Are you curious about what a healthy BMI means for you as a woman? Understanding your Body Mass Index (BMI) can be a simple yet powerful step toward managing your health and feeling your best.
But did you know that the ideal BMI range for women can change with age and individual factors? This means your healthy weight isn’t just a number on a chart—it’s unique to your body and lifestyle. You’ll discover how to find your healthy BMI, what those numbers really mean for your well-being, and why looking beyond BMI alone can help you make smarter health choices.
Keep reading to unlock the key to a healthier you, tailored just for your needs.
Healthy Bmi Ranges
Understanding healthy BMI ranges helps women maintain good health. BMI measures weight relative to height. It gives a simple number to check. This number can guide lifestyle and diet choices.
Healthy BMI ranges vary by age and individual factors. Knowing these ranges supports better health decisions. It also highlights when to seek medical advice.
Bmi Values By Age
BMI values differ slightly across age groups. For young adult women, a BMI between 18.5 and 24.9 is healthy. Women aged 40 to 59 may have a slightly higher healthy range. For women over 60, a BMI up to 27 may still be healthy. Age affects body composition and metabolism, influencing BMI norms.
Bmi Categories For Women
BMI categories help identify weight status. Underweight is below 18.5. Normal weight ranges from 18.5 to 24.9. Overweight falls between 25 and 29.9. Obesity starts at 30 and above. These categories guide health risk assessments for women.
Bmi Changes With Age
BMI tends to increase with age due to muscle loss and fat gain. Older women may have higher BMI but lower muscle mass. This change affects how BMI reflects health. Regular monitoring is important to adjust health goals as women age.
Credit: www.ramsayhealth.co.uk
Calculating Your Bmi
Calculating your Body Mass Index (BMI) is a simple way to check if your weight fits your height. It helps identify a healthy range for women, which supports overall wellness. Understanding your BMI can guide you toward better health choices.
Simple Bmi Calculation
BMI is found by dividing your weight in kilograms by your height in meters squared. The formula is easy:
For example, if you weigh 60 kg and are 1.65 meters tall, your BMI is:
This number falls within the healthy BMI range for women, which is 18.5 to 24.9.
Using Online Bmi Calculators
Many websites offer free BMI calculators. Enter your weight and height, and the tool does the math for you. These calculators save time and reduce errors. They often provide a quick interpretation of your BMI result.
Limitations Of Bmi Measurement
BMI does not measure body fat directly. It cannot tell the difference between muscle and fat. Some women with high muscle mass may have a high BMI but low body fat. Age, bone density, and body shape also affect BMI accuracy. Always consider other health factors alongside BMI.
Bmi And Body Composition
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a common tool to measure healthy weight. It compares weight to height and gives a number. This number helps to classify if someone is underweight, normal, overweight, or obese. For females, a healthy BMI usually falls between 18.5 and 24.9. But BMI alone does not show the full picture of health.
Body composition plays a big role in understanding health. It looks at what makes up the body, such as muscle, fat, and bone. Two people can have the same BMI but very different body compositions. This difference affects how healthy the BMI number really is.
Muscle Mass Vs. Fat
Muscle is denser and weighs more than fat. A woman with high muscle mass may have a higher BMI but low body fat. This means she can be healthy even if her BMI is higher. Fat does not weigh as much but takes up more space. More fat can increase health risks, even if BMI looks normal.
Bone Density Effects
Bone density varies by age, genetics, and lifestyle. Women with strong bones may weigh more. This can raise their BMI number without adding fat. Low bone density, common in older women, can lower weight and BMI. Bone health is important to consider with BMI for a true health picture.
Body Fat Percentage Comparison
Body fat percentage measures how much of the body is fat. Healthy ranges differ by age and activity level. Women with a healthy BMI can still have high body fat percentage. This can increase risk of disease. Checking body fat percentage along with BMI gives clearer insight into health.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_illustration_BAF8FF4-6963b807948449fab3a6cbce23127681.png)
Credit: www.verywellhealth.com
Health Considerations Beyond Bmi
BMI offers a quick way to estimate a healthy weight range for women. It helps identify potential health risks related to body weight. Despite its usefulness, BMI does not tell the full story about a person’s health. Other factors must be considered to get a clearer picture. Understanding these factors can lead to better health choices and personalized care.
Individual Health Factors
Body composition varies greatly among women. Muscle weighs more than fat, which can affect BMI results. Bone density also plays a role in weight and health. A person with strong bones may have a higher BMI but still be healthy. Health conditions and fitness levels influence what a healthy weight means. Thus, BMI should not be the only measure of health.
Consulting Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers offer personalized advice beyond BMI numbers. They consider medical history, lifestyle, and other health markers. A provider can help set realistic and safe weight goals. Regular check-ups ensure that weight management supports overall health. Discussing BMI results with a professional helps avoid misinterpretation. It leads to better strategies for long-term well-being.
Ethnicity And Sex Differences
Ethnicity affects body fat distribution and health risks. Some ethnic groups may face higher risks at lower BMI levels. Women and men store fat differently, impacting health outcomes. Female bodies naturally hold more fat for reproductive health. These differences mean BMI ranges may not fit all groups equally. Tailored health assessments improve accuracy and care quality.
Maintaining Optimal Bmi
Maintaining an optimal BMI is essential for women to support overall health and well-being. A healthy BMI helps reduce risks of chronic diseases and improves energy levels. It involves balanced nutrition, regular physical activity, and positive lifestyle choices. Small, consistent actions can make a big difference in keeping BMI within a healthy range.
Nutrition Tips
Eat a variety of fruits and vegetables daily. Choose whole grains over refined ones. Include lean proteins like chicken, fish, or beans. Limit sugary snacks and drinks that add empty calories. Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated. Control portion sizes to avoid overeating. Healthy eating supports steady weight and good metabolism.
Exercise And Fitness
Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week. Activities like walking, swimming, or cycling boost heart health. Strength training twice a week helps build muscle mass. Exercise improves mood and supports weight management. Find workouts you enjoy to stay motivated. Consistency is key for long-term fitness benefits.
Lifestyle Habits
Get 7 to 9 hours of quality sleep each night. Manage stress through relaxation techniques or hobbies. Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption. Stay active throughout the day, even with simple movements. Regular health check-ups help monitor BMI and overall health. Healthy habits create a strong foundation for balanced weight.
Bmi For Older Women
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a common tool to assess healthy weight. For older women, BMI needs careful understanding. Aging changes body composition and fat distribution. These changes affect what is considered a healthy BMI. Older women may have different BMI ranges than younger adults. Adjusting BMI expectations can help maintain health and mobility.
Healthy Bmi Adjustments
As women age, muscle mass usually decreases. Fat tends to increase even if weight stays the same. This means BMI may not fully reflect health risks. Experts suggest a slightly higher BMI range for older women. A BMI between 25 and 27 can sometimes be healthy. This range can protect against frailty and bone loss. Always consider BMI alongside other health factors.
Weight And Aging
Weight changes are normal with aging. Metabolism slows down, causing weight gain in some cases. Losing too much weight can also be risky. It may lead to muscle loss and weaker bones. Maintaining steady weight supports energy and independence. Focus on balanced nutrition and regular check-ups. This helps manage weight changes safely over time.
Special Fitness Guidelines
Fitness is key for healthy aging and weight control. Older women should include strength training to preserve muscle. Low-impact exercises protect joints and improve balance. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly. Flexibility and stretching reduce injury risk. Fitness plans must match individual ability and health status. Regular activity supports a healthy BMI and overall wellness.
Tools And Resources
Access to accurate tools and resources helps track a healthy BMI for females. These resources simplify understanding body mass index and its implications. They support women in maintaining or achieving a healthy weight safely and effectively.
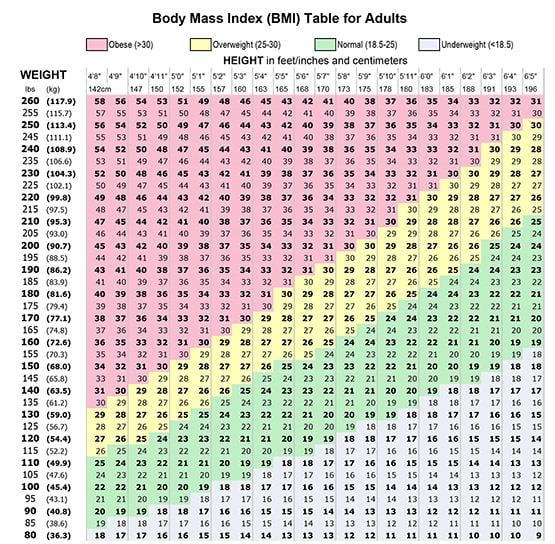
Bmi Charts And Tables
BMI charts and tables provide quick reference points. They show the healthy BMI range based on height and weight. Charts often include age-specific data for better accuracy. Using these tables, women can compare their BMI against standard ranges. This visual aid helps identify if weight is within a healthy limit.
Recommended Apps And Calculators
Apps and online calculators offer easy BMI calculation anytime. They require inputs like height, weight, and age to compute BMI. Many apps track BMI progress over time. Some provide personalized health tips based on BMI results. These tools are convenient for daily use and motivation.
Reliable Health Websites
Trusted health websites share verified BMI information and advice. These sites often come from government or medical organizations. They offer educational content and updated research. Users find guidelines on healthy weight, nutrition, and exercise. Relying on credible sites ensures accurate and safe health decisions.
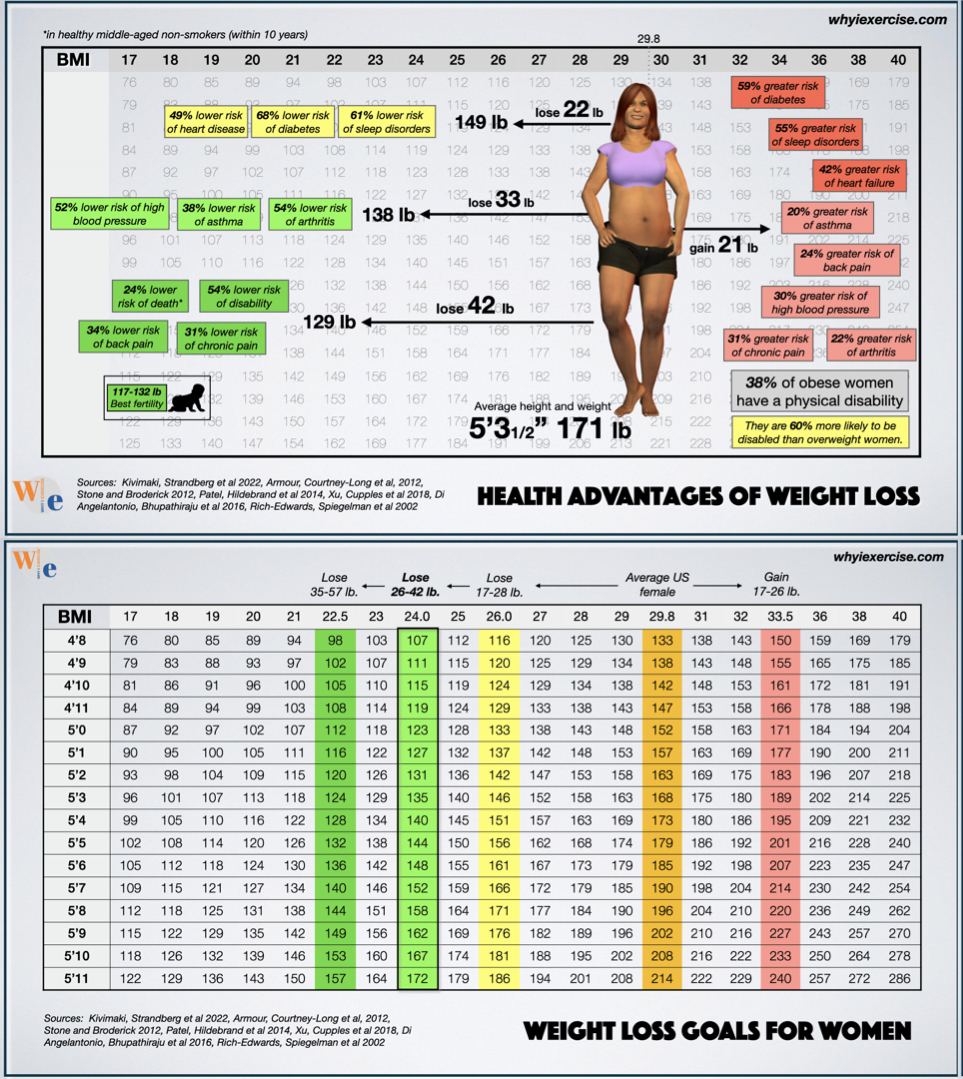
Credit: www.whyiexercise.com
Conclusion
Maintaining a healthy BMI supports overall well-being and energy. Remember, BMI is just one way to check health. Factors like muscle, age, and bone density also matter. Use BMI as a simple guide, not a full health test. Talk to a doctor for a complete health picture.
Focus on balanced eating and regular activity every day. Small, steady steps help keep your body strong and healthy. Stay mindful of your unique needs and listen to your body.


