Are you curious about your Body Mass Index (BMI) and what it means for your health? Knowing your BMI is a simple yet powerful way to understand whether your weight is in a healthy range.
But how do you accurately count your BMI, and why should you care? You’ll discover an easy method to calculate your BMI, what the numbers really mean, and how this little figure can guide you toward better health choices. Keep reading to take control of your well-being with the simple step of counting your BMI.
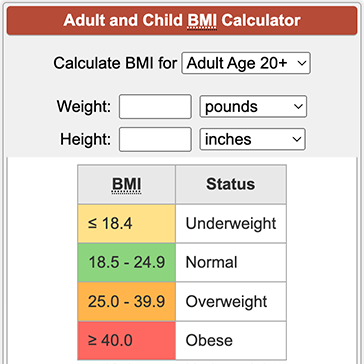
Credit: www.calculatorsoup.com
What Bmi Reveals
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a simple number that tells a lot about your body weight. It uses your height and weight to estimate if you are underweight, normal, overweight, or obese. This number helps people understand their health in a basic way. It gives clues about risks related to weight and health.
Bmi And Health Risks
BMI helps identify potential health risks linked to weight. A high BMI may signal a higher chance of heart disease, diabetes, and high blood pressure. Low BMI can also point to problems like malnutrition or weakened immunity. Doctors use BMI as a starting point to assess health and suggest lifestyle changes.
Limits Of Bmi Measurement
BMI does not measure fat directly. It can be misleading for athletes or people with strong muscles. Bone density and body shape also affect BMI results. It does not show where fat is stored in the body. Other tests and exams are needed for a full health picture.
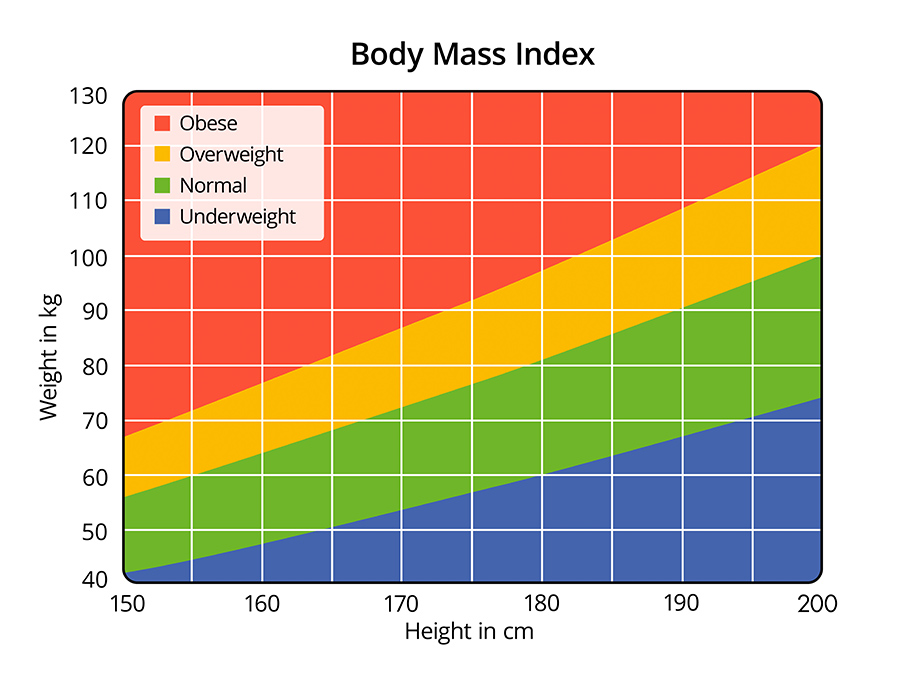
Credit: www.healthandcare.co.uk
How To Calculate Bmi
Calculating your Body Mass Index (BMI) helps you understand your body weight category. BMI shows if your weight is healthy compared to your height. It is a simple way to check your body size and health risk. You can calculate BMI yourself or use online tools for quick results.
Using The Bmi Formula
The BMI formula is easy to use. First, measure your weight in kilograms. Then, measure your height in meters. Next, square your height (multiply height by itself). Finally, divide your weight by the squared height. The formula looks like this:
For example, if you weigh 70 kg and are 1.75 meters tall, your BMI is 70 ÷ (1.75 × 1.75) = 22.86. This number helps classify your weight as underweight, normal, overweight, or obese.
Online Bmi Calculators
Online BMI calculators make the process faster. You only enter your height and weight. The calculator does the math and shows your BMI instantly. Many calculators also explain what your BMI means. Use calculators from trusted health websites for accurate results. These tools are free and easy for everyone to use.
Interpreting Your Bmi
Understanding your BMI number helps you learn about your body weight health. It shows if your weight fits your height. BMI is a simple tool but gives useful health clues.
Interpreting your BMI correctly guides you on steps to take next. It points out if you need to gain, lose, or maintain weight. Keep in mind, BMI is not a full health test but a helpful start.
Bmi Categories Explained
BMI values fall into groups that describe weight status. Underweight means your BMI is below 18.5. Normal weight ranges from 18.5 to 24.9. Overweight is 25 to 29.9. Obesity starts at 30 and above. Each group shows different health risks and advice.
These categories help doctors and you understand weight’s effect on health. They guide lifestyle and diet changes. Watch your BMI trend over time, not just one number.
Bmi And Age Considerations
BMI changes meaning with age. Children and teens have different BMI charts. Their BMI reflects growth patterns. Older adults may have lower muscle mass but still need healthy BMI.
Age affects how your body stores fat. Doctors use age-specific charts to check BMI. This way, results fit your life stage. Always consider age when checking BMI for better health insight.

Credit: www.singhmotors.com
Improving Your Bmi
Improving your BMI means making changes that support a healthier body weight. Small, consistent steps lead to lasting results. Focus on habits that balance what you eat and how you move. These two areas greatly affect your BMI and overall well-being.
Healthy Eating Habits
Choose whole foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. These foods provide important vitamins and fiber. Limit sugary drinks and processed snacks. Drink plenty of water throughout the day. Eat smaller portions to control calorie intake. Plan meals ahead to avoid unhealthy choices. Consistent meal times help regulate your metabolism. Avoid skipping meals, which can cause overeating later.
Effective Exercise Routines
Include both cardio and strength training exercises. Cardio helps burn calories and improve heart health. Strength training builds muscle, which boosts metabolism. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly. Break sessions into shorter, manageable parts if needed. Walking, cycling, or swimming are great options. Stretch before and after workouts to prevent injury. Stay active in daily life by taking stairs or walking more. Consistency matters more than intensity for lasting change.
Tracking Your Progress
Tracking your progress is key to understanding how your body changes over time. It helps you stay motivated and make better health choices. Using tools like BMI charts and regular monitoring can guide you on your fitness journey. These methods show clear signs of improvement or areas needing attention.
Using Bmi Charts
BMI charts offer a simple way to see where you stand. They compare your height and weight to standard ranges. Each category shows if you are underweight, normal, overweight, or obese. Checking your BMI on these charts regularly helps you spot trends early. It makes tracking progress easy and visual. You can see how your BMI changes as you gain muscle or lose fat.
Regular Monitoring Tips
Measure your BMI at the same time each week or month. Use consistent tools for height and weight to get accurate results. Record your numbers in a journal or app. Note any lifestyle changes that may affect your BMI. Avoid daily checks since small fluctuations are normal. Focus on long-term patterns instead of day-to-day changes. Regular monitoring keeps you accountable and focused on your goals.
Bmi And Special Populations
BMI is a useful tool to assess body weight relative to height. It helps identify risks linked to being underweight or overweight. Special groups need careful BMI interpretation. Their unique body changes can affect BMI accuracy. Understanding BMI for these groups improves health decisions.
Women And Bmi
Women’s bodies differ from men’s in muscle and fat distribution. Pregnancy changes weight and body shape temporarily. BMI may not reflect these changes well. Hormones also influence fat storage and metabolism. Women often have higher body fat percentages than men. BMI ranges for women should consider these factors. Tracking BMI over time offers better health insights than a single number.
Bmi For Children And Teens
Children and teens grow rapidly, affecting BMI calculations. BMI alone cannot define healthy weight in growing bodies. Age and sex must be factored into BMI assessments. BMI percentiles compare children with peers of the same age and gender. This method identifies risks of underweight or obesity early. Regular monitoring helps catch health issues promptly. Parents and doctors use BMI charts designed for youth.
Conclusion
Counting your BMI helps you understand your body weight better. It uses height and weight to give a simple number. This number shows if you are underweight, normal, or overweight. Remember, BMI is not perfect; it does not measure muscle or fat directly.
Use it as a guide, not a rule. Keep healthy habits like balanced eating and regular exercise. Check your BMI often to track your progress. Small changes can lead to big health improvements. Stay aware, stay active, and take care of your body every day.


