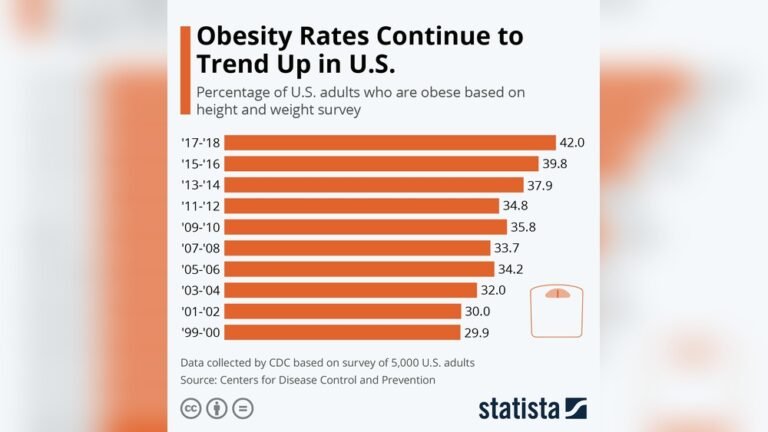
Are you aware that nearly 40% of adults in the United States are classified as obese? This isn’t just a number—it’s a reality that affects your health, your community, and the future of the nation.
Understanding the current obesity percentage in the U. S. Can help you grasp the scale of this challenge and why it matters to you personally. You’ll discover the latest stats, the states most affected, and what these numbers mean for your well-being.
Keep reading to uncover insights that could change how you think about health and lifestyle in America.
Current Obesity Rates In The Us
Obesity remains a significant health issue in the United States. A large portion of adults face challenges related to excess weight. This condition affects many aspects of life, including health, work, and daily activities.
Understanding the current obesity rates helps to see the scope of the problem. It also guides efforts to reduce obesity and improve public health.
Adult Obesity Statistics
Nearly 40% of US adults are classified as obese. This means their body mass index (BMI) is 30 or higher. Obesity increases the risk of heart disease, diabetes, and other serious illnesses.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that severe obesity rates are also rising. Severe obesity refers to a BMI of 40 or more. This group faces even greater health risks.
Trends Over Recent Years
Obesity rates have steadily increased over the past decade. The rise shows that more adults are gaining excess weight each year. Efforts to curb obesity have had limited success so far.
The COVID-19 pandemic may have contributed to recent increases. Changes in lifestyle and physical activity affected many people’s weight. Experts continue to monitor these trends closely.
State-by-state Breakdown
Obesity rates vary across US states. West Virginia consistently has the highest adult obesity rate. Mississippi and Louisiana also rank among the states with the most obesity.
Other states like Arkansas and Alabama often appear in the top five for obesity. Differences in diet, activity, and healthcare access influence these variations.
Understanding state-specific data helps target local health programs. It also highlights areas needing more support and resources.

Credit: www.cdc.gov
Top States With Highest Obesity
Obesity remains a serious health issue in the United States. Some states have much higher rates than others. Understanding where obesity is most common helps target health efforts.
The following states show the highest percentages of adult obesity. These regions face challenges related to lifestyle, diet, and access to healthcare.
West Virginia Leading The List
West Virginia holds the top spot for obesity rates in the US. Over 40% of adults here are obese. This rate is higher than the national average. Factors include limited access to healthy foods and fewer places for physical activity.
Mississippi And Louisiana Trends
Mississippi and Louisiana also show very high obesity rates. Both states often rank in the top three. Diets high in calories and low in nutrition contribute to this issue. Poverty and education levels impact health choices in these areas.
Other High-prevalence States
States like Arkansas and Alabama frequently appear among those with the highest obesity. These regions share similar challenges with West Virginia and Mississippi. Efforts to promote better nutrition and exercise are crucial here.
Measurement Methods
Measuring obesity rates in the US involves several methods to estimate body fat and health risks. These methods help track obesity trends and guide health policies. Some rely on simple calculations, while others consider body shape and fat distribution.
Traditional Bmi Approach
The Body Mass Index (BMI) is the most common way to measure obesity. It uses a person’s height and weight to calculate a number. This number shows if someone is underweight, normal, overweight, or obese. Doctors and researchers often use BMI because it is easy and fast to measure.
Updated Metrics Including Waist Size
Newer methods add waist size to BMI measurements. Waist size helps show where fat is stored on the body. Fat around the waist increases health risks more than fat in other places. Including waist measurements gives a clearer picture of obesity and related risks.
Limitations Of Bmi
BMI cannot tell the difference between muscle and fat. A muscular person may have a high BMI but low body fat. It also ignores fat distribution, which affects health risks. These limits mean BMI is not perfect for every person or group. Other tests can help provide better health assessments.

Credit: www.cdc.gov
Projected Obesity Stats For 2025
The projected obesity statistics for 2025 reveal a concerning rise in the United States. Experts predict that obesity will continue to affect a large portion of the adult population. This growth impacts health care, productivity, and quality of life across the country. Understanding these projections helps in planning better health policies and interventions.
State-level Forecasts
Each state shows different trends in obesity rates for 2025. Southern states like West Virginia and Mississippi are expected to remain among the highest. States in the Midwest also face increasing rates. Some states in the West and Northeast may see slower growth but still face challenges. These variations highlight the need for local health strategies.
Expected National Trends
At the national level, obesity rates are expected to rise above 40%. This means nearly half of all adults could be obese. The increase spans all age groups but is especially high among middle-aged adults. Rising obesity rates will likely lead to higher cases of diabetes, heart disease, and other conditions. This trend signals a growing public health concern.
Factors Driving Increases
Several factors contribute to rising obesity rates. Poor diet and lack of physical activity are major causes. Economic challenges limit access to healthy food and safe exercise spaces. Sedentary lifestyles increase with more screen time and less movement. Stress and mental health issues also play a role. These combined factors make obesity harder to control nationwide.
Demographic Differences
Obesity rates in the US vary greatly across different groups of people. These variations depend on gender, where people live, and their age. Understanding these differences can help target health efforts better. It also shows which groups face higher risks.
Gender Variations
Women in the US tend to have slightly higher obesity rates than men. This difference is linked to biological and lifestyle factors. For example, pregnancy and hormonal changes affect women’s weight. Men often have higher muscle mass, which impacts body fat calculations. Both genders face unique challenges in managing weight.
Rural Vs Urban Rates
Obesity rates are generally higher in rural areas than in cities. Rural residents often have less access to healthy food and fitness facilities. Transportation can be limited, reducing exercise opportunities. Urban areas usually offer more health programs and fresh food markets. These factors make rural populations more vulnerable to obesity.
Age Group Patterns
Obesity rates increase with age in the US. Adults aged 40 to 59 have the highest percentages. Older adults may gain weight due to slower metabolism and less physical activity. Younger adults and teens show lower obesity rates but trends are rising. Early prevention is crucial to stop weight gain over time.
Economic And Health Impacts
The economic and health impacts of obesity in the US affect millions. The rising obesity rates increase healthcare costs and strain medical systems. Obesity also raises the risk of chronic diseases, reducing life quality and increasing medical needs. These health challenges influence workforce productivity and national economic growth. Understanding these effects is vital for public health planning and policy.
Healthcare Costs
Obesity leads to higher medical expenses for individuals and society. Treatment for obesity-related conditions requires more doctor visits and medications. Hospitals face increased costs due to surgeries and emergency care for obese patients. Insurance companies pay more for chronic illness care linked to obesity. The government spends billions annually on obesity-related healthcare programs. These costs burden taxpayers and limit funds for other health needs.
Chronic Disease Risks
Obesity raises the chance of serious chronic diseases. Common conditions include type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and stroke. Obese individuals often develop high blood pressure and certain cancers. These diseases reduce life expectancy and increase disability. Managing chronic diseases requires lifelong treatment and monitoring. Early intervention and weight management can lower these health risks.
Workforce Productivity Effects
Obesity affects workers’ health and job performance. Sick days and disability leave rise among obese employees. Physical limitations can reduce work efficiency and increase errors. Employers face higher costs from lost productivity and health benefits. Obesity may also limit job opportunities for affected individuals. Supporting healthy lifestyles at work can improve productivity and reduce costs.
Comparisons With Other Countries
Obesity rates in the United States are notably high compared to many other countries. Examining these rates alongside other nations helps us understand the scale of the issue. It also reveals patterns and potential strategies for improvement. Comparing the US with Europe and other parts of the world offers valuable insights.
Us Vs Europe Obesity Rates
The US has one of the highest obesity rates among developed countries. Nearly 40% of adults in the US are obese. In contrast, most European countries report rates between 20% and 30%. Countries like Italy and France have even lower rates, often under 25%. Differences in diet, lifestyle, and healthcare systems play a role. Europeans tend to eat smaller portions and have more physical activity daily. These habits contribute to their relatively lower obesity numbers.
Global Ranking Of The Us
The US ranks near the top globally for adult obesity. Only a few countries have rates as high or higher. Pacific Island nations, such as Nauru and Tonga, have the highest obesity levels worldwide. Still, among large, developed economies, the US stands out with a significant obesity problem. This ranking highlights the urgent need for public health action. The high rate impacts healthcare costs and quality of life for millions.
Lessons From Other Nations
Many countries have successfully reduced obesity through focused policies. Japan and South Korea promote healthy eating and physical activity at all ages. They emphasize education and community programs. Some European nations tax sugary drinks and unhealthy foods. These measures encourage better food choices. The US could benefit from similar strategies. Public awareness and easier access to healthy options are key. Learning from other countries can guide effective solutions.
Efforts To Combat Obesity
Obesity remains a major health challenge in the United States. Many efforts aim to reduce obesity rates and improve public health. These efforts involve government actions, local community support, and new medical approaches. Each plays a crucial role in fighting obesity and its effects.
Government Initiatives
The government promotes healthier eating and active living through policies. Programs encourage schools to offer nutritious meals and more physical activity. Taxes on sugary drinks and junk food help reduce consumption. Public campaigns raise awareness about obesity risks and healthy choices. Funding supports research to find better prevention and treatment methods.
Community Programs
Local groups offer support and education to fight obesity. Community gardens increase access to fresh fruits and vegetables. Exercise classes and walking groups help people stay active. Workshops teach cooking skills and nutrition basics. These programs create a supportive environment for healthy habits to grow.
Emerging Treatments
New medical treatments provide more options to manage obesity. Prescription medications can help control appetite and improve metabolism. Bariatric surgery offers a solution for severe obesity cases. Technology, like apps and devices, assists with tracking diet and activity. Research continues to explore safer and more effective treatments.

Credit: www.aecf.org
Conclusion
Obesity affects a large part of the U. S. Population today. Nearly 40% of adults face this health challenge. Some states, like West Virginia, have higher rates than others. Obesity raises risks of many health problems, including diabetes and heart disease.
Simple changes in diet and activity can help reduce obesity. Communities and individuals both play key roles in making progress. Tracking obesity trends helps guide better health decisions nationwide. Awareness and action remain crucial to improving public health outcomes.