If you want to build stronger legs, boost your overall fitness, and sculpt your lower body, exercise squats with weights are one of the best moves you can add to your routine. Squats don’t just work your thighs—they target your glutes, hamstrings, and even your core, giving you a full lower-body workout in one simple move.
But when you add weights, like dumbbells or a barbell, you take your strength training to a whole new level. You’ll burn more calories, build muscle faster, and improve your balance and stability. Whether you’re a beginner or looking to push your limits, mastering weighted squats can transform your workouts and help you reach your fitness goals quicker than you think.
Ready to learn the proper way to do them and discover variations that keep things fresh? Keep reading, because we’ll guide you step-by-step to squat your way to stronger, leaner legs safely and effectively.
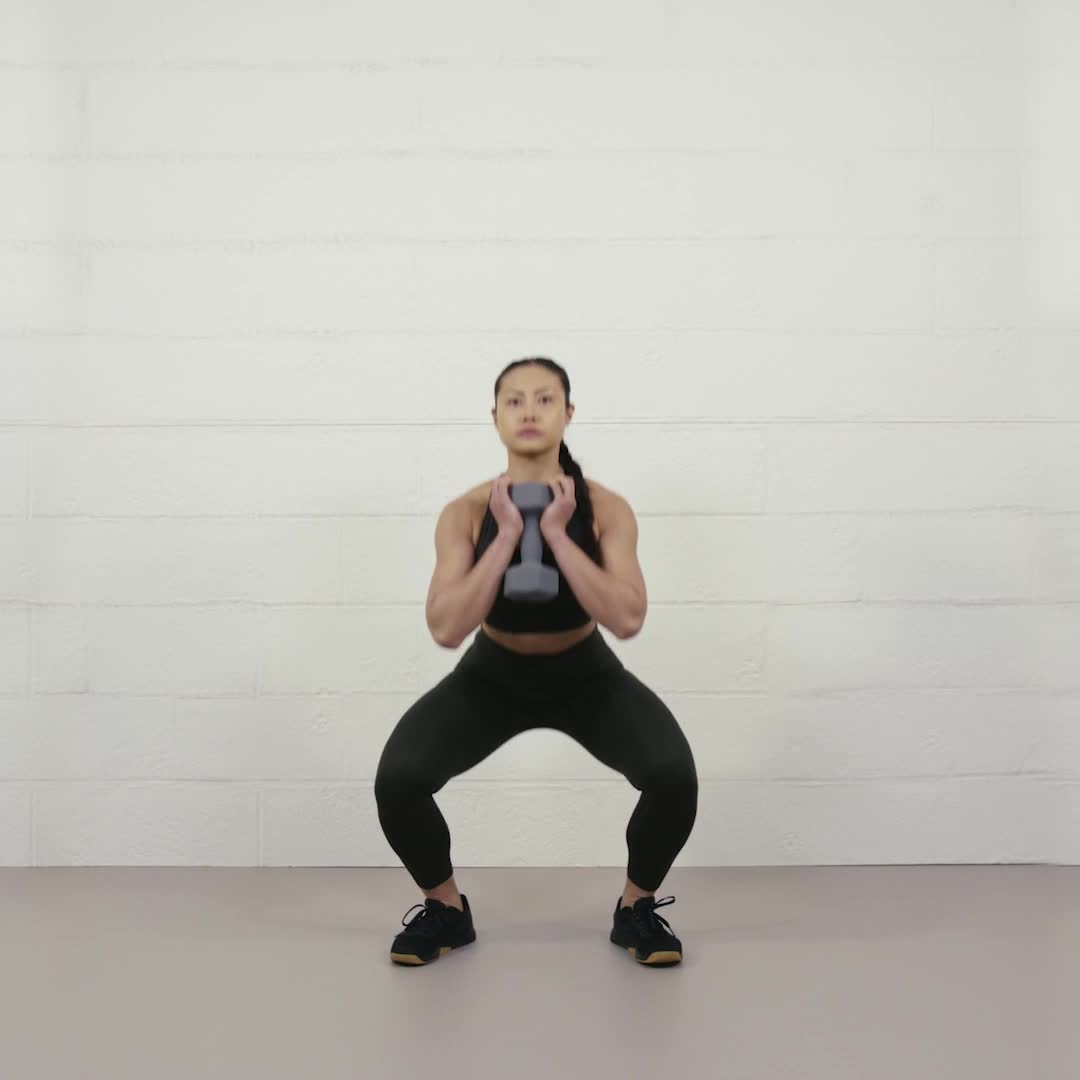

Credit: www.womenshealthmag.com
Benefits Of Weighted Squats
Weighted squats add resistance to the classic squat exercise. This resistance boosts the workout’s impact on the body. Adding weights increases effort, which leads to more benefits. Weighted squats build muscle, improve balance, and support joint health. They also enhance daily movement skills. Here are some key benefits of weighted squats.
Muscle Growth And Strength
Weighted squats target large muscle groups in the legs and hips. The added weight forces muscles to work harder. This effort causes muscles to grow stronger over time. Both quadriceps and hamstrings get a powerful workout. The glutes also develop shape and strength. Weighted squats improve overall lower body power and endurance.
Improved Balance And Stability
Carrying weights during squats challenges your balance. Your body must stabilize to keep control. This trains small stabilizer muscles in the core and legs. Improved stability helps prevent falls and injuries. It also supports better posture and coordination. Weighted squats create a strong foundation for all movement.
Bone Density And Joint Health
Adding weight to squats stresses bones slightly. This stress encourages bones to build density. Strong bones reduce the risk of fractures and osteoporosis. Weighted squats also strengthen the muscles around joints. This support protects joints from wear and tear. The exercise helps maintain healthy knees and hips as you age.
Functional Movement Enhancement
Weighted squats mimic natural movements like sitting and standing. Strength gained from squats improves everyday tasks. Lifting, bending, and climbing stairs become easier and safer. The exercise trains your body to move efficiently. Functional strength from weighted squats boosts overall mobility and independence.

Credit: training.fit
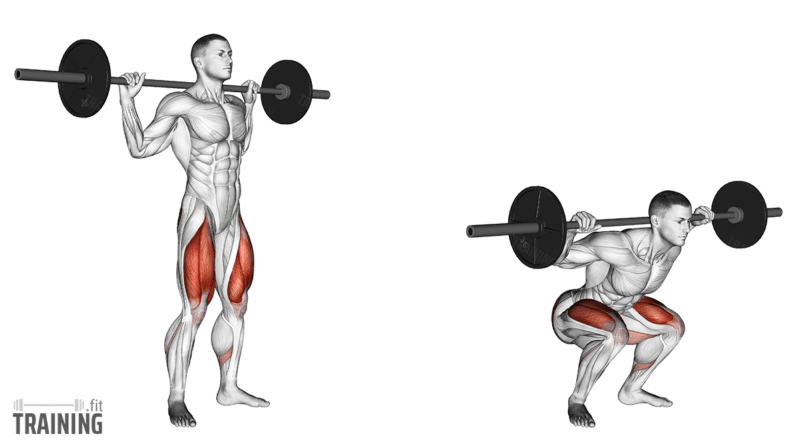
Proper Squat Techniques
Proper squat techniques ensure safety and maximize workout benefits. Squats with weights target many muscles effectively. Correct form reduces injury risk and improves strength gains. Focus on body alignment and breathing for the best results.
Learning the right way to squat helps maintain balance and control. Each part of the movement matters. Small adjustments make a big difference in performance.
Starting Position And Form
Stand with feet shoulder-width apart. Hold weights firmly at your sides or on your shoulders. Keep your chest up and shoulders back. Engage your core muscles for stability. Look straight ahead to maintain neck alignment. Begin the squat by bending at the hips and knees simultaneously.
Knee And Hip Alignment
Keep knees aligned with your toes throughout the squat. Avoid letting knees cave inward or move too far forward. Push hips back as you lower down. Lower until thighs are parallel to the floor or slightly below. Proper alignment protects joints and improves power.
Breathing Patterns
Inhale deeply before you start descending. Hold your breath briefly while lowering your body. Exhale steadily as you push back up to standing. Controlled breathing supports core stability. It also helps maintain rhythm and focus.
Common Mistakes To Avoid
Do not round your back or lean too far forward. Avoid lifting heels off the ground. Do not let knees collapse inward. Never hold your breath for too long. Avoid shallow squats that limit muscle activation. Correct these errors to prevent injury and improve gains.
Types Of Weighted Squats
Weighted squats add resistance to your workout, making your muscles work harder. They help build strength in the legs, hips, and core. Different types of weighted squats target muscles in unique ways. Choosing the right type depends on your fitness level and goals.
Dumbbell Squats
Dumbbell squats use handheld weights on each side of your body. Hold dumbbells at your sides or shoulders. This squat improves balance and muscle control. It is easier to learn and good for beginners. Dumbbell squats work the quads, hamstrings, and glutes well.
Barbell Squats
Barbell squats involve placing a weighted barbell across your upper back. This type allows lifting heavier weights. Barbell squats build strong legs and core muscles. They require good form to avoid injury. This squat is popular in strength training and bodybuilding.
Bulgarian Split Squats
Bulgarian split squats focus on one leg at a time. Place one foot behind on a bench or step. Hold weights in your hands or a barbell on your shoulders. This squat improves balance and targets the glutes deeply. It helps fix muscle imbalances between legs.
Pistol Squats
Pistol squats are single-leg squats with added weight for challenge. Hold a dumbbell or kettlebell close to your chest. This squat needs strong balance and flexibility. It works the entire leg and core muscles intensely. Pistol squats build strength and control in each leg.
Squat Variations For Different Goals
Squat exercises with weights offer many ways to meet different fitness goals. Changing the squat style targets muscles differently. Each variation suits a specific aim. Choosing the right squat helps improve results. Below are common squat variations for various goals.
Strength Building
Heavy barbell squats work well for strength. Use low repetitions with high weight. This trains muscles to generate more force. Front squats focus on quads and core. Box squats help with power and form. Rest between sets is longer for recovery.
Muscle Toning
Moderate weight with higher reps tones muscles. Dumbbell goblet squats are popular for toning. They improve shape without bulky muscle. Slow, controlled movement increases muscle engagement. Pausing at the bottom adds intensity. This style shapes legs and glutes evenly.
Endurance Training
Light weights and many repetitions build endurance. Jump squats with light dumbbells improve stamina. Bodyweight squats also help with endurance. Short breaks keep the heart rate high. This trains muscles to resist fatigue longer. Great for sports and daily activities.
Rehabilitation And Seniors
Squats with light weights or no weights aid recovery. Chair squats improve balance and mobility safely. Slow, shallow squats reduce joint strain. Resistance bands can add gentle weight. This helps rebuild strength after injury. Seniors gain better stability and confidence.
Incorporating Squats Into Your Routine
Incorporating squats with weights into your workout routine strengthens muscles and improves overall fitness. Squats target the legs, hips, and core. Using weights increases resistance, helping build muscle and burn more calories. To get the best results, follow a structured approach. This includes warming up, setting reps and sets, progressing carefully, and combining squats with other exercises.
Warm-up And Mobility Drills
Start with a light warm-up to prepare your body. Perform dynamic stretches focusing on hips, knees, and ankles. Mobility drills improve your squat form and reduce injury risks. Try leg swings, hip circles, and bodyweight squats. Warm muscles move better and handle weights safely.
Setting Reps And Sets
Choose reps and sets based on your fitness goals. For muscle growth, aim for 8-12 reps per set. For strength, lower reps around 4-6 work well. Perform 3-4 sets for balanced progress. Rest for 60-90 seconds between sets. Adjust based on how your body feels.
Progressive Overload Strategies
Increase the weight gradually to challenge muscles. Add small weight increments every week or two. You can also increase reps or sets over time. Keep proper form as you progress. This method helps avoid plateaus and encourages steady gains.
Combining With Other Exercises
Mix squats with other leg and core exercises for balanced strength. Include lunges, deadlifts, and calf raises. Add upper body moves like push-ups or rows for full-body workouts. This variety prevents boredom and promotes overall fitness.
Safety Tips And Modifications
Exercise squats with weights offer great benefits for strength and muscle growth. Safety is key to avoid injuries and ensure steady progress. Follow these tips and modifications to protect your body while performing weighted squats. Adjust your approach based on your fitness level and any physical limitations.
Chair-assisted Squats
Chair-assisted squats help beginners maintain balance and proper form. Stand in front of a sturdy chair and lower yourself slowly until your hips touch the seat. Use the chair to support your weight as you stand back up. This method reduces strain and builds confidence before adding weights.
Using Proper Equipment
Choose weights that match your current strength. Start with light dumbbells or kettlebells. Wear supportive shoes with good grip to avoid slipping. Use a weightlifting belt if lifting heavy to protect your lower back. Ensure your workout space is clear of obstacles to prevent accidents.
Listening To Your Body
Pay attention to pain or discomfort during squats. Stop immediately if you feel sharp pain in your knees, hips, or back. Mild muscle fatigue is normal, but joint pain is a warning sign. Take breaks and reduce weight if needed. Consistent pain means you should rest and reassess your technique.
When To Seek Professional Guidance
Consult a fitness professional if you are new to weighted squats. A trainer can teach you correct form and suggest suitable modifications. Seek advice if you have past injuries or health conditions. Professional guidance helps prevent injury and improves workout effectiveness.
Credit: training.fit
Conclusion
Squats with weights build strength in legs and core effectively. They improve balance and support better posture daily. Using weights increases muscle growth and burns more calories. Always focus on proper form to avoid injury. Start with lighter weights and increase gradually.
Consistency matters most for long-term fitness gains. Keep challenging yourself to see steady progress. Squats with weights fit all fitness levels well. Try adding them to your workout routine today.


