI offer options for managing weight, especially for women with high BMI levels. These drugs support weight loss alongside diet and exercise. They target appetite control, metabolism, or fat absorption.
Understanding eligibility for weight loss drugs helps women know if they qualify. Criteria vary by medication and health conditions. Medical evaluation plays a key role in deciding the right treatment.
Eligibility For Weight Loss Drugs
Women with a BMI of 30 or higher often qualify for weight loss drugs. Those with a BMI of 27 or higher can qualify if they have weight-related health issues. Common conditions include diabetes, high blood pressure, or sleep apnea.
Age and overall health impact eligibility. Doctors consider medication risks and benefits for each individual. Not everyone with a high BMI will be prescribed these drugs.
Ozempic And Semaglutide Criteria
Ozempic and Semaglutide are popular drugs affecting appetite and blood sugar. They are often prescribed for type 2 diabetes and weight loss. Women with a BMI of 30 or higher may be eligible.
Those with a BMI of 27 and health problems related to weight might also qualify. Doctors assess medical history before prescribing these medications. Regular follow-up ensures safety and effectiveness.
Importance Of Medical Evaluation
A medical evaluation is essential before starting any weight loss medication. Doctors review health history, current medications, and possible side effects. This step ensures the drug is safe and suitable.
Evaluation includes physical exams and sometimes lab tests. Ongoing monitoring helps track progress and adjust treatment. Medical guidance reduces risks and improves results.
Body Size Diversity
Body size diversity celebrates the many shapes and sizes women naturally have. Each woman’s body is unique, shaped by genetics, lifestyle, and health factors. Understanding this diversity helps us appreciate health beyond simple numbers like BMI.
Embracing Different Body Types
Women come in a wide range of body types. Some have more muscle, others carry more fat. Each type can be healthy in its own way. Embracing this variety reduces stigma and promotes self-acceptance. It encourages women to focus on how they feel, not just how they look.
Beyond Bmi: Holistic Health
BMI measures weight relative to height but misses many health details. It does not show muscle strength, bone density, or fat distribution. A woman with high muscle may have a high BMI but be very fit. Holistic health looks at nutrition, activity, and mental wellness too. This approach supports a fuller view of well-being.
Mental And Emotional Well-being
Body size diversity connects deeply to mental health. Feeling pressured to fit one size harms self-esteem and confidence. Accepting different body shapes helps reduce anxiety and depression. Emotional health is a key part of overall wellness. Supporting all body types fosters kindness and positive self-image.
Credit: www.ramsayhealth.co.uk
Credit: www.eatsmartmovemorenc.com
Conclusion
Understanding the BMI index for females helps track general health. It provides a simple way to estimate if weight is healthy for height. Remember, BMI does not measure muscle or fat directly. Body composition and personal health vary from person to person.
Use BMI as a starting point, not the only guide. Always talk to a healthcare professional for advice tailored to you. Keeping a balanced diet and staying active supports a healthy BMI. Small changes can lead to better health over time.
Stay informed and listen to your body’s needs.