Are you curious about what your BMI index means and how it affects your health as a man? Understanding your Body Mass Index (BMI) is a simple yet powerful way to get a snapshot of your overall fitness and risk for health issues.
But did you know that BMI isn’t just a number—it’s a key that can unlock insights about your body composition, lifestyle, and even your future well-being? You’ll learn exactly what the BMI index for men is, why it matters, and how to interpret your results to make smarter health choices.
Ready to take control of your health and see what your BMI really says about you? Keep reading to discover the facts every man should know.
Credit: austingynecomastiacenter.com
Men’s Bmi Basics
Understanding the Body Mass Index (BMI) is important for men who want to track their health. BMI gives a quick estimate of body fat based on height and weight. It helps identify if a man is underweight, normal, overweight, or obese. This simple number can guide lifestyle choices and health plans.
Knowing your BMI is a good first step toward better health. It shows if weight is in a healthy range or if changes are needed. Men can use BMI to monitor their fitness progress over time. The number is easy to calculate and understand, making it a useful tool for many.
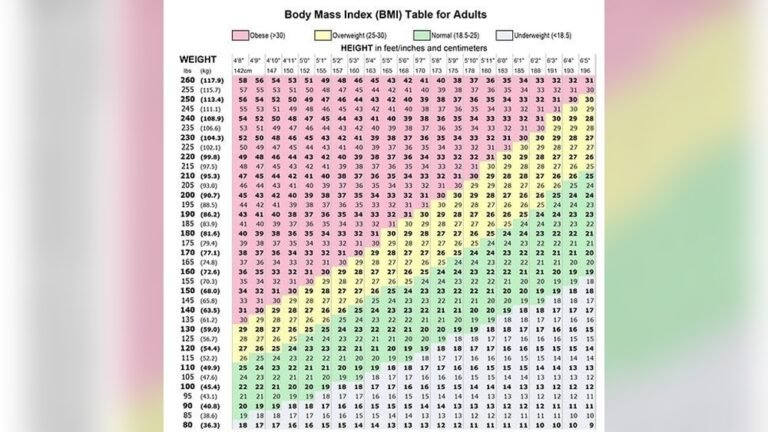
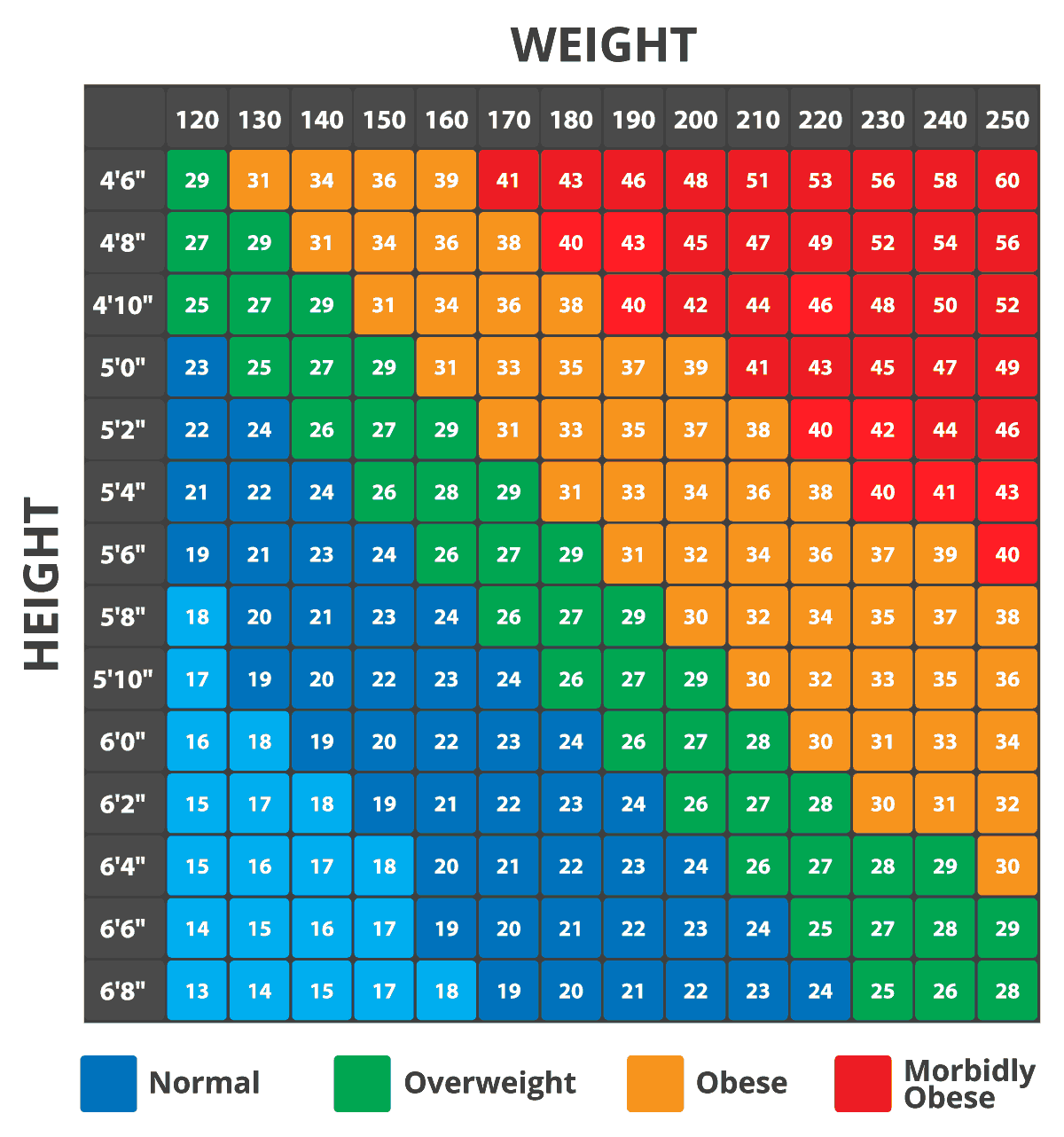
Bmi Categories For Men
BMI numbers fit into specific categories that show weight status. A BMI below 18.5 means underweight. A BMI from 18.5 to 24.9 is normal weight. BMI between 25 and 29.9 indicates overweight. A BMI of 30 or higher is obese. These categories help men see where they stand.
Each category links to health risks. Being underweight may cause weakness or illness. Overweight and obesity increase the chance of heart disease and diabetes. Staying in the normal range lowers health risks and supports well-being.
How To Calculate Bmi
Calculate BMI by dividing weight in kilograms by height in meters squared. Use this formula: BMI = weight (kg) / [height (m)]². For pounds and inches, multiply weight by 703, then divide by height squared. This makes BMI easy to find using simple math.
Many online calculators can also find BMI quickly. Measure height and weight accurately for the best results. Keep in mind, BMI is a guide, not a full health check. Muscle mass or body type can affect the number.
Ideal Bmi Range For Men
The ideal BMI range for men helps identify a healthy body weight. It measures weight relative to height. This simple calculation can guide men to maintain good health. Staying within the ideal range lowers risks of diseases like diabetes and heart problems.
Men should aim for a BMI that supports energy and strength. The right BMI varies by age and body type. Understanding these differences ensures better health decisions. This section explains healthy BMI values and age-related variations for men.
Healthy Bmi Values
A BMI between 18.5 and 24.9 is considered healthy for most men. This range suggests a balanced weight for height. Values below 18.5 may indicate underweight. Above 24.9, the risk of health issues may rise.
Men with a BMI in the healthy range often have lower chances of heart disease and diabetes. It supports good physical fitness and energy levels. Doctors use these values as a basic health guide.
Bmi Differences By Age
BMI can vary as men age. Muscle mass tends to decrease while fat may increase. This change affects BMI without always showing true health status.
For men over 65, a slightly higher BMI range of 25 to 27 may be healthier. This range helps protect against frailty and bone loss. Younger men should aim for the standard healthy range.
Age changes how BMI relates to health risks. Older men should consider other measures like waist size and muscle strength. Consulting a healthcare provider gives the best advice for healthy weight as men age.
Bmi And Body Composition
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a common tool to assess men’s health. It measures weight relative to height. But BMI alone does not show body composition. Understanding muscle and fat is key to interpreting BMI correctly. Body composition affects health more than BMI numbers alone.
Muscle Vs. Fat Impact
Muscle weighs more than fat. A man with high muscle mass may have a high BMI. This does not mean he is unhealthy. Fat stores increase health risks like heart disease. Muscle supports metabolism and strength. BMI cannot tell the difference between muscle and fat. This limits BMI’s accuracy in athletic or muscular men.
Body Fat Distribution
Where fat is stored matters for health. Fat around the belly is riskier than fat on hips or thighs. Abdominal fat links to diabetes and heart problems. BMI does not show fat location on the body. Men should also measure waist size for better risk assessment. Combining BMI with waist measurement offers a clearer health picture.
Age And Bmi Variations
Body Mass Index (BMI) changes as men age. Age affects body fat, muscle, and bone density. These changes make BMI a less precise measure over time. Understanding age-related BMI variations helps men track their health better. Adjusting BMI expectations is important for accurate health insights.
Men’s bodies lose muscle and gain fat with age. This shift can raise BMI even if weight stays stable. Older men may have higher BMI but not more fat. Awareness of these changes guides healthy lifestyle choices.
Bmi For Older Men
Older men often have different BMI ranges than younger men. Muscle loss and fat gain affect BMI readings. A BMI considered overweight in younger men may be normal for older men. Some studies suggest a slightly higher BMI is healthier for older adults. This range helps protect against health risks like falls and frailty.
Doctors may use adjusted BMI values for men over 65. This adjustment reflects changes in body composition. It improves health risk assessments and guides better care plans. Older men should focus on overall health, not just BMI numbers.
Adjusting Bmi Expectations With Age
Standard BMI categories do not fit all ages. Age changes body structure and fat distribution. Men should expect BMI to shift naturally over time. Higher BMI might not mean poor health in older age.
Other measures like waist size and muscle strength matter more with age. Combining BMI with these checks gives a clearer health picture. Regular health assessments help men maintain good weight and fitness as they grow older.
Bmi Limitations For Men
The Body Mass Index (BMI) is a quick way to estimate body fat based on height and weight. It is widely used to assess health risks related to weight. Still, BMI has its limitations, especially for men. Understanding these limits helps avoid false conclusions about one’s health.
BMI does not measure muscle, bone, or fat separately. This can lead to misleading results. Men with high muscle mass might be labeled overweight or obese. Yet, their body fat could be low. This shows why BMI alone cannot always reflect true health status.
Why Bmi Can Be Misleading
BMI calculates weight divided by height squared. It does not consider muscle weight or bone density. Men who work out regularly often have more muscle. Muscle weighs more than fat. So, their BMI may show as high, but they are healthy. Older men may lose muscle but keep the same BMI. This can hide health risks linked to fat gain.
Body fat distribution also matters. BMI cannot detect where fat is stored. Fat around the belly increases health risks. BMI treats all fat the same. It misses the difference between dangerous and less harmful fat.
Other Health Metrics To Consider
Waist circumference is a simple way to check fat around the belly. A larger waist means higher risk for heart disease and diabetes. Waist-to-hip ratio is another useful measure. It compares waist size to hip size. This ratio helps identify unhealthy fat patterns.
Body fat percentage gives a clearer picture of fat versus muscle. Tools like skinfold calipers or bioelectrical impedance help estimate body fat. Consulting a doctor can provide more accurate health assessments. They may use tests like DEXA scans or hydrostatic weighing.
Blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels also show health risks. Combining these with BMI provides a fuller view of health. This approach helps men make better decisions about diet and exercise.
Using Bmi To Guide Fitness
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a simple tool that helps men understand their body weight in relation to height. Using BMI to guide fitness can provide clear insights. It acts as a starting point to shape fitness routines and track changes over time. Men can use BMI to set realistic goals and measure their progress effectively.
Setting Fitness Goals
Knowing your BMI helps define fitness targets. Men with a high BMI may aim to reduce body fat. Those with a low BMI might focus on building muscle. Setting goals based on BMI keeps fitness plans focused and practical. It encourages healthy weight management tailored to individual needs.
Tracking Progress With Bmi
Regularly checking BMI reveals how well fitness plans work. Tracking changes can show fat loss or muscle gain. It provides motivation by making progress visible. Men can adjust workouts or diets based on BMI trends. This simple measure supports staying on the right fitness path.
When To Consult A Doctor
Knowing when to consult a doctor about your BMI is important for men’s health. BMI is a useful tool but has limits. It does not show the full picture of your health. Medical advice helps understand your unique health needs.
Consulting a doctor is wise if your BMI is very high or low. Also, seek help if you notice sudden weight changes or health issues. A doctor can check if your weight affects your overall health.
Personalized Health Assessments
Doctors offer personalized health assessments beyond just the BMI number. They consider muscle mass, bone density, and fat distribution. These factors affect your health more than BMI alone.
A healthcare provider reviews your medical history and lifestyle habits. This helps create a clear health profile. Personalized advice can guide better weight management and disease prevention.
Beyond Bmi Screening
BMI screening is just one step in health evaluation. Doctors may recommend other tests like blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels. These tests reveal risks that BMI cannot show.
Regular check-ups help track changes in your body and health risks. Men with chronic conditions or family history should see doctors more often. Early detection improves treatment success and quality of life.

Credit: www.health.harvard.edu

Credit: www.braceability.com
Conclusion
Tracking your BMI helps understand your health better. Men should use it as a simple guide. Remember, muscle weighs more than fat, so BMI isn’t perfect. Age and body type affect your ideal BMI range. Always talk to a doctor for a full health check.
Keeping a healthy BMI supports a balanced lifestyle. Small changes in weight can improve overall well-being. Stay active, eat well, and monitor your progress regularly. Your health matters—use BMI as one helpful tool.