Have you ever wondered how obesity rates differ across the globe and what that means for you and your health? Understanding “Obesity by Nation” isn’t just about numbers—it’s about uncovering patterns that affect millions, including possibly your own community.
From small island nations with the highest obesity rates to countries leading the fight against it, the story of obesity worldwide is both surprising and eye-opening. Dive in to discover where your country stands, what factors contribute to these rankings, and how this global issue might impact your life or those around you.
Keep reading—you might find insights that could change the way you think about health and wellness forever.
Credit: www.voronoiapp.com
Global Obesity Rankings
Global obesity rankings reveal how widespread obesity is across different countries. These rankings help understand which nations face the biggest challenges with obesity. They also highlight where obesity rates are much lower. The data comes from health organizations tracking adult obesity worldwide. Studying this information shows patterns and trends in global health.
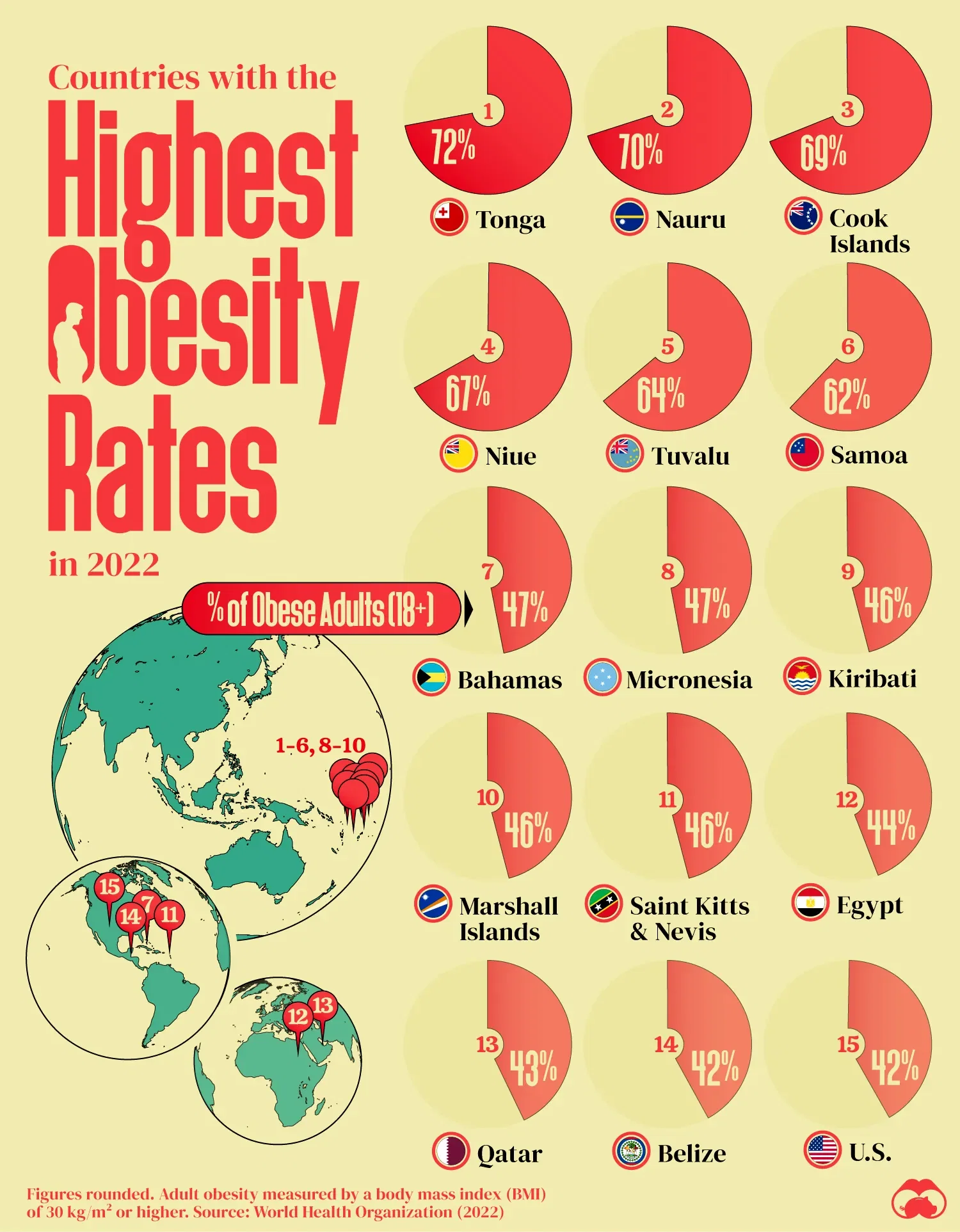
Top Obese Nations
Some countries have very high obesity rates. Pacific island nations lead this list. Tonga tops with about 72.5% of adults classified as obese. Nauru and Tuvalu follow closely with rates over 60%. These nations face unique challenges like diet changes and limited resources. The United States also ranks high, with about 36% obesity among adults. Many states within the U.S. report even higher numbers.
Countries With Lowest Obesity
Several countries show much lower obesity rates. Many Asian nations fall into this group. Japan, South Korea, and Vietnam report adult obesity rates below 10%. These countries often have diets rich in vegetables and fish. Active lifestyles also contribute to lower obesity levels. Their health policies focus on prevention and education.
Regional Differences
Obesity rates vary widely between regions. North America and Oceania have some of the highest rates. Europe shows moderate levels, with some countries higher than others. Africa and parts of Asia generally have lower obesity rates. Economic factors, food availability, and culture all influence these differences. Urbanization and lifestyle changes also play important roles.
Credit: commons.wikimedia.org
Obesity In The United States
Obesity is a major health challenge in the United States. It affects millions of adults and children across the country. The rising number of overweight individuals increases the risk of diseases like diabetes and heart problems. Understanding obesity in the U.S. helps identify ways to improve public health and reduce medical costs.
National Obesity Rate
The national obesity rate in the United States is about 42.4%. This means more than four in ten adults have obesity. This rate has steadily increased over the past decades. It places the U.S. among the countries with the highest obesity levels worldwide.
States With Highest Obesity
Some states have higher obesity rates than others. West Virginia consistently ranks as the state with the highest obesity rate. Mississippi and Louisiana often follow closely behind. Arkansas and Alabama also appear in the top five states with the most obese adults. These states face unique challenges related to diet and physical activity.
Factors Driving U.s. Obesity
Several factors drive obesity in the United States. Poor diet choices, including high intake of processed foods, play a big role. Sedentary lifestyles due to jobs and technology reduce physical activity. Economic factors limit access to healthy food for many people. Stress and lack of sleep also contribute to weight gain. Tackling these causes is essential to lower obesity rates.
Obesity Comparisons: U.s. Vs. China
Obesity rates differ greatly between the U.S. and China. These differences reflect diverse lifestyles, diets, and health outcomes. Understanding this gap helps reveal how culture and environment shape health.
Adult Obesity Rates
The U.S. has one of the highest adult obesity rates worldwide. Over 40% of American adults are obese. In contrast, China’s adult obesity rate is much lower, around 6%. This vast difference highlights contrasting public health challenges. The U.S. faces a growing obesity epidemic, while China is still managing rising but lower rates.
Lifestyle And Diet Differences
American diets often include high amounts of processed foods and sugars. Fast food and large portion sizes are common. Physical activity levels are generally low. China’s traditional diet focuses on vegetables, rice, and lean proteins. People eat smaller portions and fewer processed foods. Daily routines often involve more walking and physical tasks.
Health Implications
High obesity rates in the U.S. lead to more cases of diabetes, heart disease, and stroke. Health care costs rise with obesity-related illnesses. China’s lower obesity rate means fewer chronic diseases related to weight. Still, urbanization and lifestyle changes are increasing obesity risks. Both countries face health challenges but at very different scales.
Economic Impact Of Obesity
Obesity affects more than health; it impacts the economy deeply. Countries face rising costs due to obesity-related issues. The financial strain touches healthcare, workforce, and overall economic growth. Understanding these effects helps nations plan better strategies.
Healthcare Costs
Obesity leads to many chronic diseases like diabetes and heart problems. Treating these conditions requires expensive medical care. Hospitals spend billions yearly on obesity-related treatments. These costs burden public health systems and increase insurance premiums. Preventive care often costs less than treating diseases later.
Workforce Productivity
Obesity reduces worker efficiency and increases sick days. Employees with obesity may face physical limitations and fatigue. This lowers overall productivity and raises absence rates. Businesses lose money due to decreased worker output and higher healthcare claims. Healthy workers contribute more actively and consistently.
Global Economic Burden
Obesity’s impact goes beyond individual countries; it affects the global economy. The combined healthcare and productivity losses reach hundreds of billions annually. Developing countries face growing challenges with rising obesity rates. Global trade and economic stability may also suffer from the burden. Tackling obesity worldwide is essential for sustainable growth.
Childhood Obesity Trends
Childhood obesity is a growing concern worldwide. It affects children’s health and their future well-being. Tracking trends helps understand where the problem is worst. It also shows which actions can reduce obesity rates in young people.
Global Child Obesity Rates
Childhood obesity rates vary widely by country. Some nations face rates above 20%, while others remain below 5%. High-income countries often have higher rates due to lifestyle and diet changes. Low- and middle-income countries see rising rates as urbanization grows. The global average continues to increase each year, causing health experts to raise alarms.
Influencing Factors
Several factors drive childhood obesity trends. Poor diet with high sugar and fat content plays a big role. Sedentary lifestyles and low physical activity levels also contribute significantly. Genetics can influence a child’s risk but lifestyle is more critical. Economic status impacts access to healthy food and safe play areas. Advertising of unhealthy foods targets children and affects their choices.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing childhood obesity requires combined efforts from families, schools, and governments. Promoting balanced diets with fruits and vegetables is essential. Increasing children’s physical activity through sports and outdoor play helps too. Schools should provide healthy meals and nutrition education. Policies limiting junk food marketing to children can reduce unhealthy eating. Community programs creating safe spaces encourage active lifestyles.

Credit: www.voronoiapp.com
Obesity Measurement And Data Sources
Measuring obesity across nations requires clear, reliable data. Understanding these measurements helps track health trends worldwide. Different metrics provide insight into obesity levels. Data sources collect and report this information. Together, they shape global health policies and strategies.
Bmi And Other Metrics
BMI, or Body Mass Index, is the most common obesity measure. It calculates weight relative to height. A BMI over 30 usually indicates obesity. Other metrics include waist circumference and body fat percentage. These help capture obesity’s impact more fully. Using multiple metrics improves accuracy and understanding.
Key Global Data Repositories
Several organizations gather obesity data worldwide. The World Health Organization (WHO) leads global data collection. The Global Burden of Disease Study offers detailed obesity reports. The World Obesity Federation tracks obesity trends by country. National health surveys also provide valuable local data. These sources help compare obesity rates internationally.
Challenges In Data Collection
Collecting obesity data faces many challenges. Different countries use varied measurement methods. Some lack resources for regular health surveys. Cultural factors may affect data accuracy. Stigma around obesity can cause underreporting. These issues can limit data reliability and coverage. Improving data collection is crucial for better health planning.
Obesity In Europe
Obesity affects many countries across Europe, with rates varying widely. Some nations face high obesity levels, while others maintain healthier populations. Understanding these differences helps in shaping better health strategies. Europe’s diverse cultures, diets, and lifestyles influence obesity rates significantly.
Most Obese European Countries
Several European countries report high obesity rates. Turkey, Malta, and the United Kingdom rank among the most obese. In these countries, over 30% of adults are obese. Sedentary lifestyles and unhealthy diets contribute to this trend. Rising obesity increases risks of diabetes and heart disease.
Lowest Obesity Rates In Europe
Countries like Switzerland, Italy, and Norway have the lowest obesity levels. Their obesity rates are often below 15%. Traditional diets rich in fruits, vegetables, and fish help maintain healthy weights. Active lifestyles and strong public health policies support these low rates.
Policy Responses
European governments implement various policies to fight obesity. These include promoting physical activity and healthy eating. Some countries tax sugary drinks and unhealthy foods. Schools often provide nutrition education and healthier meals. Early intervention helps reduce obesity in younger generations.
Health Risks Linked To Obesity
Obesity affects millions worldwide and leads to serious health problems. It raises the chance of many illnesses and lowers life quality. Understanding the health risks linked to obesity helps nations address this growing issue effectively.
Chronic Diseases
Obesity increases the risk of many chronic diseases. People with obesity often develop type 2 diabetes. Heart disease is also common due to high blood pressure and cholesterol. Stroke risks rise with excess body fat. Certain cancers, like breast and colon cancer, occur more in obese individuals. Joint problems such as arthritis happen because of extra weight on bones.
Mental Health Effects
Obesity impacts mental health deeply. Many people with obesity face depression and anxiety. Social stigma and low self-esteem add to emotional stress. Poor body image lowers confidence and happiness. Some experience isolation due to mobility issues. Mental health care must be part of obesity treatment plans.
Mortality Rates
Obesity shortens life expectancy worldwide. Higher body mass index (BMI) links to increased death risk. Severe obesity can reduce life by several years. Death from heart disease, diabetes, and cancer rises with obesity. Countries with high obesity rates see more premature deaths. Addressing obesity saves lives and improves public health.
Conclusion
Obesity rates differ widely from nation to nation. Some countries face serious health challenges due to high obesity. Others maintain lower rates through healthier lifestyles. Understanding these differences helps in shaping better health policies. Everyone benefits from more awareness and action.
Small changes in diet and exercise can improve health. Tackling obesity needs global cooperation and local effort. The future depends on learning from the fattest and fittest nations. Healthy choices today lead to stronger communities tomorrow.

