Are you curious about where you stand on the obesity scale? Understanding your Body Mass Index (BMI) can be a simple yet powerful way to learn about your weight status and its impact on your health.
But what exactly is the obesity scale BMI, and why does it matter for you? This article will guide you through what BMI is, how it’s calculated, and what your number means for your well-being. By the end, you’ll have clear insights to help you take control of your health journey with confidence.
Keep reading to discover how a small number can reveal big truths about your body.
Bmi Basics
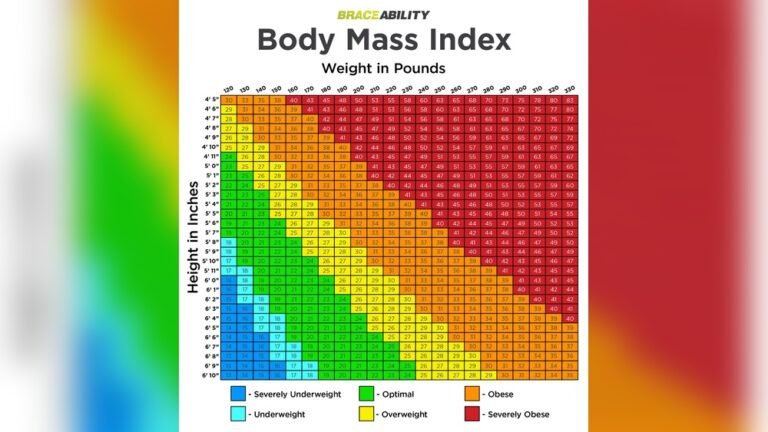
The Body Mass Index (BMI) is a simple way to check if a person has a healthy weight. It uses height and weight to give a number. This number helps to see if someone is underweight, normal, overweight, or obese. BMI is useful for adults as a quick screening tool.
BMI does not measure body fat directly. It works best for most adults but can be less accurate for athletes or people with more muscle. Always ask a doctor for a full health check if needed.
Bmi Formula
The BMI formula is easy to use. Divide a person’s weight in kilograms by their height in meters squared. This means height is multiplied by itself.
BMI = Weight (kg) / Height (m)²For example, if a person weighs 70 kg and is 1.75 meters tall, the BMI is 70 divided by (1.75 x 1.75).
Weight Categories
BMI numbers help group people by weight status. The main categories are:
- Underweight: BMI less than 18.5
- Normal weight: BMI 18.5 to 24.9
- Overweight: BMI 25 to 29.9
- Obese: BMI 30 or higher
These categories guide health advice. Higher BMI can increase health risks like heart disease and diabetes. Still, BMI is one of many tools to understand health better.
Credit: www.beliteweight.com
Limitations Of Bmi
The Body Mass Index (BMI) is a common tool to estimate body fat. It helps classify weight status as underweight, normal, overweight, or obese. BMI uses a simple formula based on height and weight. Despite its ease, BMI has clear limitations. It does not measure body fat directly or consider body composition.
BMI can sometimes mislead about a person’s health. It may not reflect muscle mass, bone density, or fat distribution. These factors affect health risks but are not included in the BMI calculation. Understanding these limits helps in interpreting BMI results better.
Muscle Mass And Bmi
Muscle weighs more than fat. People with high muscle mass may have a high BMI. Athletes often fall into overweight or obese BMI categories. Their body fat may actually be low. BMI cannot distinguish between muscle and fat weight. This can cause false labeling as overweight or obese.
This limitation means BMI is not perfect for everyone. People with strong, muscular builds need other methods to assess health. Body fat percentage or waist measurements provide better insight in these cases.
When To Seek Professional Advice
BMI is a useful first step but not a diagnosis. Talk to a healthcare provider for a full health assessment. They can consider other factors like diet, activity, and family history. A professional can recommend tests to measure body fat and risks.
Seek advice if BMI results seem inconsistent with your health. Professionals help create a plan tailored to your needs. Relying on BMI alone might miss important health details. Expert guidance ensures accurate evaluation and better health decisions.
Health Risks Linked To Obesity
Obesity is more than a number on the BMI scale. It can cause serious health problems. Understanding the risks helps in making better choices for your body and mind.
Extra body weight strains many systems inside the body. This strain can lead to diseases that affect daily life and long-term health.
Chronic Diseases
Obesity raises the chance of developing many chronic diseases. These include type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and high blood pressure. Excess fat affects how the body uses insulin. This can cause blood sugar levels to become too high. Heart disease risk grows as fat builds up around organs and arteries. High blood pressure often comes with extra weight, stressing the heart and vessels.
Obesity also increases the risk of certain cancers. These include breast, colon, and liver cancer. Fat tissue can produce hormones that may encourage cancer growth. Managing weight helps reduce the risk of these serious illnesses.
Joint And Mobility Issues
Extra weight puts heavy pressure on joints like knees and hips. This stress can wear down cartilage, causing pain and stiffness. Many people with obesity suffer from osteoarthritis. This condition limits movement and reduces quality of life.
Mobility becomes harder as obesity progresses. Simple activities like walking or climbing stairs turn into challenges. Poor mobility also affects mental health and independence. Maintaining a healthy weight eases joint pain and improves movement.
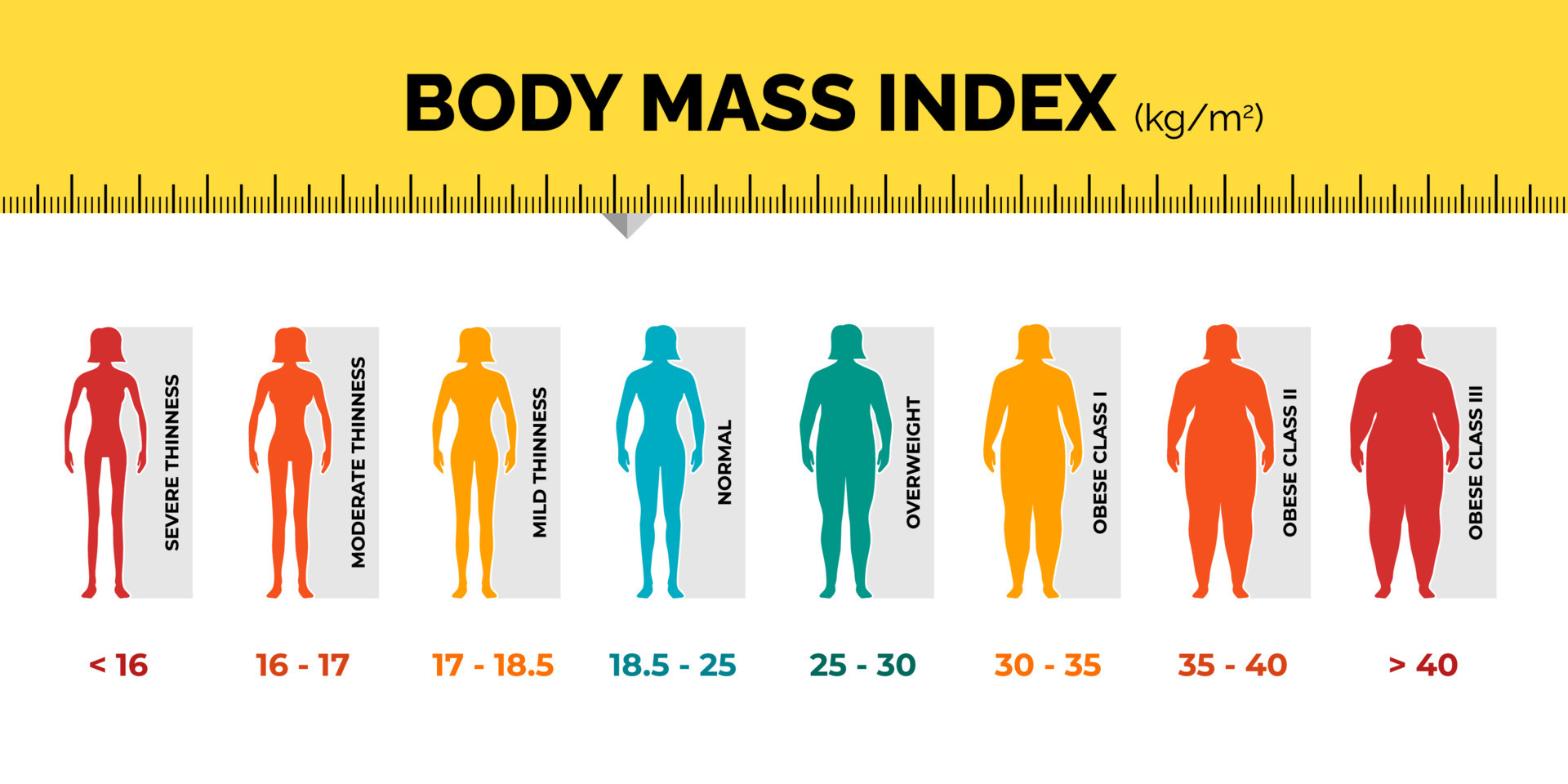
Class Iii Obesity Insights
Class III obesity represents the highest category on the obesity scale. It is sometimes called severe or morbid obesity. Understanding this category helps highlight serious health risks and the need for proper care. This section explores what defines Class III obesity and its effects on health.
Definition And Criteria
Class III obesity is defined by a Body Mass Index (BMI) of 40 or more. BMI is a simple calculation using weight and height. A BMI above 40 means the person carries excess body fat that can harm health. This classification helps doctors identify individuals who need intensive treatment.
Health Implications
Class III obesity increases the risk of many serious health problems. These include heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and stroke. People with this level of obesity often face challenges like joint pain and difficulty breathing. Early medical intervention can reduce these risks and improve quality of life.
Bmi For Children And Teens
BMI for children and teens helps track healthy growth patterns. It differs from adult BMI by considering age and sex. This approach gives a clearer picture of youth weight status over time. Parents and healthcare providers use BMI to spot potential health risks early. Understanding these numbers supports better health decisions for young ones.
Growth Curves
Growth curves show how a child’s BMI compares to others the same age and sex. These curves come from large groups of children to represent typical growth. Doctors use percentiles to explain results. For example, a child in the 85th percentile weighs more than 85% of peers. Growth curves help monitor healthy development and spot changes early.
Assessing Youth Weight Status
To assess youth weight status, BMI percentiles guide the classification. Below the 5th percentile may indicate underweight. Between the 5th and 85th percentile is considered healthy weight. The 85th to 95th percentile signals overweight, and above 95th is obese. This system helps tailor advice and treatment for children and teens. Regular checks can prevent future health problems.

Credit: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Calculating And Tracking Your Bmi
Calculating and tracking your Body Mass Index (BMI) helps monitor your weight status. BMI is a simple number derived from your weight and height. It provides a quick check of whether you fall into underweight, normal, overweight, or obese categories. Regularly tracking BMI can guide healthy lifestyle choices and alert you to potential health risks.
Using Online Calculators
Many websites offer free BMI calculators. Enter your weight in kilograms or pounds and height in meters or inches. The calculator quickly gives your BMI number. This method saves time and avoids manual errors. You can use the calculator on your phone, tablet, or computer anytime. Some tools also track your BMI over days or weeks for better monitoring.
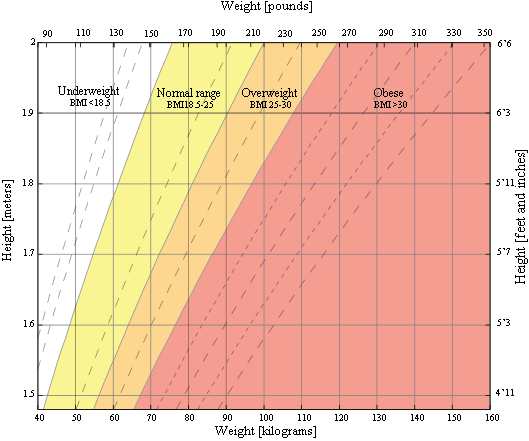
Interpreting Results
Your BMI number places you in a weight category. Below 18.5 means underweight. Between 18.5 and 24.9 is normal weight. From 25 to 29.9 indicates overweight. A BMI of 30 or above signals obesity. This number is a screening tool, not a diagnosis. Muscle mass and body composition can affect accuracy. Consult a healthcare provider for a detailed health assessment.
Healthy Living Strategies
Healthy living strategies play a key role in managing obesity and maintaining a healthy Body Mass Index (BMI). These approaches focus on balanced nutrition and regular physical activity. Both are essential to improve overall health and reduce the risks related to obesity. Simple changes in daily habits can lead to better weight control and increased energy levels. Following practical tips helps create a sustainable lifestyle that supports weight loss and well-being.
Balanced Diet Tips
Eating a balanced diet means consuming a variety of foods in the right amounts. Include plenty of fruits and vegetables every day. Choose whole grains instead of refined grains for better fiber intake. Lean proteins like chicken, fish, and beans help build muscle and keep you full. Limit sugary drinks, processed foods, and high-fat snacks. Drinking enough water supports metabolism and reduces hunger. Small, frequent meals can keep energy steady and prevent overeating.
Physical Activity Recommendations
Regular physical activity is important to burn calories and improve heart health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly. Activities like walking, swimming, or cycling are easy to start. Strength training helps build muscle and boost metabolism. Find activities you enjoy to stay motivated. Even short bursts of movement throughout the day add up. Avoid sitting for long periods; take breaks to stretch or walk.
When To Consult Healthcare Providers
Knowing when to consult healthcare providers about your BMI is crucial for good health. BMI measures body fat based on weight and height. It helps identify if your weight poses health risks. Consulting a professional ensures the right steps for your wellbeing. Professionals offer advice beyond just numbers. They consider your overall health and lifestyle.
Comprehensive Weight Assessment
Healthcare providers perform a thorough weight assessment. They look at BMI along with other health factors. This includes waist size, blood pressure, and medical history. They check for conditions linked to obesity like diabetes. This full evaluation helps create a clear health picture. It guides better decisions about weight management.
Personalized Health Plans
Doctors design health plans based on each person’s needs. These plans include diet, exercise, and sometimes medications. They set realistic goals that fit your lifestyle. Regular follow-ups track progress and adjust the plan as needed. Personalized plans improve your chances of success. They support long-term healthy habits and weight control.
Credit: www.calculator.net
Conclusion
The obesity scale BMI helps people understand their weight category clearly. It uses simple height and weight numbers to give a score. This score shows if someone is underweight, normal, overweight, or obese. Keep in mind, BMI is a quick tool, not a full health test.
Muscle mass and other factors can affect the result. Always talk to a doctor for a full health check. Knowing your BMI can guide you to a healthier lifestyle and better choices. Stay informed, stay healthy.