Are you curious about what a healthy BMI range for women really means for your body and well-being? Understanding your Body Mass Index (BMI) can be a simple way to gauge if your weight is in a healthy zone, but it’s more than just a number.
Your ideal BMI can vary based on your age, lifestyle, and unique body composition. You’ll discover clear guidelines on healthy BMI ranges for women, why these ranges matter, and important factors to consider beyond the scale. Whether you’re aiming to maintain your current weight or looking to make changes, knowing your healthy BMI range empowers you to take control of your health with confidence.
Keep reading to find out what your numbers mean and how to use them to support a healthier you.
Credit: www.ramsayhealth.co.uk
Ideal Bmi Range For Women
The ideal BMI range for women helps indicate a healthy weight for their height. It provides a simple way to assess body fat levels. Maintaining a BMI within this range can reduce risks of many health issues. Women’s bodies change over time, so the ideal BMI might vary by age and other factors.
Bmi Categories Explained
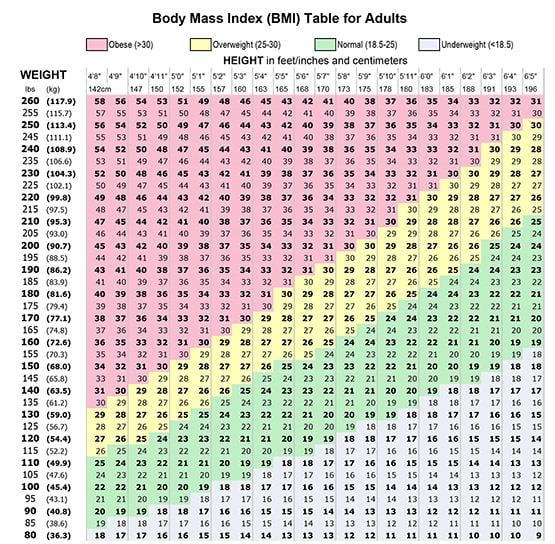
BMI categories classify body weight into groups. Underweight is below 18.5, normal weight is 18.5 to 24.9. Overweight ranges from 25 to 29.9. Obesity starts at 30 and above. These categories guide health assessments but do not tell the whole story about body health.
Healthy Bmi By Age Group
Healthy BMI ranges differ slightly by age group. Younger women often have a lower ideal BMI. For women aged 20 to 39, 18.5 to 24.9 is typical. Women aged 40 to 59 may have a healthy range up to 27. Older women, 60 and above, might have a slightly higher ideal BMI, around 25 to 28.
Bmi Variations With Age
As women age, muscle mass decreases and fat often increases. This shift can change BMI without affecting health negatively. A higher BMI in older women may be normal and not harmful. Age-related changes mean BMI should be one of several health measures used. Consult healthcare providers for personalized advice.
Limitations Of Bmi
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a common tool used to estimate a healthy weight range for women. It uses height and weight to calculate a number that suggests if someone is underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese. Despite its popularity, BMI has notable limitations. It does not capture the full picture of a person’s health or body makeup. Understanding these limits helps women interpret their BMI scores more wisely and avoid misunderstandings about their health.
Muscle Mass And Bone Density Effects
BMI does not separate muscle from fat. Women with high muscle mass may have a high BMI but low body fat. Athletes often fall into this category. Bone density also affects BMI. Women with denser bones may weigh more, raising their BMI despite having a healthy body fat level. This means BMI can label muscular or strong-boned women as overweight or obese incorrectly.
Bmi And Body Composition
BMI measures total weight, not fat percentage or fat location. It cannot tell if weight comes from fat or lean tissue. Body composition varies widely among women. Two women can have the same BMI but very different health profiles. One might have more fat around the belly, which raises health risks. The other might carry more lean muscle, which is healthier. BMI misses these important details.
When Bmi Might Mislead
BMI can be misleading for certain groups of women. Older women often lose muscle and gain fat but keep the same weight. Their BMI may stay normal while health risks rise. Pregnant women also experience weight changes that affect BMI accuracy. Women with certain medical conditions may have unusual body composition not reflected by BMI. Relying solely on BMI can lead to wrong health judgments in these cases.
Additional Health Indicators
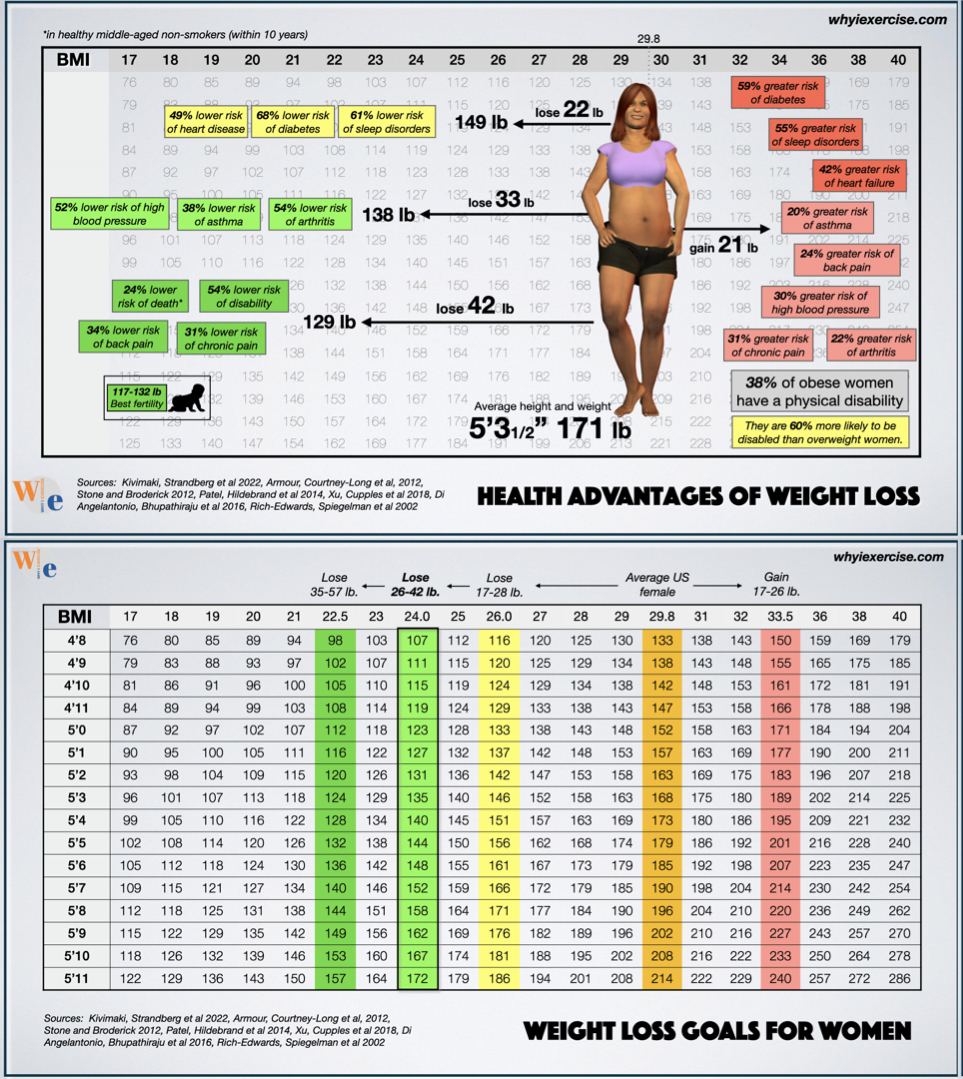
Understanding a healthy BMI range for women is important. Yet, other health indicators offer a clearer health picture. These indicators help assess risks that BMI alone might miss. They include waist size, body fat levels, and lifestyle habits. Each plays a key role in overall health and wellbeing.
Waist Circumference Importance
Waist circumference measures abdominal fat. Excess fat around the waist links to heart disease and diabetes. Women with a waist circumference above 35 inches face higher health risks. This measure helps identify hidden dangers even if BMI seems normal. Keeping waist size in check supports better health outcomes.
Body Fat Percentage
Body fat percentage shows how much fat you carry. It differs from BMI, which only uses weight and height. Healthy body fat ranges vary by age but generally fall between 21% and 33% for women. High body fat levels increase risks for many chronic diseases. Monitoring body fat gives a better view of fitness and health.
Lifestyle And Physical Activity
Active lifestyles improve heart health, mood, and weight control. Regular exercise lowers disease risk and boosts energy. Sedentary habits increase chances of obesity and related problems. A balanced diet combined with daily physical activity supports healthy BMI and overall wellness. Small changes in habits make big health differences.
Credit: www.whyiexercise.com
Calculating And Using Bmi
Understanding the healthy BMI range for women begins with learning how to calculate and use BMI. Body Mass Index (BMI) is a simple tool that estimates body fat based on height and weight. It helps women know if their weight falls within a healthy range. This section explains how to calculate BMI, use online tools, and interpret the results.
How To Calculate Bmi
To calculate BMI, divide your weight in kilograms by your height in meters squared. The formula is: BMI = weight (kg) / height (m)². For example, if you weigh 65 kg and are 1.7 meters tall, your BMI is 65 divided by 2.89, which equals about 22.5. You can also calculate BMI using pounds and inches by multiplying your weight by 703, then dividing by your height in inches squared.
Bmi Calculators And Tools
Online BMI calculators make it easy to find your BMI. Enter your weight and height, and the tool does the math for you. Many health websites offer free calculators. Some apps track BMI over time to help monitor changes. These tools are fast, simple, and accurate for most adults.
Interpreting Your Bmi Results
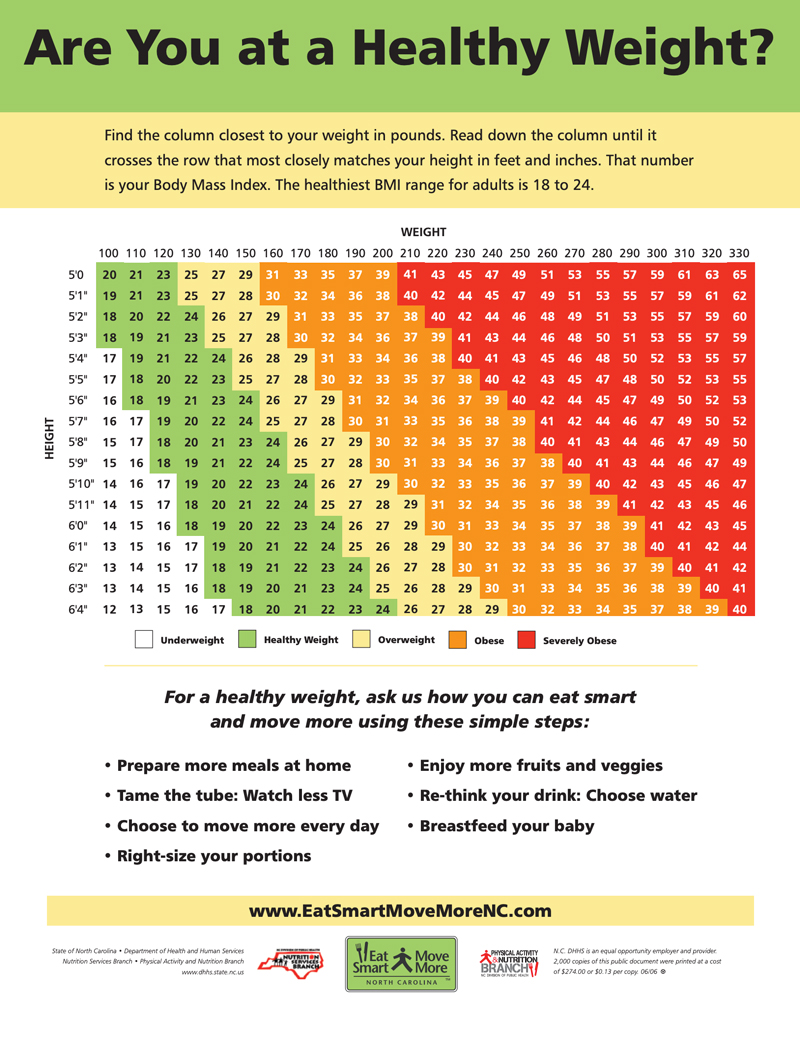
BMI results fall into categories: underweight, normal weight, overweight, and obese. A BMI between 18.5 and 24.9 usually indicates a healthy weight for women. Below 18.5 suggests underweight, and over 25 indicates overweight or obesity. Keep in mind, BMI does not measure muscle or bone weight. Use it as a general guide, not a strict rule.
Customizing Weight Goals
Setting weight goals based on BMI is not one-size-fits-all. Women differ in health needs, body types, and lifestyles. Customizing weight goals helps create realistic and healthy plans. It also supports better long-term success and well-being.
Consulting Healthcare Providers
Talk with doctors or dietitians before choosing a weight goal. They understand your health history and current conditions. Experts can suggest safe BMI ranges suited to your needs. This advice helps avoid risks and sets clear, achievable targets.
Considering Ethnicity And Genetics
Ethnic background influences body shape and fat distribution. Some groups may have different healthy BMI ranges than others. Genetics also affect metabolism and weight gain patterns. Adjust weight goals by considering these factors for better accuracy.
Adapting Goals For Older Adults
Healthy BMI ranges change as women age. Older adults may benefit from slightly higher BMI targets. This supports muscle and bone health during aging. Tailoring goals to age helps maintain strength and reduces health risks.
Maintaining Optimal Wellness
Maintaining optimal wellness means keeping your body and mind in good shape. It supports a healthy BMI range for women and boosts overall health. Simple daily habits can make a big difference. Focus on good nutrition, staying active, and tracking your progress. These steps help you feel better and prevent health issues.
Balanced Nutrition Tips
Eating a variety of foods gives your body the nutrients it needs. Include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins in meals. Limit sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats. Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated. Small, frequent meals can keep energy steady throughout the day. Avoid skipping meals to maintain a stable metabolism.
Regular Physical Activity
Exercise helps control weight and improves heart health. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate activity most days. Walking, swimming, or cycling are good options. Strength training builds muscle and supports a healthy metabolism. Find activities you enjoy to stay motivated. Regular movement reduces stress and boosts mood.
Monitoring Progress And Adjustments
Track your weight and BMI regularly to see changes. Use a journal or app to note food intake and exercise. Adjust habits if progress stalls or if goals change. Consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice. Staying aware helps maintain balance and avoid setbacks. Consistency is key to long-term wellness.
Credit: www.eatsmartmovemorenc.com
Conclusion
Maintaining a healthy BMI range supports overall well-being for women. Keep in mind, BMI is a simple tool, not a full health measure. Factors like age, muscle, and bone density affect your ideal weight. Regular check-ups help tailor advice to your unique needs.
Focus on balanced eating and staying active every day. Small changes lead to lasting health benefits. Stay informed and listen to your body’s signals. Healthy living is a journey, not a quick fix.


