Understanding your BMI levels as a female is more than just knowing a number—it’s about gaining insight into your health and well-being. Have you ever wondered what your BMI really says about your body?
Whether you’re aiming to maintain a healthy weight, lose a few pounds, or simply want to understand how your body measures up, knowing your BMI can be a powerful tool. You’ll discover what different BMI levels mean specifically for women, how age affects these numbers, and practical tips to keep your BMI in a healthy range.
Ready to take control of your health and unlock the secrets behind your BMI? Let’s dive in.
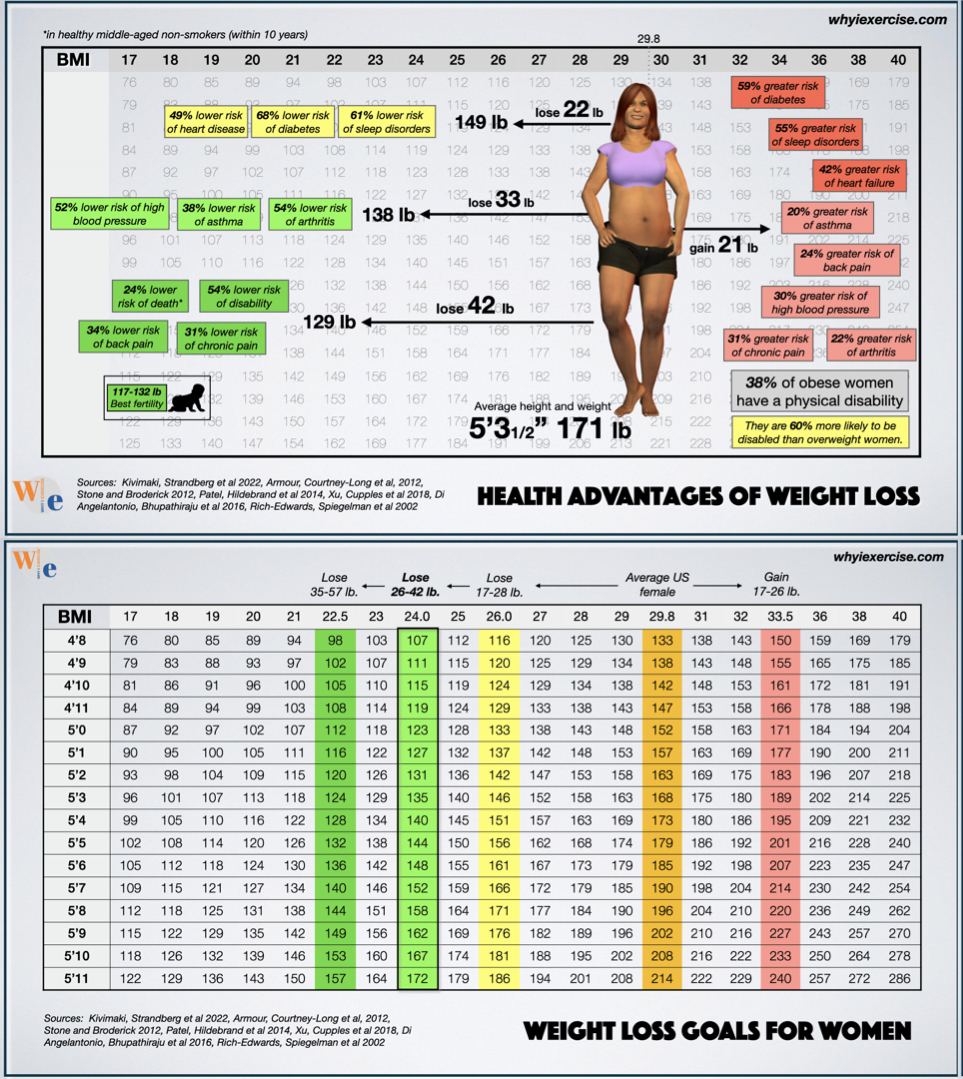
Credit: www.whyiexercise.com
Bmi Basics For Women
Understanding BMI basics helps women track their health. Body Mass Index, or BMI, offers a simple way to estimate body fat. This measurement uses height and weight to give a number. Women can use this number to see if they are underweight, healthy, or overweight. Knowing your BMI can guide healthier lifestyle choices. It serves as a quick health check without needing special tools.
Bmi Calculation Method
BMI is calculated by dividing weight in kilograms by height in meters squared. The formula is: BMI = weight (kg) ÷ height (m)². For those using pounds and inches, the formula changes to BMI = (weight ÷ height²) × 703. This calculation provides a number that falls into specific categories. It is easy to do at home or with online calculators.
Bmi Categories Explained
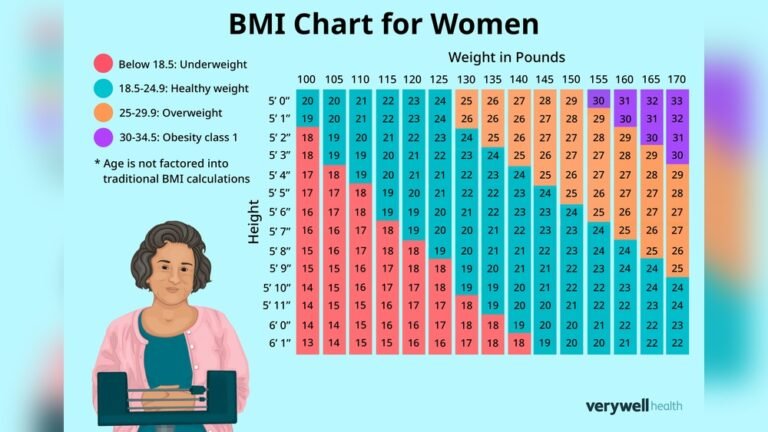
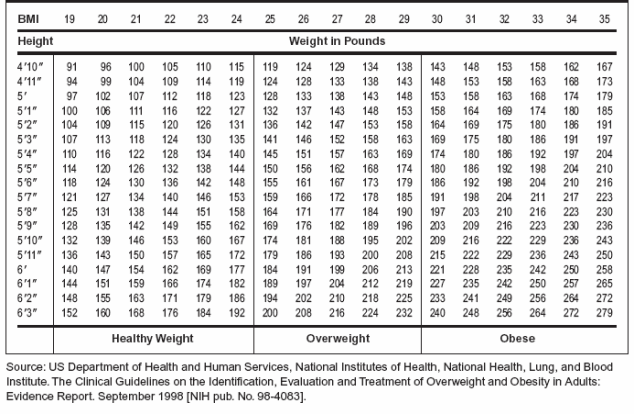
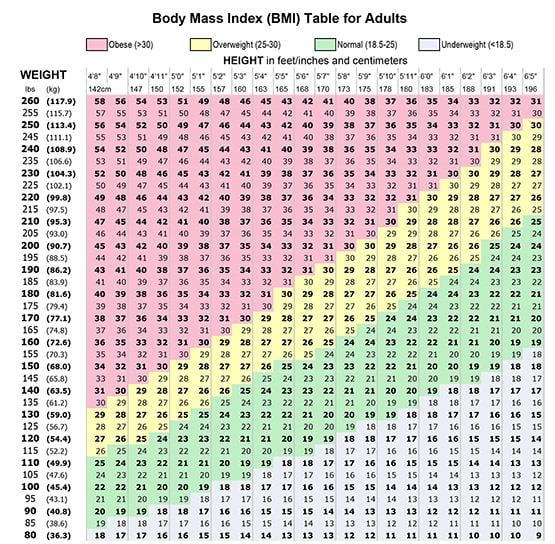
BMI results fall into several categories. Below 18.5 means underweight. A range of 18.5 to 24.9 indicates a healthy weight. Between 25 and 29.9 shows overweight. Above 30 signals obesity. Each category points to different health risks. Women should understand these ranges to monitor their well-being.
Why Bmi Matters For Women
BMI offers a quick look at weight-related health risks. Women with high BMI face greater chances of heart disease and diabetes. Low BMI can mean nutrient deficiencies or weakened immunity. Tracking BMI helps women maintain a balanced weight. It supports early action to prevent health problems. Doctors often use BMI to guide health advice.
Credit: www.cancer.org
Age-specific Bmi Insights
BMI values change with age and body development. Different age groups need unique BMI standards. These standards help track healthy growth and weight status. Understanding age-specific BMI guides better health decisions.
Body changes across life stages affect BMI interpretation. Children, adults, and older women all have different BMI ranges. This section explains these differences clearly and simply.
Bmi For Children And Teens
Children and teens use BMI percentiles instead of fixed numbers. These percentiles compare a child’s BMI to others of the same age and sex. A BMI in the 85th to 94th percentile shows overweight. Above the 95th percentile means obesity. Below the 5th percentile may indicate underweight. Growth charts from health agencies help track this.
Adult Female Bmi Ranges
Adult women’s BMI is divided into standard ranges. A BMI from 18.5 to 24.9 is healthy. Between 25 and 29.9 indicates overweight. A BMI of 30 or more signals obesity. These ranges help assess risk for diseases like diabetes and heart issues. BMI alone does not show muscle or fat percentage.
Bmi Considerations For Older Women
Older women often have different body compositions. Muscle loss and fat gain affect BMI accuracy. A slightly higher BMI might be healthy for older women. Doctors consider other factors like bone density and overall health. BMI is one tool among many for this group.
Bmi And Pregnancy
Understanding BMI during pregnancy is important for the health of both mother and baby. Pregnancy brings many changes to a woman’s body, including weight gain. Tracking BMI helps monitor if this weight gain is healthy or needs attention. It supports better care and healthier outcomes.
Calculating Bmi During Pregnancy
Calculating BMI while pregnant differs from usual methods. The standard BMI formula uses weight and height, but pregnancy weight includes the baby, placenta, and fluids. Doctors often calculate BMI before pregnancy or early in the first trimester. This initial BMI helps guide healthy weight gain goals throughout pregnancy. Regular weight check-ups track progress without recalculating BMI each time.
Healthy Weight Guidelines For Expecting Mothers
Healthy weight gain depends on pre-pregnancy BMI. For women with a normal BMI, gaining between 25 and 35 pounds is typical. Those with lower BMI may need to gain more, while higher BMI women might gain less. Staying within recommended weight ranges lowers risks of complications. Balanced nutrition and regular prenatal visits support safe weight gain. Every pregnancy is unique, so follow healthcare advice closely.
Health Implications Of Bmi Levels
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a key measure to understand health risks related to body weight. For females, maintaining a healthy BMI is vital for overall well-being. BMI levels that are too low or too high can lead to various health problems. Understanding these risks helps women take better care of their health.
Risks Of Low Bmi
A low BMI often means the body lacks enough fat and muscle. This can cause weakness, tiredness, and poor immune function. Women with low BMI may face issues like bone loss and irregular menstrual cycles. In severe cases, it can lead to malnutrition or eating disorders. Low BMI can also affect mental health, causing anxiety or depression.
Risks Of High Bmi
A high BMI indicates excess body fat, which stresses the heart and joints. Women with high BMI have a higher chance of developing high blood pressure. It also raises the risk of sleep apnea and breathing difficulties. High BMI can reduce energy levels and increase fatigue. It often leads to lower self-esteem and social challenges.
Bmi And Chronic Diseases
BMI levels strongly link to chronic diseases in women. High BMI increases the risk of type 2 diabetes and heart disease. It also raises chances of stroke and certain cancers, like breast and ovarian cancer. Low BMI can weaken the body’s defense against infections and slow recovery. Tracking BMI helps in early detection and prevention of these diseases.
Beyond Bmi: Other Health Measures
BMI is a common way to check body weight against height. It shows if a female’s weight is under, normal, or overweight. Still, BMI alone does not tell the full health story. Other measures help to understand body shape and fat better. These help see risks that BMI might miss.
Waist-to-hip Ratio
This ratio compares waist size to hip size. It shows where fat is stored on the body. A higher ratio means more fat around the waist, which can raise health risks. Measuring waist-to-hip ratio helps find risks linked to heart disease and diabetes. It is a simple test that adds value beyond BMI.
Body Fat Percentage
This measure shows the amount of fat compared to total body weight. It gives a clearer picture of fitness and health. Women with the same BMI can have very different body fat percentages. Knowing body fat helps track fitness progress and health more precisely than BMI. Tools like calipers or scales can estimate this number.
Limitations Of Bmi
BMI does not separate fat from muscle. Muscular women may have a high BMI but low body fat. It does not show fat distribution or health risks clearly. It also does not adjust for age, bone density, or ethnicity. Relying on BMI alone can lead to wrong health conclusions. Other measures help provide a fuller health view.
Credit: www.ramsayhealth.co.uk
Bmi And Weight Management
Body Mass Index (BMI) plays a vital role in weight management for women. It helps identify whether a woman is underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese. Knowing your BMI level guides choices for healthier living. Managing weight effectively often starts with understanding this simple number.
Setting Realistic Weight Goals
Set weight goals based on your BMI and overall health. Avoid aiming for drastic changes quickly. Small, steady progress leads to lasting results. Consider your lifestyle, age, and body type when planning goals. Realistic targets reduce frustration and keep motivation high.
Diet And Exercise Tips
Choose balanced meals rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins. Limit sugary and processed foods to improve BMI levels. Regular exercise boosts metabolism and helps control weight. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate activity most days. Combining diet and exercise improves overall health and BMI.
Medical Treatments And Bmi
Some women may need medical help to manage BMI. Doctors may recommend treatments for obesity or related health issues. Options include medications, counseling, or surgery in severe cases. Medical care supports weight loss when lifestyle changes are not enough. Always consult a healthcare provider for safe options.
Bmi And Medication Eligibility
Body Mass Index (BMI) plays a key role in determining eligibility for certain medications, especially weight loss drugs for women. BMI levels help healthcare providers decide if medication is a safe and suitable option. Understanding the link between BMI and medication eligibility can guide women toward the best treatment plans.
Qualifying For Weight Loss Drugs
Most weight loss drugs require a BMI of 30 or higher. Women with a BMI of 27 or more may also qualify if they have weight-related health issues. These can include diabetes, high blood pressure, or sleep apnea. Doctors use BMI as a quick way to assess if medication might help.
Role Of Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers assess more than just BMI. They review medical history and current health conditions. Providers decide the best treatment, balancing benefits and risks. They monitor progress and side effects throughout the medication course. Open communication with providers improves treatment success.
Lifestyle Changes With Medication
Medication works best combined with lifestyle changes. Healthy eating and regular exercise support weight loss efforts. Women should adopt habits that maintain long-term health. Medication is not a quick fix but part of a broader plan. Consistency and patience are key to success.
Conclusion
Understanding BMI levels for females helps track health and wellness. Maintaining a healthy BMI supports better energy and reduces risks. Regular check-ups and balanced lifestyle choices improve overall well-being. Remember, BMI is one of many health tools to use. Focus on gradual, steady changes for lasting results.
Stay informed and consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice. Small steps lead to big health benefits over time.