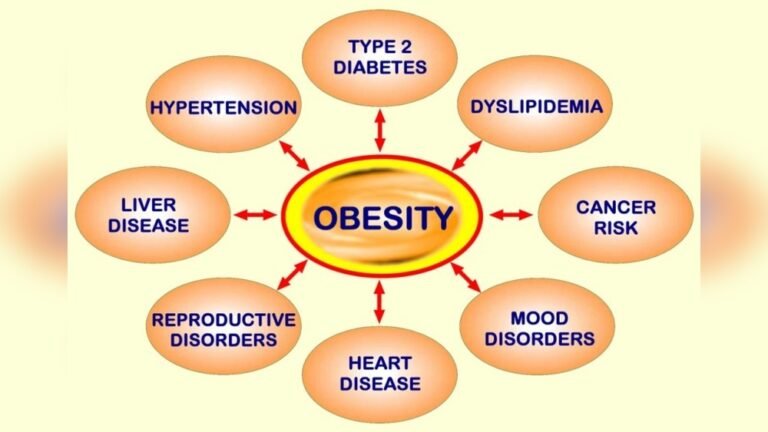
Are you aware that carrying extra weight does more than just change how you look? Obesity can quietly trigger a range of serious health problems that affect your heart, liver, joints, and even your sleep.
Understanding the diseases caused by obesity isn’t just important—it could be life-changing for you. You’ll discover which health risks are linked to obesity and how they might be affecting your body right now. Keep reading to learn how recognizing these dangers can empower you to take control of your health and make choices that protect your future.
Don’t wait until it’s too late—your well-being depends on what you do today.
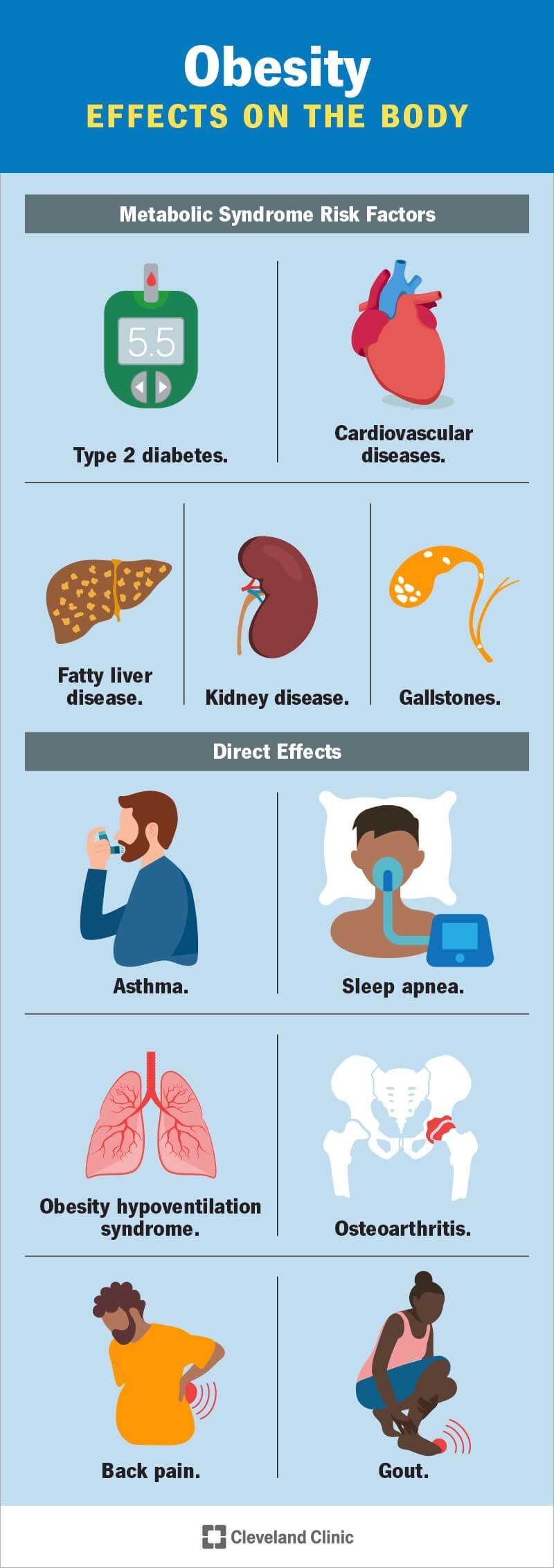
Credit: my.clevelandclinic.org
Obesity And Heart Disease
Obesity significantly raises the chance of heart disease. Excess body fat stresses the heart. This condition leads to serious health problems that affect millions worldwide. Understanding how obesity impacts the heart helps in managing and preventing these risks.
High Blood Pressure Risks
Obesity often causes high blood pressure. Extra weight forces the heart to work harder. This increased effort raises blood pressure levels. High blood pressure damages arteries and the heart muscle. It increases the risk of heart attacks and heart failure.
Cholesterol And Stroke
Obesity affects cholesterol levels negatively. It raises bad cholesterol (LDL) and lowers good cholesterol (HDL). This imbalance causes fatty deposits in blood vessels. Narrowed vessels reduce blood flow to the brain. The result can be a stroke, which may cause lasting damage or death.
Impact On Heart Function
Extra fat around the body strains heart function. The heart enlarges to pump blood effectively. This enlargement weakens the heart over time. Poor heart function reduces oxygen supply to the body. It leads to fatigue, shortness of breath, and heart failure risks.

Credit: www.researchgate.net
Cancer Linked To Obesity
Obesity increases the risk of many health issues. Among them, cancer linked to obesity stands out as a serious concern. Excess body fat changes the body’s environment, creating conditions that can help cancer grow. Understanding this link helps highlight the importance of maintaining a healthy weight for cancer prevention.
Common Obesity-related Cancers
Obesity raises the risk of several types of cancer. These include breast cancer, especially after menopause. Colon and rectal cancers are also more common in people with obesity. Endometrial cancer, which affects the lining of the uterus, shows a strong link to obesity. Other cancers include kidney, liver, and pancreatic cancers. These cancers develop more often in people with excess body fat.
Mechanisms Behind Cancer Risks
Fat tissue produces hormones like estrogen that can fuel some cancers. It also causes chronic inflammation, which may damage cells. Insulin resistance and higher insulin levels promote cell growth, raising cancer risk. Obesity changes how the immune system works, reducing its ability to fight cancer cells. These combined effects make it easier for cancer to start and grow in the body.
Digestive Disorders
Obesity affects many parts of the body, including the digestive system. Excess fat can cause serious digestive disorders. These problems reduce quality of life and may need medical care. Understanding these disorders helps in managing risks and symptoms.
Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease happens when fat builds up in the liver. Obesity is a main cause. This fat makes the liver swell and work less well. It can lead to liver damage or even failure. People with fatty liver often feel tired and weak. Early diagnosis helps prevent serious damage.
Gastroesophageal Reflux
Obesity increases pressure on the stomach. This pressure pushes stomach acid up into the esophagus. The result is gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD. GERD causes heartburn, chest pain, and difficulty swallowing. Over time, it can harm the esophagus lining. Treatment includes lifestyle changes and sometimes medication.
Gallbladder Problems
Obesity raises the risk of gallstones and gallbladder disease. Extra fat changes the balance of bile in the gallbladder. This leads to stone formation and inflammation. Gallbladder problems cause pain, nausea, and digestion issues. Surgery might be needed to remove the gallbladder in severe cases.
Respiratory Issues
Obesity affects many parts of the body, including the lungs and breathing system. Excess weight puts pressure on the chest and lungs. This pressure makes breathing harder. It also raises the risk of serious breathing problems. The following sections explain two common respiratory issues linked to obesity.
Sleep Apnea And Breathing
Sleep apnea is a condition where breathing stops and starts during sleep. Fat deposits around the neck block the airway. This blockage causes short pauses in breathing. These pauses lower oxygen levels in the blood. Sleep apnea leads to poor sleep and daytime tiredness. It also raises the risk of heart problems and stroke. People with obesity have a higher chance of developing sleep apnea.
Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome
Obesity hypoventilation syndrome (OHS) happens when the lungs do not get enough air. Excess fat makes the chest wall stiff and less flexible. The brain may not respond well to high carbon dioxide levels. This leads to slow and shallow breathing. People with OHS have low oxygen and high carbon dioxide in their blood. This condition can cause serious heart and lung damage if untreated. Weight loss is a key step to improve breathing in OHS.
Joint And Bone Problems
Obesity puts extra pressure on your joints and bones. This strain can cause pain and damage over time. Joint and bone problems become common health issues for many people with obesity. These problems reduce comfort and limit daily activities. Understanding these effects helps highlight the importance of managing weight for joint health.
Osteoarthritis Effects
Osteoarthritis is a common joint disease linked to obesity. Excess weight wears down cartilage in the joints faster. This causes pain, stiffness, and swelling. The knees, hips, and lower back often suffer the most. Over time, joint damage worsens and movement becomes painful. Obesity increases the risk of developing osteoarthritis and speeds up its progression.
Mobility Challenges
Carrying extra weight makes moving harder and slower. Joint pain limits walking, standing, and climbing stairs. This leads to less physical activity and muscle weakness. Reduced mobility can cause a cycle of weight gain and more joint problems. Many people with obesity face daily challenges in staying active and independent.
Metabolic Complications
Obesity triggers many metabolic complications that affect the body’s normal functions. Excess fat changes how the body processes energy and controls sugar levels. These changes increase the risk of serious diseases. Understanding these metabolic issues helps highlight the dangers of obesity and the need for healthy habits.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is common in people with obesity. It happens when the body cannot use insulin properly. Insulin helps control blood sugar levels. High blood sugar can damage organs and nerves. Obesity causes the body to become less sensitive to insulin. This leads to higher sugar levels in the blood. Managing weight reduces the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Simple diet changes and exercise improve blood sugar control.
Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance means the body’s cells ignore insulin signals. The pancreas produces more insulin to compensate. Over time, this wears out the pancreas. Insulin resistance often leads to type 2 diabetes. Obesity increases fat around organs, which worsens insulin resistance. This condition raises the risk of heart disease and stroke. Losing weight helps restore insulin sensitivity. Early action can prevent serious health problems.
Mental Health Concerns
Obesity affects more than just the body. It also impacts mental health deeply. People living with obesity often face emotional and psychological challenges. These issues can reduce quality of life and make daily tasks harder. Understanding these mental health concerns is vital for overall well-being.
Depression And Anxiety
Obesity increases the risk of depression and anxiety disorders. Chemical changes in the brain linked to obesity may trigger these conditions. Social stigma and discrimination worsen feelings of sadness and fear. Many people with obesity feel isolated and hopeless. This emotional distress can lead to a cycle of unhealthy habits.
Self-esteem Issues
Low self-esteem is common among individuals with obesity. Negative body image affects confidence and social interactions. People may avoid activities or events due to embarrassment. This can lead to loneliness and withdrawal from friends and family. Building positive self-esteem is crucial for mental health recovery.

Credit: thegastrosurgeon.com
Preventing Obesity-related Diseases
Preventing diseases linked to obesity is crucial for a healthier life. Excess weight raises the chance of heart disease, diabetes, and joint problems. Simple steps can lower these risks and improve your well-being.
Lifestyle Changes
Small changes in daily routines make a big difference. Avoid sitting for long periods. Take breaks to walk or stretch. Reducing screen time helps control weight gain. Managing stress with relaxation techniques also supports a healthy lifestyle.
Importance Of Regular Exercise
Exercise strengthens the heart and improves blood flow. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate activity most days. Walking, cycling, or swimming are excellent options. Regular exercise helps burn calories and builds muscle, which boosts metabolism. It also lowers blood pressure and blood sugar levels.
Healthy Eating Habits
Choose foods rich in nutrients and low in fat and sugar. Eat plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Limit processed foods and sugary drinks. Control portion sizes to avoid overeating. Drinking water instead of soda helps reduce calorie intake. Balanced meals keep energy steady and support weight control.
Benefits Of Weight Loss
Weight loss offers many benefits that improve life quality. Shedding excess pounds reduces health risks and boosts daily function. It helps the body work better and supports long-term wellness.
Even a small amount of weight loss can make a big difference. It lessens the strain on the heart and joints. It also positively affects mood and energy levels. The benefits reach beyond physical changes to mental and metabolic health.
Improved Physical Health
Losing weight lowers blood pressure and reduces heart disease risk. It helps control blood sugar and prevents type 2 diabetes. Joint pain often decreases, making movement easier and less painful. Sleep quality tends to improve, reducing problems like sleep apnea. The body feels lighter, and daily tasks become less tiring.
Enhanced Mental Well-being
Weight loss can boost self-esteem and confidence. People often feel happier and less stressed. Anxiety and depression symptoms may lessen. Improved sleep supports better mood and mental clarity. Increased energy encourages a more active lifestyle and social engagement.
Metabolic Improvements
Weight loss improves how the body processes fats and sugars. It reduces inflammation and lowers cholesterol levels. These changes decrease the risk of metabolic syndrome. Insulin sensitivity improves, helping to prevent diabetes. Overall metabolism becomes more efficient, supporting sustained health.
Conclusion
Obesity can cause many serious health problems. These include heart disease, diabetes, and joint pain. It can also lead to sleep issues and liver disease. Controlling weight helps reduce these risks. Simple lifestyle changes make a big difference. Eating well and staying active improve overall health.
Small steps today protect your body tomorrow. Staying informed helps you make better choices. Taking care of your body is important for a long, healthy life.