Are you aware of how closely obesity and cardiovascular disease are connected? If you’ve been wondering how excess weight might be affecting your heart, you’re not alone.
Obesity isn’t just about appearance—it can seriously impact your heart’s health and increase your risk for life-threatening conditions. Understanding this link could be the key to protecting your heart and improving your quality of life. Keep reading to discover what obesity does to your cardiovascular system and what steps you can take right now to lower your risk.
Your heart deserves this attention.
Link Between Obesity And Heart Health
Obesity significantly affects heart health. Excess body fat strains the cardiovascular system. It increases the risk of heart disease and complications. Understanding the link between obesity and heart health helps in prevention and treatment.
Impact On Blood Vessels
Obesity causes inflammation in blood vessels. This inflammation damages the vessel walls. Fat deposits build up, narrowing the arteries. Narrow arteries reduce blood flow and oxygen supply. This condition increases the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Changes In Cardiac Structure
Excess weight forces the heart to work harder. The heart muscle thickens and enlarges. This enlargement weakens the heart’s ability to pump blood. Over time, it can lead to heart failure. Structural changes increase the chance of irregular heartbeats.
Effects On Blood Pressure
Obesity raises blood pressure levels. Extra fat tissue demands more blood flow. This increases resistance in blood vessels. Higher resistance forces the heart to pump harder. Persistent high blood pressure damages the heart and arteries.
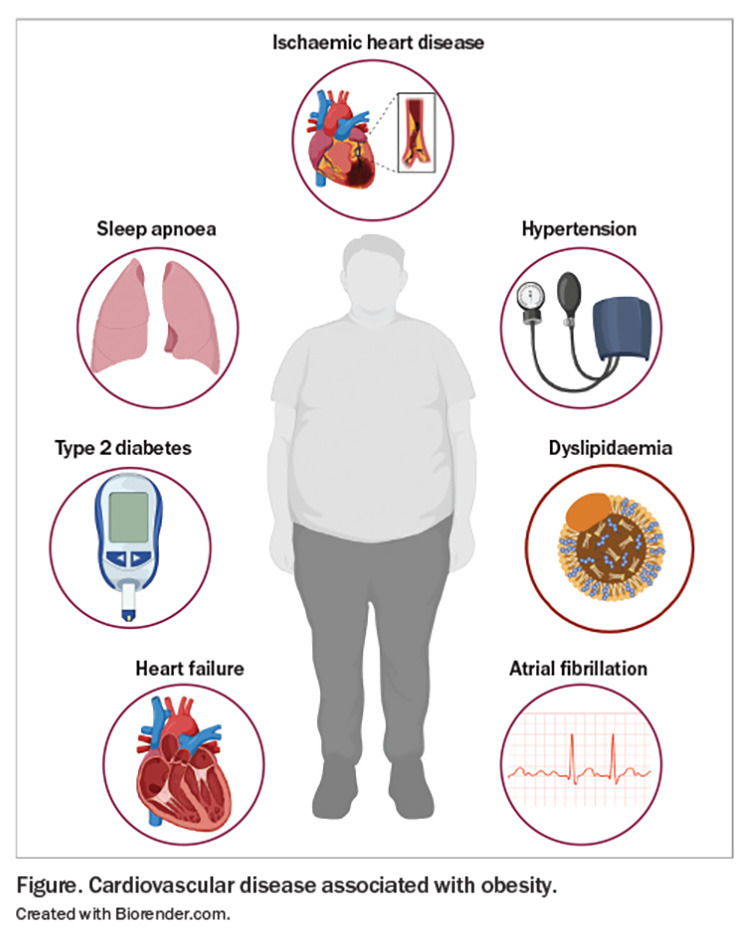
Common Cardiovascular Risks From Obesity
Obesity raises many risks for heart health. Excess fat affects how the heart works and the blood vessels. This condition leads to several common problems that increase the chance of heart disease. Understanding these risks helps in managing and preventing serious heart issues.
Atherosclerosis Development
Obesity speeds up the buildup of plaque in arteries. Fat deposits and inflammation narrow the blood vessels. This condition, called atherosclerosis, reduces blood flow. It forces the heart to work harder and raises blood pressure. Over time, clogged arteries can cause severe heart problems.
Increased Risk Of Heart Attack
Obesity raises the chance of heart attacks. The extra fat causes high cholesterol and blood pressure. These factors damage the heart’s arteries. Blocked arteries stop blood flow to the heart muscle. This blockage results in a heart attack, which can be fatal.
Stroke And Obesity Connection
Obesity also increases stroke risk. It causes high blood pressure and thickened blood. These issues can lead to blood clots or bleeding in the brain. Both conditions result in a stroke. Managing weight helps reduce this dangerous risk.
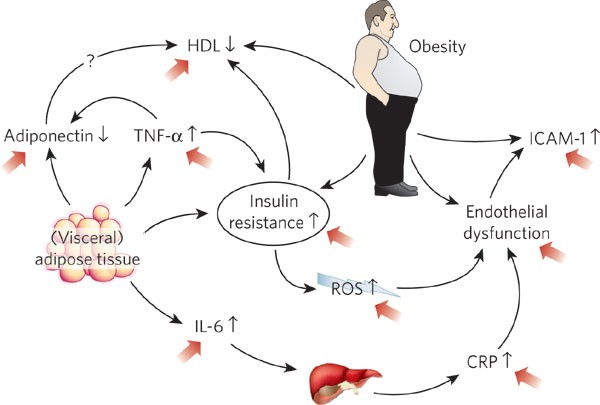
Metabolic Factors Influencing Heart Disease
Metabolic factors play a key role in the link between obesity and heart disease. Obesity causes changes in the body’s metabolism that increase heart disease risk. These changes affect insulin use, cholesterol levels, and inflammation. Understanding these metabolic factors helps explain why obesity harms heart health.
Role Of Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance means the body’s cells do not respond well to insulin. This condition is common in people with obesity. Insulin resistance causes high blood sugar levels. It also raises blood pressure and damages blood vessels. These effects increase the chance of heart disease and stroke.
Cholesterol And Fat Profiles
Obesity often leads to unhealthy cholesterol and fat levels. It raises bad cholesterol (LDL) and lowers good cholesterol (HDL). High LDL causes fat to build up in arteries. This buildup narrows arteries and reduces blood flow. High triglycerides, a type of fat in the blood, also increase heart disease risk.
Inflammation And Heart Damage
Obesity causes chronic inflammation in the body. Fat cells release substances that trigger inflammation. This inflammation damages the heart and blood vessels over time. It can lead to plaque formation in arteries. Plaque buildup raises the risk of heart attacks and heart failure.
Credit: endocrinology.medicinetoday.com.au
Obesity’s Effect On Heart Function
Obesity affects the heart in many serious ways. Excess body fat forces the heart to work harder. This extra work can change how the heart looks and how it functions. Understanding these changes helps explain the link between obesity and heart problems.
Changes In Heart Muscle
Extra fat causes the heart muscle to grow larger. This condition is called hypertrophy. A thicker heart muscle can become stiff. Stiffness reduces the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively. Over time, these changes can weaken the heart.
Impact On Heart Rhythm
Obesity increases the risk of irregular heartbeats. Fat deposits around the heart affect its electrical system. This can cause arrhythmias, or abnormal rhythms. Irregular rhythms may lead to serious complications like stroke.
Heart Failure Risks
Obesity raises the chance of heart failure. The heart struggles to meet the body’s increased demands. Overworked heart muscles may fail to pump blood properly. This leads to symptoms like fatigue and shortness of breath.
Preventive Strategies For Cardiovascular Health
Preventing cardiovascular disease requires a clear focus on healthy lifestyle choices. Managing weight, eating right, and staying active are key steps to protect heart health. These strategies reduce risks linked to obesity and improve overall well-being. Simple changes can make a big difference.
Weight Management Techniques
Controlling body weight is vital for heart health. Aim for a steady, gradual weight loss through balanced eating and exercise. Avoid crash diets that can harm the body. Tracking food intake and physical activity helps maintain progress. Seeking support from healthcare providers or support groups improves success. Small, consistent efforts yield lasting results.
Dietary Recommendations
Choose foods that support cardiovascular health. Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limit saturated fats, trans fats, and added sugars. Reduce salt intake to control blood pressure. Drinking plenty of water aids metabolism. Preparing meals at home allows better control over ingredients. Healthy eating protects arteries and lowers cholesterol.
Importance Of Physical Activity
Regular physical activity strengthens the heart and blood vessels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly. Activities like walking, cycling, or swimming are excellent choices. Exercise helps burn calories and manage weight. It also lowers blood pressure and improves cholesterol levels. Staying active boosts mood and energy. Consistency is key for long-term benefits.
Credit: www.nature.com
Medical Treatments And Interventions
Medical treatments and interventions play a crucial role in managing obesity and reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease. These treatments focus on lowering risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and insulin resistance. A combination of medications, surgical procedures, and regular monitoring helps improve heart health and overall well-being.
Medications For Risk Reduction
Medications often target conditions linked to obesity and heart disease. Doctors may prescribe drugs to lower blood pressure, reduce cholesterol, or control blood sugar levels. These medicines help reduce strain on the heart and prevent complications. Patients must take these medications as directed and report any side effects to their healthcare provider.
Surgical Options
Surgery can be an option for patients with severe obesity who have not succeeded with other treatments. Bariatric surgery helps reduce stomach size, limiting food intake and promoting weight loss. Weight loss surgery can lead to significant improvements in heart health and decrease the risk of cardiovascular events. Surgery requires careful evaluation and lifelong lifestyle changes to maintain benefits.
Monitoring And Follow-up Care
Regular check-ups are essential for patients with obesity and heart disease risk. Doctors monitor vital signs, weight, and lab results to adjust treatments as needed. Follow-up care helps detect early signs of complications and ensures medications remain effective. Ongoing support encourages patients to maintain healthy habits and reduce cardiovascular risks over time.
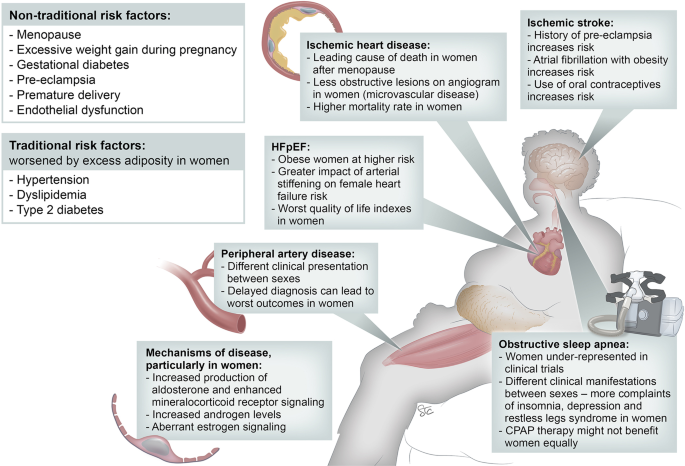
Obesity And Cardiovascular Disease In Different Populations
Obesity affects people differently across populations. Its impact on cardiovascular disease varies by gender, age, ethnicity, and genetics. Understanding these differences helps to identify at-risk groups. It also guides better prevention and treatment strategies for cardiovascular health.
Gender Differences
Men and women show different risks for heart disease linked to obesity. Men often have more abdominal fat, increasing heart disease risk. Women tend to store fat in hips and thighs, which may be less harmful. After menopause, women’s heart disease risk rises due to fat distribution changes. Hormones also play a role in these gender differences.
Age-related Risks
Obesity raises cardiovascular risk at all ages but affects older adults more. Aging slows metabolism and increases fat buildup around organs. This visceral fat leads to higher blood pressure and cholesterol. Younger people with obesity may develop heart disease later in life. Early weight management is key to reducing long-term risks.
Ethnic And Genetic Factors
Ethnic groups show different obesity patterns and heart disease risks. For example, South Asians have higher cardiovascular risk at lower body weights. African Americans often face higher rates of obesity and hypertension. Genetics influence how fat is stored and processed in the body. These factors make tailored health advice essential for diverse populations.
Credit: www.nature.com
Emerging Research And Future Directions
Research on obesity and cardiovascular disease is rapidly advancing. Scientists explore new causes and treatments. These discoveries aim to improve heart health and reduce obesity’s impact. The future holds promising directions in understanding and managing these linked conditions.
New Insights In Disease Mechanisms
Recent studies reveal how fat tissue affects the heart and blood vessels. Inflammation caused by obesity plays a key role in damaging arteries. Researchers identify signals from fat cells that worsen heart disease. Understanding these signals helps target treatments more effectively.
Scientists also study how obesity changes the heart’s structure and function. These changes increase the risk of heart failure and arrhythmias. New findings help explain why some people with obesity develop severe heart problems. This knowledge guides personalized care plans.
Innovative Therapies
New drugs focus on reducing inflammation and improving metabolism. These therapies aim to lower cardiovascular risks in people with obesity. Clinical trials test medications that target fat tissue and insulin resistance. Some show promising results in reducing heart events.
Researchers also explore lifestyle programs combined with medical treatments. These programs improve weight loss and heart health together. Surgery methods continue evolving to offer safer, more effective options. Future therapies may combine several approaches for better outcomes.
Role Of Technology In Management
Technology plays a growing role in managing obesity and heart disease. Wearable devices monitor heart rate, activity, and sleep patterns daily. Data from these devices help doctors adjust treatments quickly. Mobile apps support healthy eating and exercise habits.
Artificial intelligence analyzes patient data to predict cardiovascular risks. This allows early intervention and personalized care. Telemedicine expands access to specialists for remote patients. Technology improves how patients and providers work together for better heart health.
Conclusion
Obesity greatly raises the risk of heart disease and related problems. Excess weight strains the heart and blood vessels. This can lead to high blood pressure and artery damage. Managing weight helps protect the heart and improve health. Simple lifestyle changes make a big difference over time.
Eating well and staying active reduce risks effectively. Taking care of your body supports a stronger heart. Small steps today can prevent serious issues tomorrow.


